Final ID: Th0084
Contrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging-based Perfusion Impairment Metrics in PAD and Neural Network-based 1-year Prediction
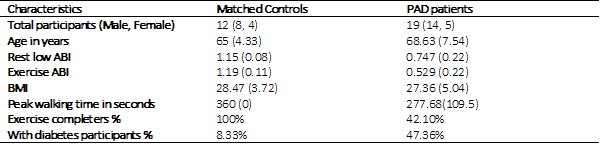
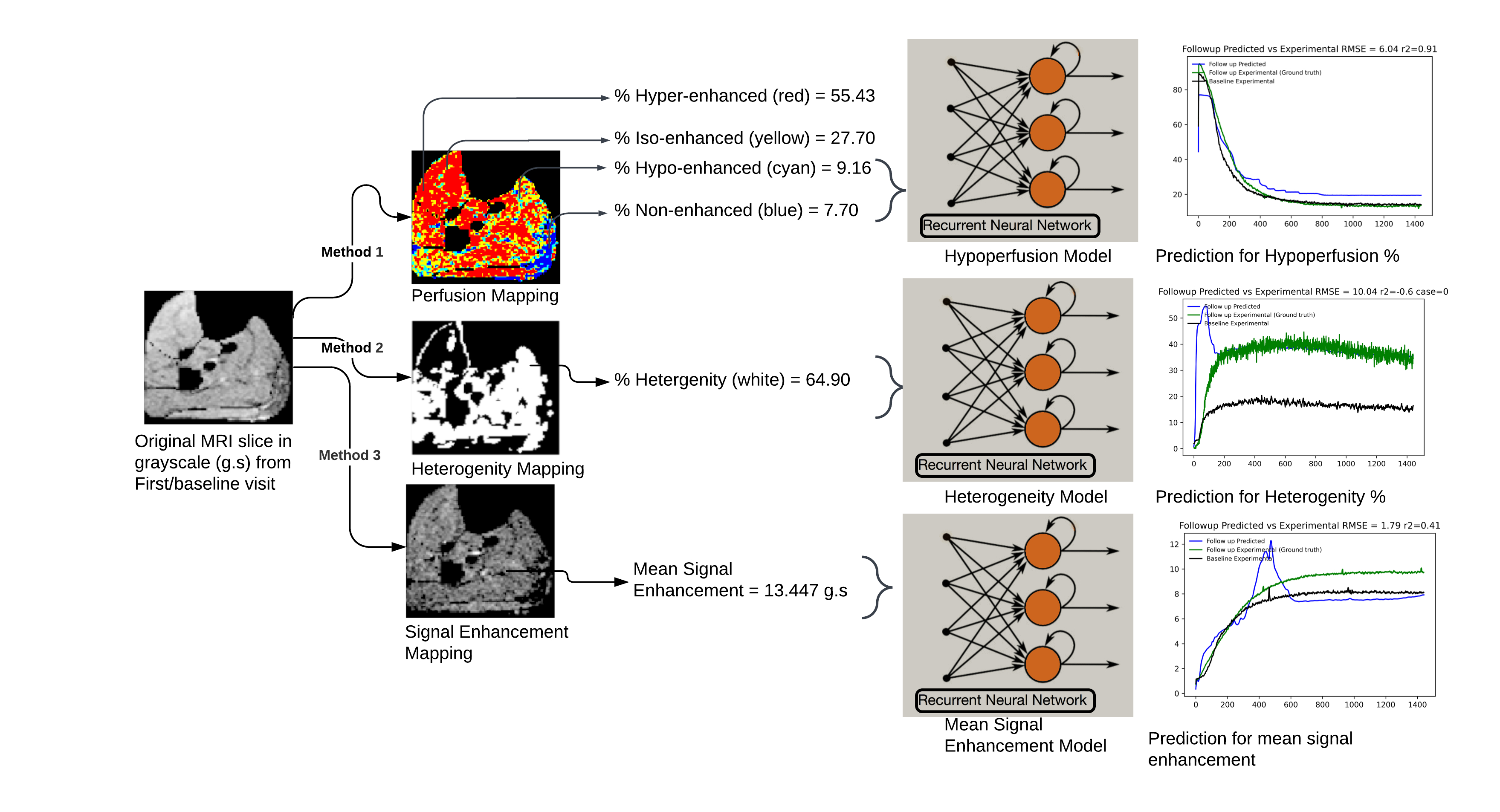
Abstract Body: Introduction: The 2019 American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines highlight perfusion assessment and imaging in peripheral artery disease (PAD) as critical, yet unmet needs in clinical practice. We hypothesized that over the course of 1-year the microcirculation of the skeletal calf muscles will not change in matched controls but marked variations will be observed due to structural and functional impairment in PAD patients. Methods: The perfusion in tissue can be mapped and quantified in various metrics, we have proposed three novel variables viz. hypoperfusion (Hy) %, heterogeneity (He) %, and mean signal enhancement (MSE), as a perfusion metric to represent frame-wise perfusion impairment in contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRIs) among PAD patients. With these three variables referred to as impairment, we calculated the association of baseline, and 1-year perfusion change in matched controls and PAD patients. Cross-sectional CE-MRIs of 31 participants (controls=12, PAD=19) were acquired from the mid-calf level at a supine position during the baseline visit and at the 1-year follow-up. A self-enhancement based perfusion mapping (SEPM) algorithm was developed to identify the three proposed perfusion metrics from the CE-MRIs. All CE-MRIs were post-processed to remove faulty and noisy frames, and later semi-automatically segmented into five muscle compartments to represent the anterior muscle (AM), lateral muscle (LM), deep posterior muscle (DM), soleus muscle (SM), and gastrocnemius muscles (GM) groups. Results: Our experiment shows He % in GM and SM were significantly higher in PAD patients than in matched controls (p<0.05).There was a lower association of all 3 perfusion metrics changes from baseline to 1-year in PAD patients compared to the matched controls. In a sub-group analysis of PAD subgroups, showed an ‘increase in Hy %’ in PAD groups with other complications like diabetes and reduced ability to walk. The recurrent neural networks (RNNs) were separately trained and tested (6:4) using these perfusion variables as features from baseline visits, so a prediction can be done for the 1-year. The overall prediction calculated via root mean squared error (RMSE) (MSE: 4.05, He: 13.74%, Hy: 18.87%), and R2 is moderately good. Conclusion: Our finding indicate that calf muscle CE-MRI-based proposed perfusion metrics are associated with PAD progression and could be used to train RNNs for predicting patients’ 1-year perfusion characteristics.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Cross-scale Causal Machine Learning Framework Pinpoints Mgl2+ Macrophage Orchestrators of Balanced Arterial Growth
Han Jonghyeuk, Kong Dasom, Schwarz Erica, Takaesu Felipe, Humphrey Jay, Park Hyun-ji, Davis Michael E
3D Statistical Shape Analysis Predicts Type A Aortic Dissection Better Than Aortic DiametersMarway Prabhvir, Campello Jorge Carlos Alberto, Wagner Catherine, Baker Timothy, Burris Nicholas