Final ID: Sa1307
Secukinumab Attenuates Postresuscitation Neurologic Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Cardiac Arrest
Abstract Body: Introduction
Brain injury following cardiac arrest (CA) is a major contributor to poor outcomes in post-CA patients. Inflammation plays a crucial role in driving this process. Interleukin-17A (IL-17A), a key cytokine, is central to regulating inflammatory homeostasis. Recent studies have suggested that elevated plasma levels of IL-17A are associated with poorer outcomes in post-CA patients. However, the precise role of elevated plasma IL-17A remains unclear. In this study, we used Secukinumab, a recombinant monoclonal antibody targeting IL-17A, as an intervention in a rat CA model to evaluate its effects on neurological function and cytokine levels.
Hypothesis
Intravenous administration of Secukinumab could improve neurological dysfunction in rats post-CA.
Methods
Thirty-nine male Sprague-Dawley rats (350g-400g) were randomly divided into three groups (n=13): Sham group, Control group, and Secukinumab group. Except for the Sham group, asphyxia was induced for 8 minutes, followed by cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the Control and Secukinumab groups. Secukinumab (15 mg/kg) was administered intravenously at the onset of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). Ten rats from each group were ensured to survive until the end of the study for behavioral tests, including neurologic deficit score (NDS) evaluations at 24, 48, and 72 hours post-CA, the Y-maze test at 4 days post-CA, and the Morris water maze test at 7-11 days post-CA. Additionally, three rats from each group were sacrificed 24 hours post-CA to measure the levels of IL-6 and neuron-specific enolase (NSE) in brain tissue and plasma.
Results
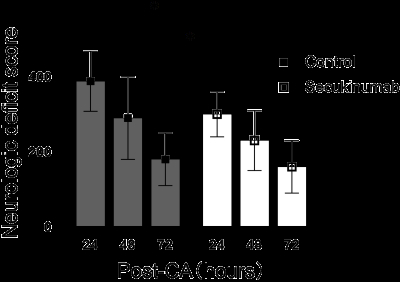
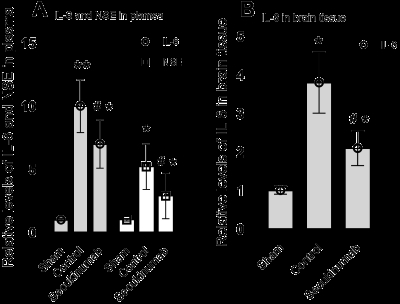
A total of sixty-five rats were used in the present study. Compared to the control group, the Secukinumab group demonstrated significantly better performance in the (NDS) (Figure 1, p<0.01). Additionally, the Secukinumab group exhibited a significantly greater spontaneous alternation rate in the Y-maze (19%±9% vs 33%±9%, p<0.05). In the Morris water maze, the Secukinumab group showed a significant decrease in escape latency on the fifth day of training (25.7s±9.6s vs 17.8s±6.8s, p<0.05). The platform crossing was also significantly increased (0.9±1.5 vs 2.6±1.8, p<0.05). Moreover, the levels of IL-6 and NSE in brain tissue and plasma were significantly reduced in the Secukinumab group compared to the control group (Figure 2, p<0.05).
Conclusions
In conclusion, Secukinumab demonstrated neuroprotective effects in a rat model of post-CA.
Brain injury following cardiac arrest (CA) is a major contributor to poor outcomes in post-CA patients. Inflammation plays a crucial role in driving this process. Interleukin-17A (IL-17A), a key cytokine, is central to regulating inflammatory homeostasis. Recent studies have suggested that elevated plasma levels of IL-17A are associated with poorer outcomes in post-CA patients. However, the precise role of elevated plasma IL-17A remains unclear. In this study, we used Secukinumab, a recombinant monoclonal antibody targeting IL-17A, as an intervention in a rat CA model to evaluate its effects on neurological function and cytokine levels.
Hypothesis
Intravenous administration of Secukinumab could improve neurological dysfunction in rats post-CA.
Methods
Thirty-nine male Sprague-Dawley rats (350g-400g) were randomly divided into three groups (n=13): Sham group, Control group, and Secukinumab group. Except for the Sham group, asphyxia was induced for 8 minutes, followed by cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the Control and Secukinumab groups. Secukinumab (15 mg/kg) was administered intravenously at the onset of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). Ten rats from each group were ensured to survive until the end of the study for behavioral tests, including neurologic deficit score (NDS) evaluations at 24, 48, and 72 hours post-CA, the Y-maze test at 4 days post-CA, and the Morris water maze test at 7-11 days post-CA. Additionally, three rats from each group were sacrificed 24 hours post-CA to measure the levels of IL-6 and neuron-specific enolase (NSE) in brain tissue and plasma.
Results
A total of sixty-five rats were used in the present study. Compared to the control group, the Secukinumab group demonstrated significantly better performance in the (NDS) (Figure 1, p<0.01). Additionally, the Secukinumab group exhibited a significantly greater spontaneous alternation rate in the Y-maze (19%±9% vs 33%±9%, p<0.05). In the Morris water maze, the Secukinumab group showed a significant decrease in escape latency on the fifth day of training (25.7s±9.6s vs 17.8s±6.8s, p<0.05). The platform crossing was also significantly increased (0.9±1.5 vs 2.6±1.8, p<0.05). Moreover, the levels of IL-6 and NSE in brain tissue and plasma were significantly reduced in the Secukinumab group compared to the control group (Figure 2, p<0.05).
Conclusions
In conclusion, Secukinumab demonstrated neuroprotective effects in a rat model of post-CA.
More abstracts on this topic:
Cooling the Intestines Offers Superior Protection in the Mouse Stroke Model
Liu Chunli, Park Yujung, Olivas Garcia Yamileck, Villa Jose, Osterli Emily, Chen Yingxin, Hu Bingren
BXOS110 for Acute Ischemic Stroke Treatment (BEST): A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 TrialDing Yarong, Li Shuya, Wang Zhe, Li Zixiao, Meng Xia, Zhao Xingquan, Wang Yongjun, Li Zixiao