Final ID: Sa506
Early Serial Somatosensory Evoked Potentials Can Assess Brain Injury Severity and Recovery in Swine Cardiac Arrest Models
Abstract Body: Introduction: Bilateral absent cortical N20 somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) at 12 and 24 hours after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) can predict poor neurologic outcome in cardiac arrest patients. However, it remains unknown if early SSEPs can be used to assess the efficacy of neuroprotective therapies after cardiac arrest. We hypothesized that the rate of SSEP recovery during the first 24 hours after ROSC can differentiate brain injury severity.
Methods: Eighteen Yorkshire swine (50-60 kg) were subjected to 5 (VF-5) or 10 minutes (VF-10) of ventricular fibrillation followed by advanced cardiac life support until ROSC. Sham animals were included to control for the effects of sedatives and instrumentation. Bilateral median nerves were stimulated with 35 mA at the forepaws. Cortical signal amplitudes were collected for 1 hour before cardiac arrest (baseline), for the first 4 hours after ROSC, and at 6, 12, 18, and 24 hours after ROSC for 15 minutes at each time point. Two-way ANOVAs were performed to determine inter- and intra-group differences using GraphPad Prism.
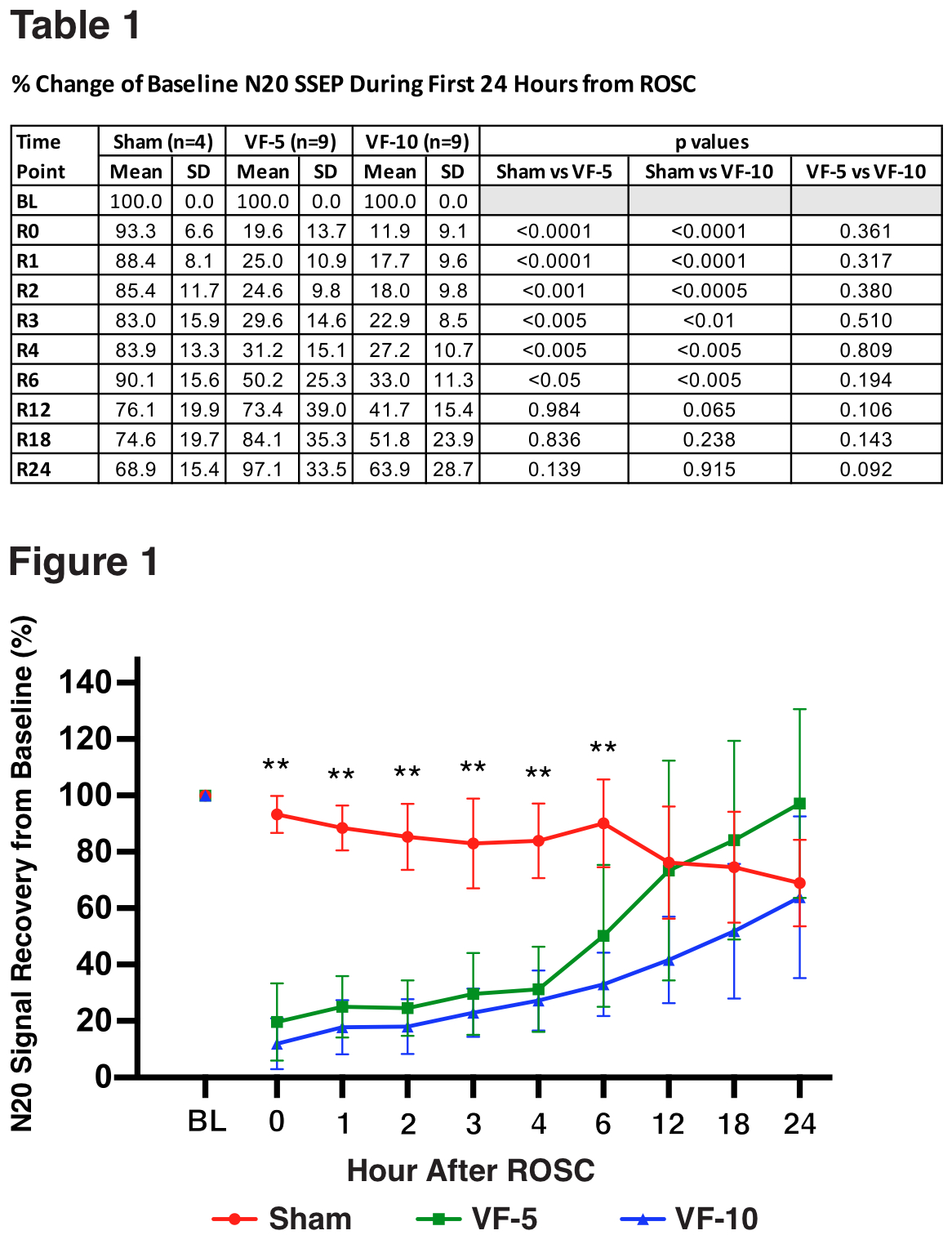
Results: VF-5 (n= 9) and VF-10 (n=9) animals showed similar and significant N20 suppression from baseline during the first 6 hours after ROSC compared to sham animals (n = 4; Table 1, Figure 1), but both recovered during the first 24 hours after ROSC. VF-10 animals showed trends toward slower N20 recovery compared to VF-5 animals. VF-5 animals demonstrated mean (SD) N20 recovery to 97.1 (33.5)% of baseline by 24 hours after ROSC, whereas VF-10 animals (n= 9) had mean (SD) N20 recovery of 63.9 (28.7)% of baseline by 24 hours after ROSC. Sham animals (n=4) demonstrated the known attenuating effect of Propofol on N20 amplitude to a mean (SD) of 68.9 (15.4)% of baseline by 24 hours after ROSC.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates the feasibility of using serial N20 cortical SSEPs to assess brain function recovery and potentially quantify brain injury severity during the first 24 hours after ROSC in swine cardiac arrest models. Future studies are needed to better understand the impact of prolonged sedation on N20 amplitude and correlate the rate of N20 recovery with blood-based biomarkers and histological findings to confirm the construct validity of early SSEPs in our swine cardiac arrest models.
Methods: Eighteen Yorkshire swine (50-60 kg) were subjected to 5 (VF-5) or 10 minutes (VF-10) of ventricular fibrillation followed by advanced cardiac life support until ROSC. Sham animals were included to control for the effects of sedatives and instrumentation. Bilateral median nerves were stimulated with 35 mA at the forepaws. Cortical signal amplitudes were collected for 1 hour before cardiac arrest (baseline), for the first 4 hours after ROSC, and at 6, 12, 18, and 24 hours after ROSC for 15 minutes at each time point. Two-way ANOVAs were performed to determine inter- and intra-group differences using GraphPad Prism.
Results: VF-5 (n= 9) and VF-10 (n=9) animals showed similar and significant N20 suppression from baseline during the first 6 hours after ROSC compared to sham animals (n = 4; Table 1, Figure 1), but both recovered during the first 24 hours after ROSC. VF-10 animals showed trends toward slower N20 recovery compared to VF-5 animals. VF-5 animals demonstrated mean (SD) N20 recovery to 97.1 (33.5)% of baseline by 24 hours after ROSC, whereas VF-10 animals (n= 9) had mean (SD) N20 recovery of 63.9 (28.7)% of baseline by 24 hours after ROSC. Sham animals (n=4) demonstrated the known attenuating effect of Propofol on N20 amplitude to a mean (SD) of 68.9 (15.4)% of baseline by 24 hours after ROSC.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates the feasibility of using serial N20 cortical SSEPs to assess brain function recovery and potentially quantify brain injury severity during the first 24 hours after ROSC in swine cardiac arrest models. Future studies are needed to better understand the impact of prolonged sedation on N20 amplitude and correlate the rate of N20 recovery with blood-based biomarkers and histological findings to confirm the construct validity of early SSEPs in our swine cardiac arrest models.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Preliminary 10X Genomics Xenium Profiler Spatial Transcriptomics Map of Renin-Angiotensin System Genes in the Mouse Subfornical Organ
Hantke Guixa Ana, Vazirabad Ibrahim, Mathieu Natalia, Muskus Veitia Patricia, Brozoski Daniel, Grobe Justin, Nakagawa Pablo, Sigmund Curt
A refined definition for low-risk pulmonary arterial hypertension patients including mortality and morbidityFauvel Charles, Liu Yongqi, Correa-jaque Priscilla, Everett Allen, Kanwar Manreet, Vanderpool Rebecca, Sahay Sandeep, Lin Shili, Benza Raymond