Final ID: LBP68
Detection of Large Vessel Occlusion Using AI: Evaluating RapidAI versus VizAI in Detection of LVO on CT Angiography in a Large Consecutive Patient Series of 1,591 Code Strokes (DUEL)
Purpose: To evaluate the performance of RapidAI and VizAI LVO detection software in a large sample of consecutive code stroke patients presenting to a comprehensive stroke center using both detection products simultaneously.
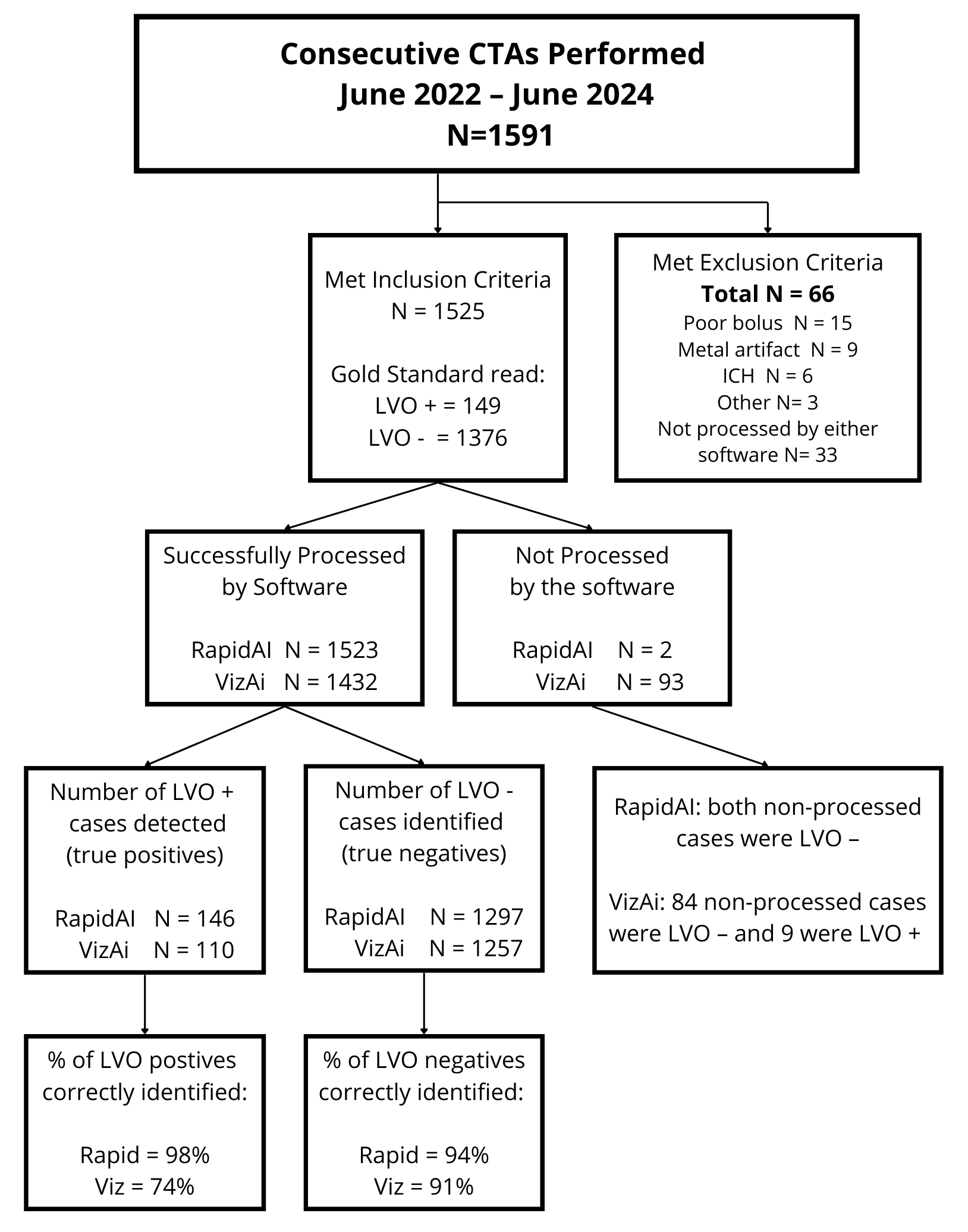
Methods: In this retrospective analysis, CTA data from consecutive code stroke patients between June 2022 and June 2024 were reviewed. LVO diagnosis was confirmed by radiology reports combined with an expert review of both CTA and CT perfusion (CTP) imaging. LVO was defined as occlusion or high-grade stenosis of the intracranial internal carotid artery (ICA) or the middle cerebral artery (MCA) M1 segment defined anatomically along its course from the MCA origin to its genu at the inferior aspect of the Sylvian fissure. High-grade stenosis was verified on CTA and/or an accompanying perfusion deficit in the ICA/MCA territory on CTP. Cases were excluded if not sent for AI processing, or if there was poor bolus, metal artifact, or brain hemorrhage present. The diagnostic accuracy of each software was compared.
Results: Of the 1591 consecutive CTAs performed over the study duration, 66 cases were excluded (33 not processed with AI; 33 with poor bolus, metal artifact, or brain hemorrhage), leaving 1,525 cases for analysis. Among cases meeting inclusion criteria (M=709; F=816, Unknown=1; Age average=67.8 years), 149 (10%) had an LVO, and 1376 were LVO negative. Rapid software successfully processed 1,523 (>99%) eligible cases, and Viz successfully processed 1,432 (90%). Rapid identified 146 (98%) LVOs compared with 110 (74%) by Viz (P =0.000000002). Rapid correctly identified 94% of LVO-negative cases compared to 91% for Viz (P=0.004). Rapid detected 39 LVOs not detected by Viz, whereas Viz detected 3 LVOs missed by Rapid.
Conclusion: RapidAI detected a higher percentage of LVOs compared to VizAI (98% vs 74%) and correctly identified more LVO-negative cases (94% vs 91%). Viz did not detect 26% of the LVOs, with 23% due to failure to process eligible cases. The substantial number of LVOs missed by the VIZ software could lead to delay in LVO diagnosis and treatment times.
More abstracts on this topic:
Patel Zeel, Liu Yang, Wengrofsky Perry, Yoon Sung-han
A Contemporary Machine Learning-Based Risk Stratification for Mortality and Hospitalization in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Using Multimodal Real-World DataFudim Marat, Weerts Jerremy, Patel Manesh, Balu Suresh, Hintze Bradley, Torres Francisco, Micsinai Balan Mariann, Rigolli Marzia, Kessler Paul, Touzot Maxime, Lund Lars, Van Empel Vanessa, Pradhan Aruna, Butler Javed, Zehnder Tobias, Sauty Benoit, Esposito Christian, Balazard Félix, Mayer Imke, Hallal Mohammad, Loiseau Nicolas
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.