Final ID: LBP32
Elastase Mediated White Matter Damage in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: Microglia - Neutrophils Pas De Deux
Abstract Body: Background: Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is widely present in elderly individuals accounting for 20%-25% of stroke as well as contributing to 45% of dementia cases worldwide. White matter lesions (WMLs), the most common feature of CSVD, are characterized by myelin degeneration and oligodendrocytes loss.
Objectives: To characterize the pathological features of neutrophil elastase ELANE in the context of chronic brain injuries, including impairments of white matter tracts in CSVD.
Methods: Patients plasma ELANE levels were measured using ELISA. Brain ELANE expression was detected using western blot and ELISA in a rodent model of CSVD with bilateral common carotid artery stenosis (BCAS). WMLs was determined using MBP/Olig2 immunostaining, Luxol fast blue and transmission electron microscopy. Neurological performance was assessed by rotarod, narrow-elevated beam, novel object recognition, Y-maze, and Morris water maze tests. Primary murine OPCs and CG4 cells were used in vitro. LC-MS/MS were used to analyze cleavage sites. Sivelestat was investigated in BCAS mice. ELANE expression in postmortem brain tissues from CSVD patients using multiplex immunofluorescence staining.
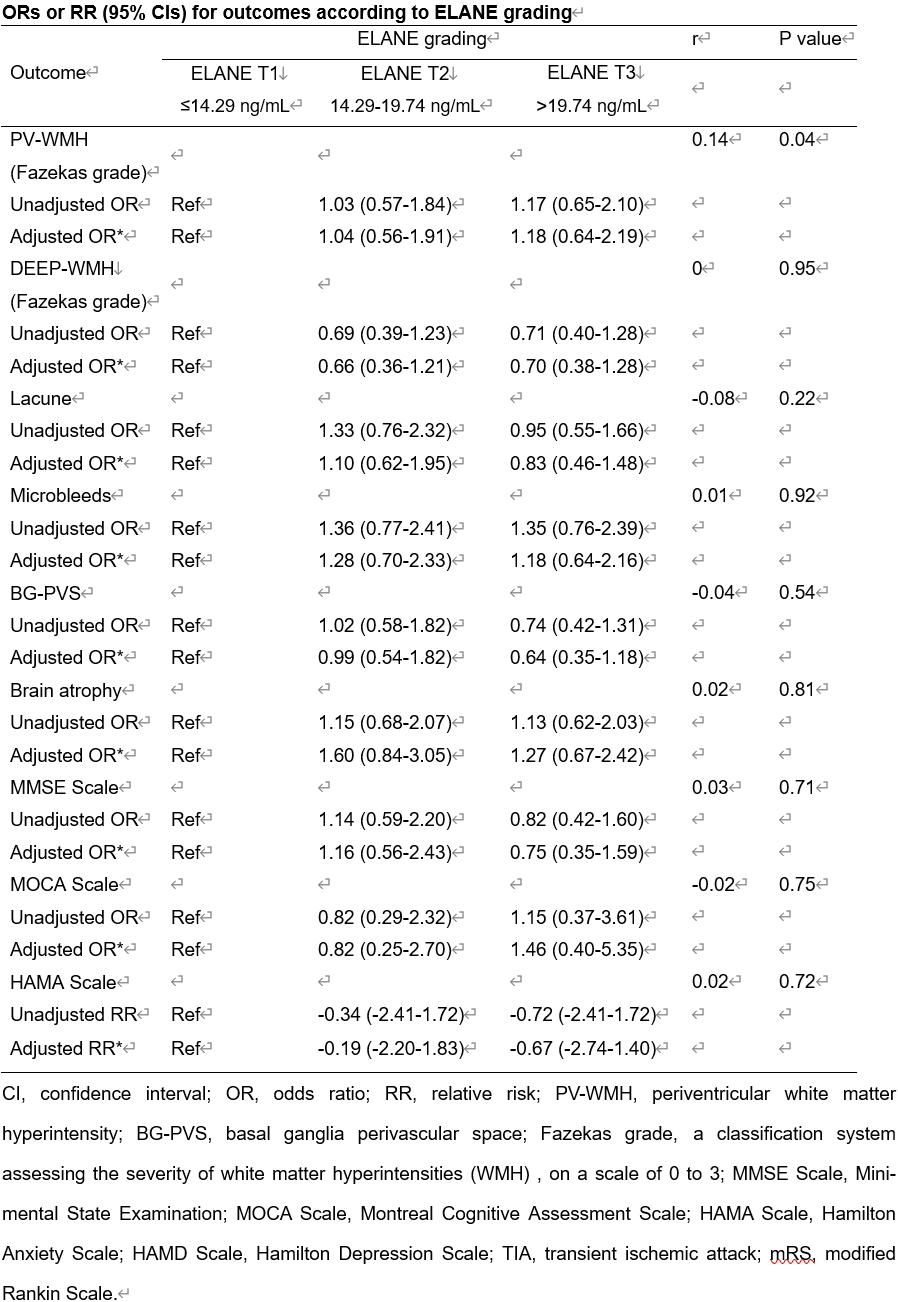
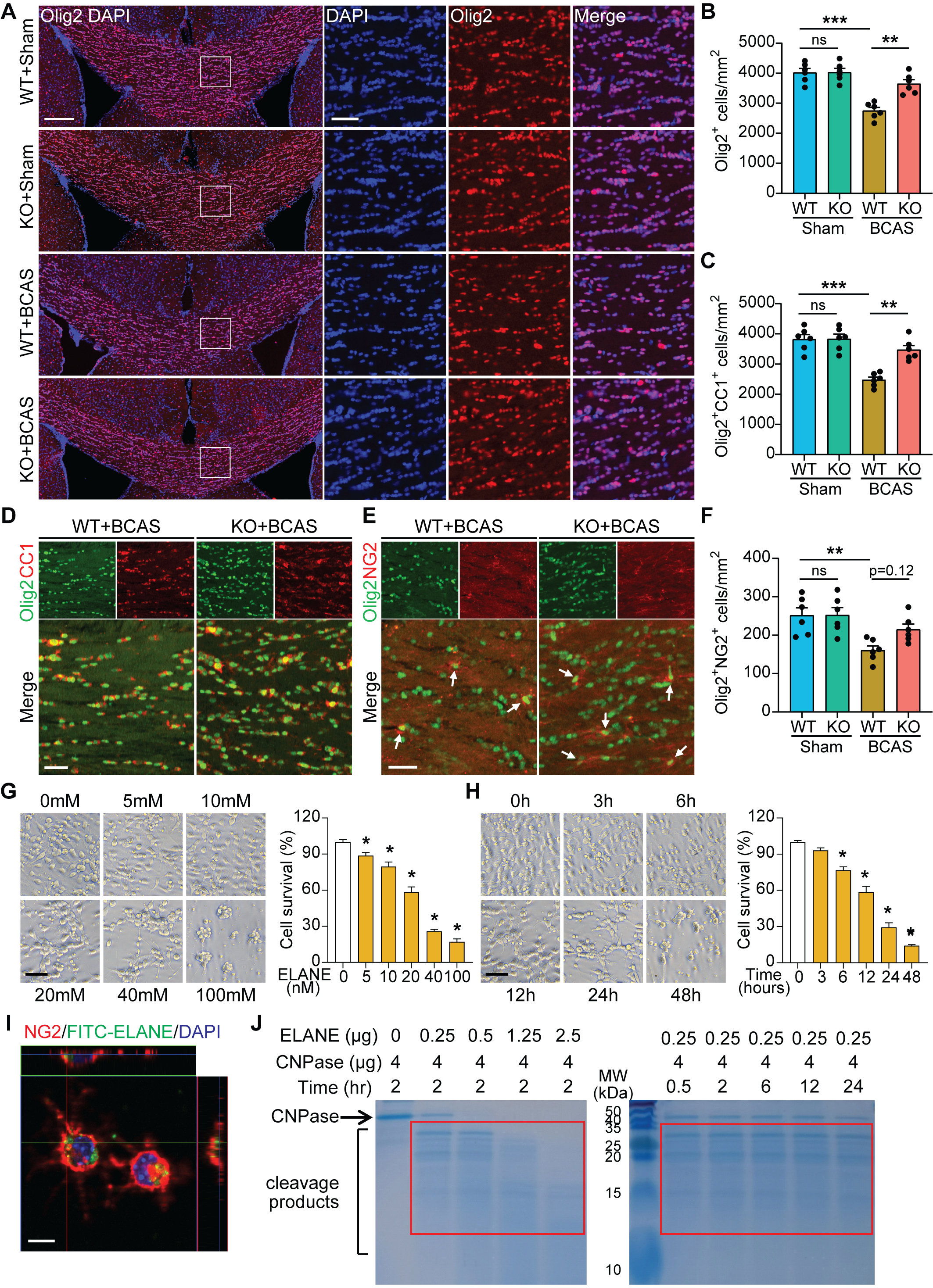
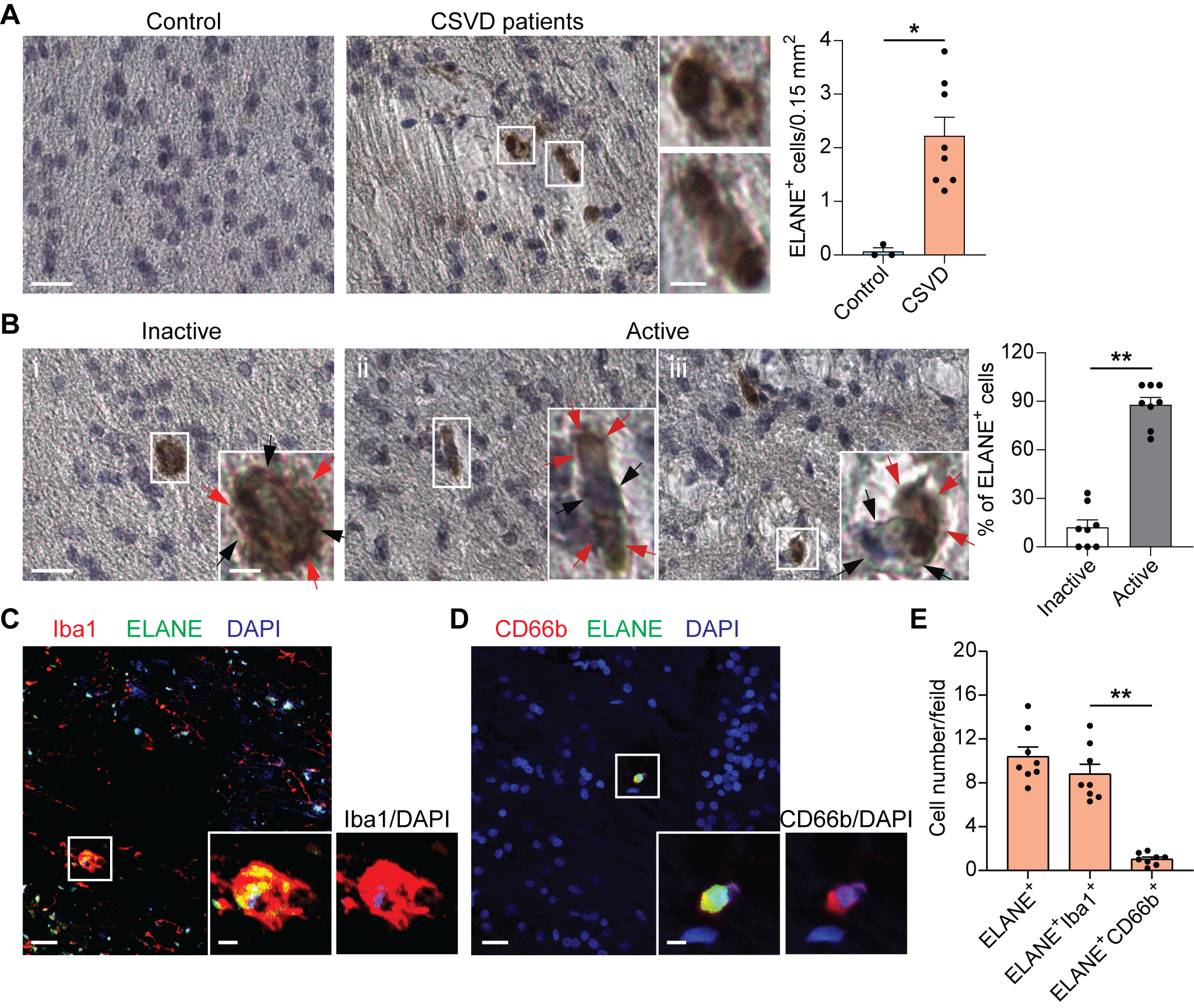
Results: We established a positive correlation between plasma levels of ELANE and periventricular white matter hyperintensity in a cohort of CSVD patients. Upregulated ELANE was detected in microglia and neutrophils in BCAS mice. Genetic ELANE deficiency significantly alleviated oligodendrocyte loss, reducing WMLs and ameliorating sensorimotor and cognitive impairments in BCAS mice. In vitro studies demonstrated that ELANE triggered time-dependent and dose-dependent oligodendrocyte lineage cell death. Mechanistically, ELANE, accumulated by oligodendrocytes, cleaved the phosphodiesterase domain of 2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphodiesterase. Pharmacological inhibition of ELANE with Sivelestat reduced oligodendrocyte loss and WMLs leading to the restoration of neurological improvements in BCAS mice. In post-mortem brain specimens of CSVD patients ELANE accumulated within WMLs being predominantly localized in microglia rather than in the brain-infiltrating neutrophils.
Conclusions: This study provides new insights into the pathogenetic mechanism of microglia-derived ELANE acting in conjunction with neutrophil elastase to induce oligodendrocyte damage and the development of WMLs, identifying ELANE as a promising therapeutic target for managing small vessel disease and vascular dementia.
Objectives: To characterize the pathological features of neutrophil elastase ELANE in the context of chronic brain injuries, including impairments of white matter tracts in CSVD.
Methods: Patients plasma ELANE levels were measured using ELISA. Brain ELANE expression was detected using western blot and ELISA in a rodent model of CSVD with bilateral common carotid artery stenosis (BCAS). WMLs was determined using MBP/Olig2 immunostaining, Luxol fast blue and transmission electron microscopy. Neurological performance was assessed by rotarod, narrow-elevated beam, novel object recognition, Y-maze, and Morris water maze tests. Primary murine OPCs and CG4 cells were used in vitro. LC-MS/MS were used to analyze cleavage sites. Sivelestat was investigated in BCAS mice. ELANE expression in postmortem brain tissues from CSVD patients using multiplex immunofluorescence staining.
Results: We established a positive correlation between plasma levels of ELANE and periventricular white matter hyperintensity in a cohort of CSVD patients. Upregulated ELANE was detected in microglia and neutrophils in BCAS mice. Genetic ELANE deficiency significantly alleviated oligodendrocyte loss, reducing WMLs and ameliorating sensorimotor and cognitive impairments in BCAS mice. In vitro studies demonstrated that ELANE triggered time-dependent and dose-dependent oligodendrocyte lineage cell death. Mechanistically, ELANE, accumulated by oligodendrocytes, cleaved the phosphodiesterase domain of 2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphodiesterase. Pharmacological inhibition of ELANE with Sivelestat reduced oligodendrocyte loss and WMLs leading to the restoration of neurological improvements in BCAS mice. In post-mortem brain specimens of CSVD patients ELANE accumulated within WMLs being predominantly localized in microglia rather than in the brain-infiltrating neutrophils.
Conclusions: This study provides new insights into the pathogenetic mechanism of microglia-derived ELANE acting in conjunction with neutrophil elastase to induce oligodendrocyte damage and the development of WMLs, identifying ELANE as a promising therapeutic target for managing small vessel disease and vascular dementia.
More abstracts on this topic:
The Impact of Proteolytic Modifications on Lipoprotein Metabolism
Voy Clairity, Karakashian Alexander, Carter Abby, Mobilia Maura, Neupane Khaga, Hage Olivia, Gordon Scott
Neuropathological Substrates of Cognitive Impairment in a Mouse Model of Chronic Progressive Carotid Artery StenosisBah Thierno, Cullen Abigail, Davis Catherine, Walker Ashley, Pike Martin, Raber Jacob, Alkayed Nabil
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)