Final ID: LB34
Identification of potential neuroprotective drug targets for ischemic stroke from genetic insights: a Mendelian randomization study
Abstract Body: Introduction
Stroke is a major cause of death and disability worldwide. Although tremendous progress has been achieved in the neuroprotective treatment of ischemic stroke (IS), a large minority of patients continue to respond poorly to existing medications, owing in part to a lack of appropriate therapeutic targets.
Methods
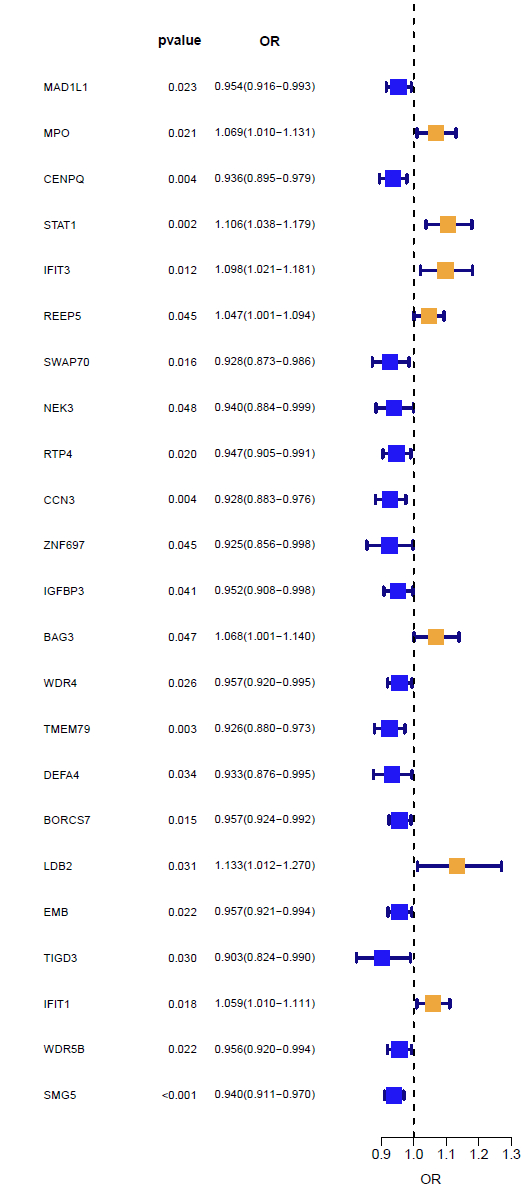
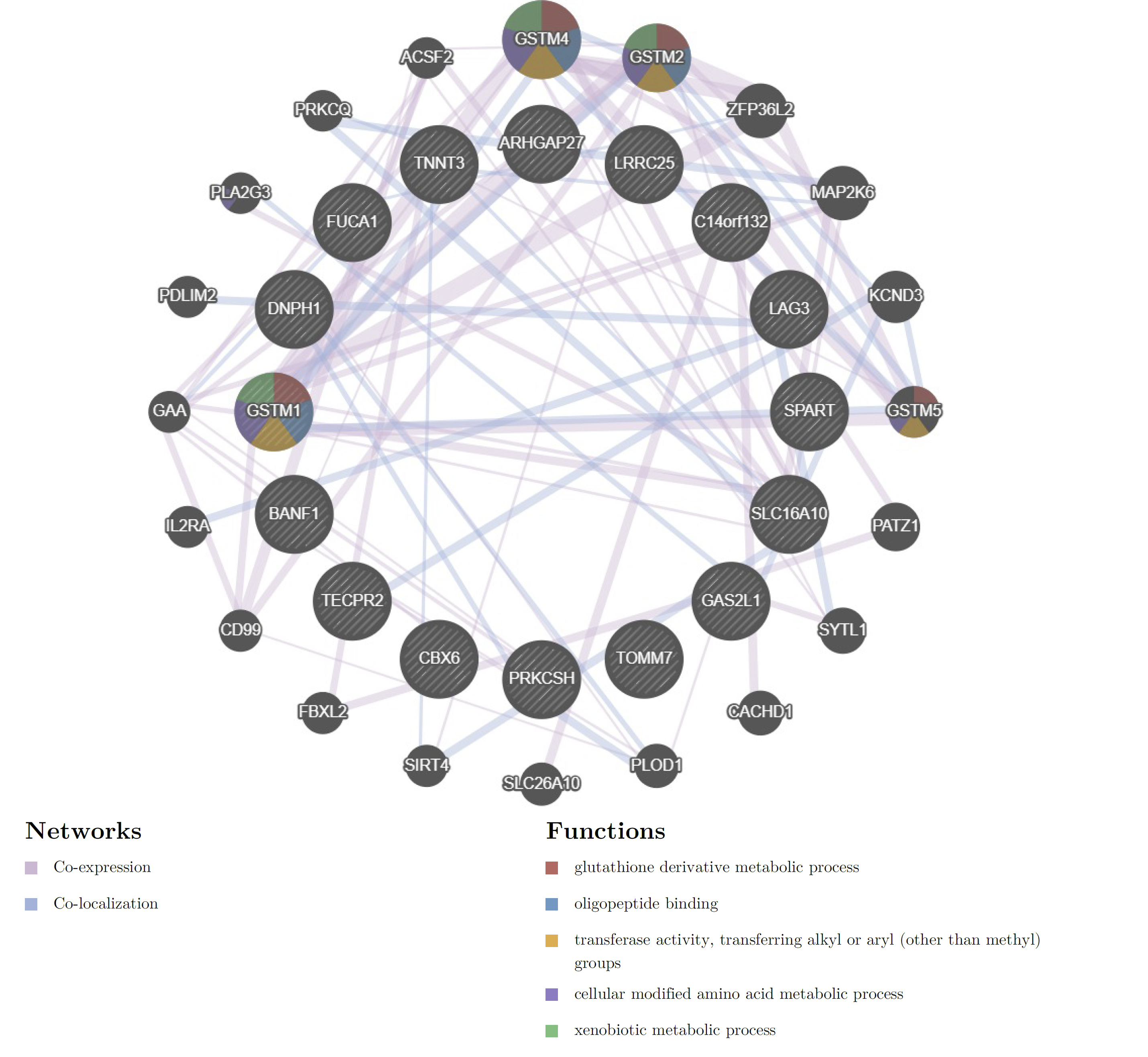
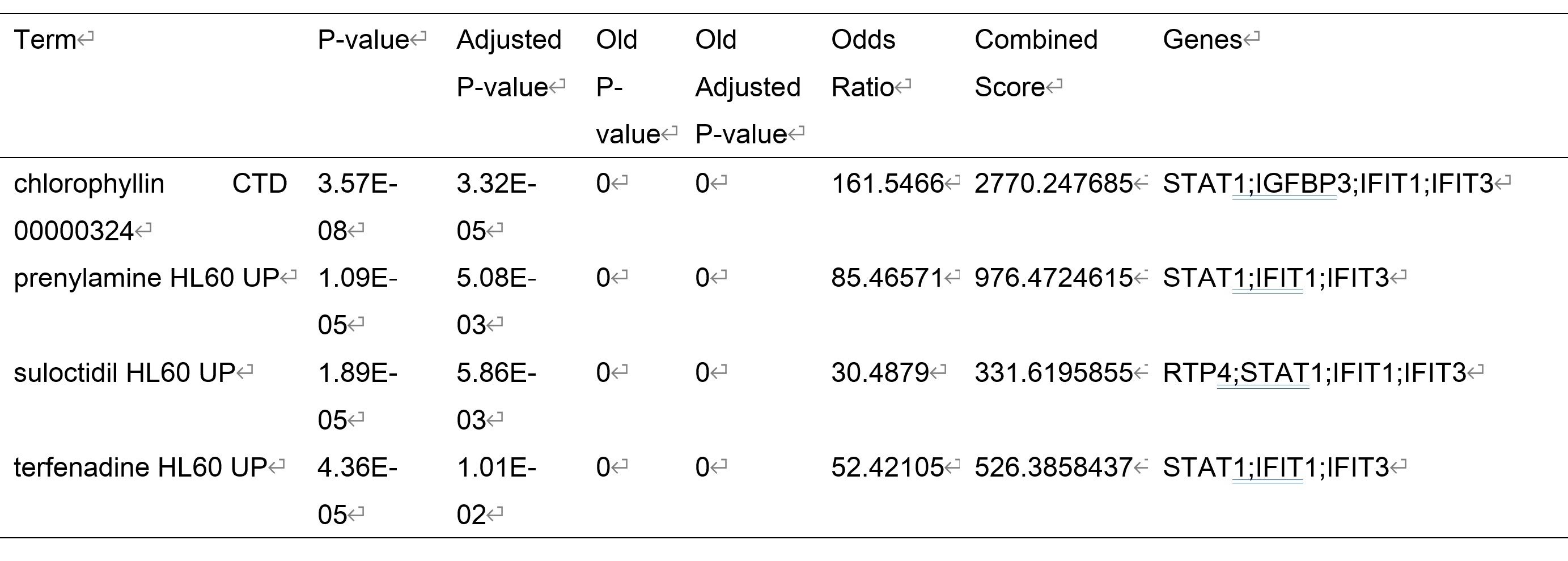
To find new neuroprotective targets for IS, a Mendelian randomization (MR) was performed. Cis-expression quantitative trait loci (cis-eQTL, exposure) data were obtained from the eQTLGen Consortium (sample size 31,684). Summary statistics for ID (outcome) were obtained from the two largest independent cohorts: sample sizes of 440,328 (34,217 cases and 406,111 controls) and 218,792 (12,632 cases and 206,160), respectively. Colocalization analysis was used to test whether RA risk and gene expression were driven by common SNPs. Drug prediction and molecular docking were further used to validate the medicinal value of drug targets.
Results
Four drug targets were significant in both cohorts in MR analysis and supported by localization. These genes are strongly associated with immune function in terms of biological significance. Molecular docking showed excellent binding for drugs and proteins with available structural data.
Conclusion
This study identifies four potential drug targets for IS. Drugs designed to target these genes have a higher chance of success in clinical trials and are expected to help prioritize IS drug development and save on drug development costs.
Stroke is a major cause of death and disability worldwide. Although tremendous progress has been achieved in the neuroprotective treatment of ischemic stroke (IS), a large minority of patients continue to respond poorly to existing medications, owing in part to a lack of appropriate therapeutic targets.
Methods
To find new neuroprotective targets for IS, a Mendelian randomization (MR) was performed. Cis-expression quantitative trait loci (cis-eQTL, exposure) data were obtained from the eQTLGen Consortium (sample size 31,684). Summary statistics for ID (outcome) were obtained from the two largest independent cohorts: sample sizes of 440,328 (34,217 cases and 406,111 controls) and 218,792 (12,632 cases and 206,160), respectively. Colocalization analysis was used to test whether RA risk and gene expression were driven by common SNPs. Drug prediction and molecular docking were further used to validate the medicinal value of drug targets.
Results
Four drug targets were significant in both cohorts in MR analysis and supported by localization. These genes are strongly associated with immune function in terms of biological significance. Molecular docking showed excellent binding for drugs and proteins with available structural data.
Conclusion
This study identifies four potential drug targets for IS. Drugs designed to target these genes have a higher chance of success in clinical trials and are expected to help prioritize IS drug development and save on drug development costs.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Curious Complete Heart Block with Carfilzomib
Shah Mohammed, Rahman Naveed, Al-mohamad Talal, Batra Sejal, Vyas Apurva
A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials: Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitors as a Therapeutic Strategy for HypertensionMarzano Luigi, Merlo Matteo, Pizzolo Francesca, Friso Simonetta
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)