Final ID: LBP28
Cerebral Oedema Outcome in Patients with Early Sedation after Endovascular Thrombectomy in Large Infarct A Secondary Analysis of the ANGEL-ASPECT Trial
Malignant cerebral oedema is common in patients with large infarcts. The aim of this study was to investigate the outcomes of cerebral oedema in patients of large infarcts needing early sedation after endovascular thrombectomy (EVT).
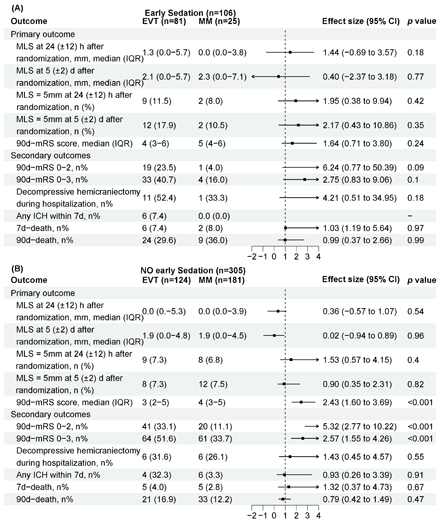
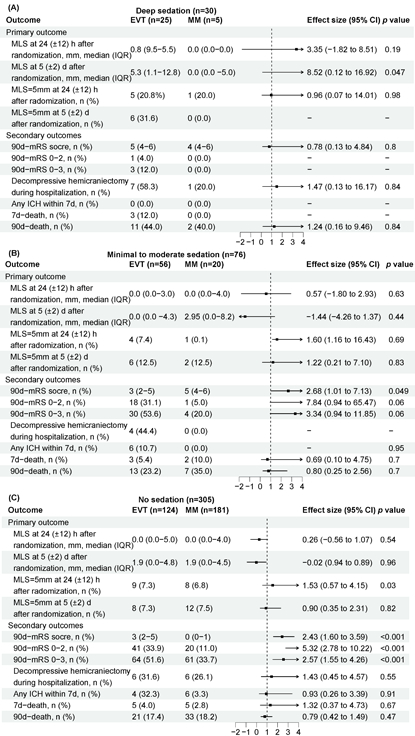
Methods: This is a secondary analysis of the Endovascular Therapy in Acute Anterior Circulation Large Vessel Occlusive Patients with a Large Infarct Core (ANGEL-ASPECT), a randomized clinical trial conducted between October 2, 2020, and May 18, 2022. This trial enrolled 456 patients within 24 hours of stroke onset due to large infarcts. Patients with complete data on sedation within 24 hours after randomization were included and categorized into early sedation group or a non-early sedation group, according to whether they accepted sedation within 24 hours after randomization. The primary outcome was midline shift (MLS) within 7 days after randomization. An exploration analysis was performed to evaluate the association of sedation level with oedema outcomes between groups.
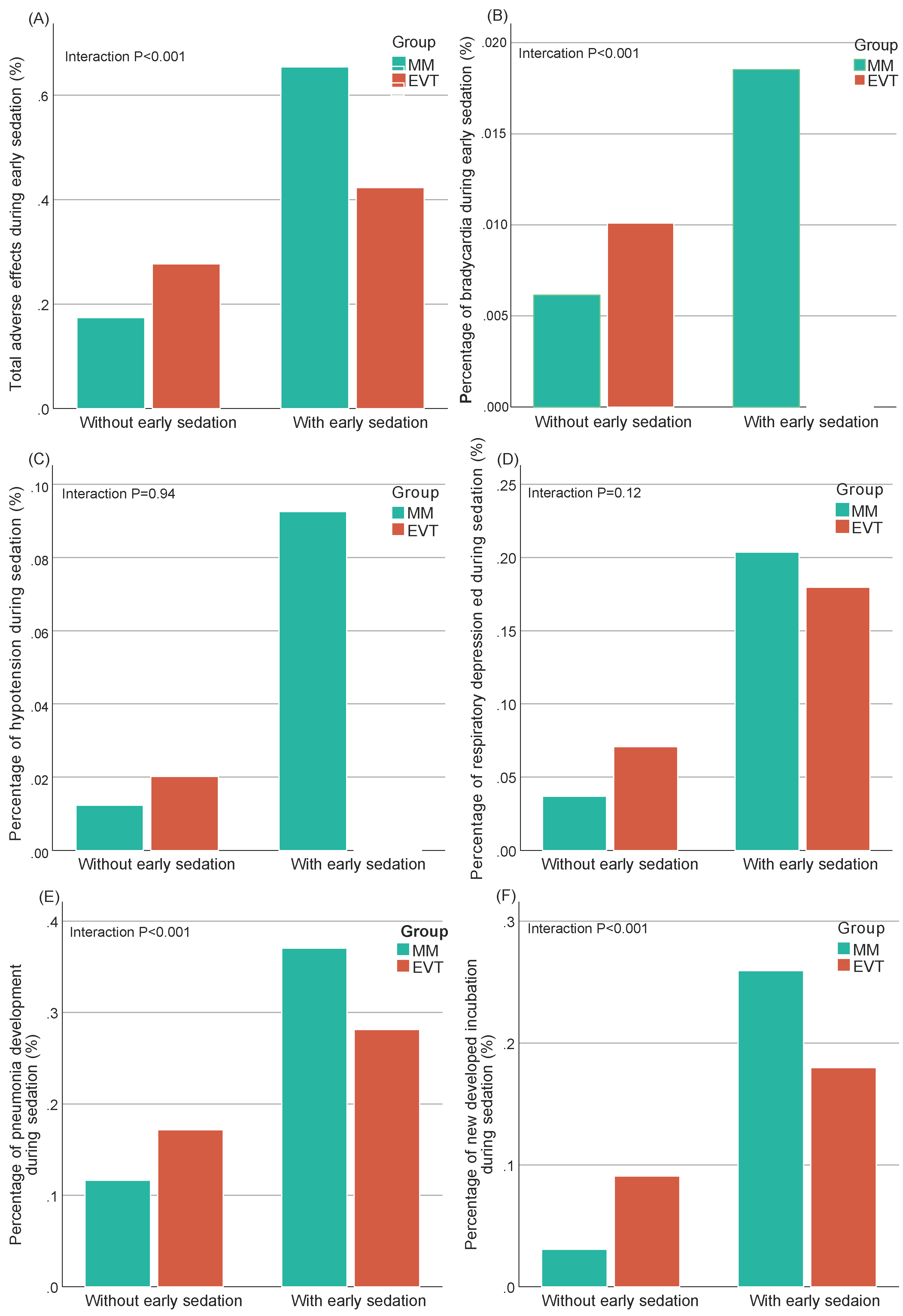
Results: A total of 411 patients were included, with a mean (standard deviation [SD]) age of 65.8 [9.9] years, and 265 (64.5%) female). No significant difference was observed in MLS at 24 (±12) h or and at 5 (±2) d after randomization between EVT and MM group whether an early sedation was conducted or not. However, MLS at 5 (±2) d was higher when early deep sedation was monitored in EVT groups comparing with that in MM group (median [IQR], 5.3 [1.1-12.8] vs. 0.0 [0.0-5.0]; aβ [95%OR], 8.52 [0.12 to 16.92]; p=0.047). Patients needing early sedation was not associated with a better functional outcome after EVT, comparing to those who did not need early sedation. When considering adverse effects, higher rates of bradycardia, pneumonia and incubation developed during sedation were observed in MM group (P-interaction<0.001). Other outcomes including malignant oedema, decompressive hemicraniectomy during hospitalization, any intracranial hemorrhage within 7 days and death rate did not differ between each group.
Conclusion: When needing early sedation under different situations, patients might not benefit significantly from EVT in terms of the overall cerebral oedema or functional outcome. If early sedation was recommended, deep sedation and sedation without reperfusion treatment in large infarcts should be prudent. Further studies are also expected to explore if a cause-result relationship existed between sedation and oedema outcomes after EVT.
More abstracts on this topic:
Fudim Marat, Weerts Jerremy, Patel Manesh, Balu Suresh, Hintze Bradley, Torres Francisco, Micsinai Balan Mariann, Rigolli Marzia, Kessler Paul, Touzot Maxime, Lund Lars, Van Empel Vanessa, Pradhan Aruna, Butler Javed, Zehnder Tobias, Sauty Benoit, Esposito Christian, Balazard Félix, Mayer Imke, Hallal Mohammad, Loiseau Nicolas
A distinct clot transcriptomic signature is associated with atrial fibrillation-derived ischemic stroke in the INSIGHT RegistrySeah Carina, Rivet Dennis, Fraser Justin, Kellner Christopher, Devarajan Alex, Vicari James, Dabney Alan, Baltan Selva, Sohrabji Farida, Pennypacker Keith, Nanda Ashish, Woodward Britton
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.