Final ID: WMP41
Evaluation of a Digital Cognitive Self-Assessment Method for Post-Stroke Cognitive Decline
Hypothesis: This study aims to investigate the feasibility of using the XpressO online self-administered cognitive assessment and compare its ability to detect PSCD with the MoCA short form (MoCA-sf) at our out-patient stroke clinic.
Methods: Patients at the clinic with a history of ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes were included. We used <12 as the cutoff to determine low performance on the MOCA-sf. After their clinic visit, participants consented and completed a screening survey on stroke risk factors, followed by both the MoCA-sf and XpressO assessments. Completion times for both assessments were recorded, and results were analyzed using R Studio.
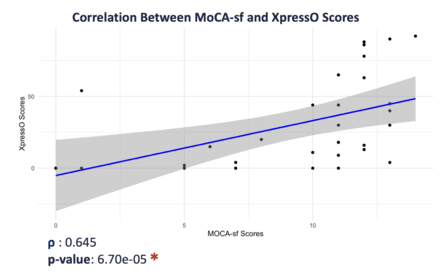
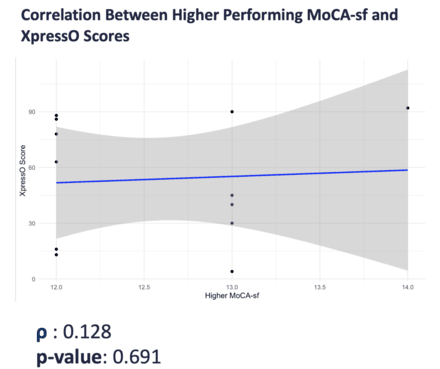
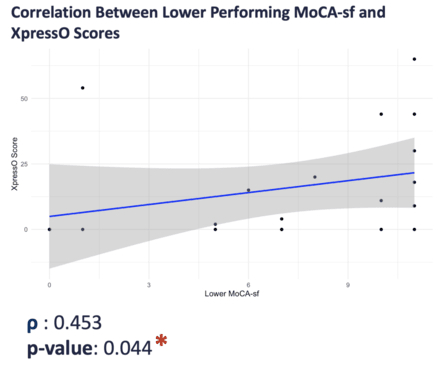
Results: We enrolled 32 patients and 32 completed the assessment. The results of this study found a moderate correlation between Xpresso and MOCA-sf (ρ = 0.645, p = 6.70e-05). When stratified by cognitive function, no significant correlation was observed between XpressO and higher MoCA-sf (≥12) scores (ρ = 0.128, p = 0.691). The average time to complete the assessment was 6.63 minutes for MOCA –sf and 6.28 minutes for Xpresso. This difference was not significant. However, when stratified by cognitive function, there was a significant difference in completion time between XpressO (4.43 minutes) and MoCA-sf (5.83 minutes).
Conclusion: The results suggest that XpressO is better at detecting severe cognitive decline but is less sensitive to milder impairments. Time to complete each test differed significantly only in patients with higher cognitive function, with XpressO being faster than MoCA in this group. XpressO’s lack of significant correlation with higher MoCA-sf scores makes it less suitable as a standalone tool for PSCD screening in outpatient stroke clinics. XpressO can be used to identify patients at risk for severe PSCD, but higher XpressO scores should not eliminate the possibility of PSCD in patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
Rajith Gokul, Erzinger Gabriel, Rizwan Ahmed Aisha, Silva Yasmin, Noll Giovani, Hussain Masaraf, Premraj Lavienraj
Diagnostic Accuracy of Cone-Beam CT for Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage in Suspected Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysisFerrone Nicholas, Katz Jeffrey, Sanelli Pina, Sanmartin Maria, O'hara Joseph, Jimenez Jean, Ferrone Sophia, Lee Un Jung, Morales Jaclyn, White Timothy, Wang Jason
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.