Final ID: TP115
Differences in the Medical Management of Post-Stroke Sequelae Among Patients Treated with Mechanical Thrombectomy vs Intravenous Thrombolysis
Abstract Body: Background: Mechanical thrombectomy (MT) as treatment for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) has demonstrated superior functional outcomes compared to intravenous thrombolysis (IVT). Yet AIS survivors often experience a range of unstudied post-stroke complications which negatively affect patient reported outcomes. To inform clinical practice, we assessed 90-day differences in the medical management of common stroke post-complications among patients treated with MT vs. IVT.
Methods: A retrospective cohort of hospitalized AIS patients treated with IVT or MT were identified from Electronic Medical Records of 92 large healthcare organizations (01/2015-09/2024). Matched propensity scores were used to adjust for baseline differences across 36 factors. Outcomes included the use of medication(s) for the management of fatigue, spasticity, mood, sleep, seizure, neurogenic bowel & neurogenic bladder. Pre-specified subgroup analyses included differences in post-stroke sequelae management stratified by NIHSS scores of ≤9 (mild AIS) or >9 (moderate/severe AIS) & differences in post-stroke sequelae between AIS patients treated with MT vs MT + IVT.
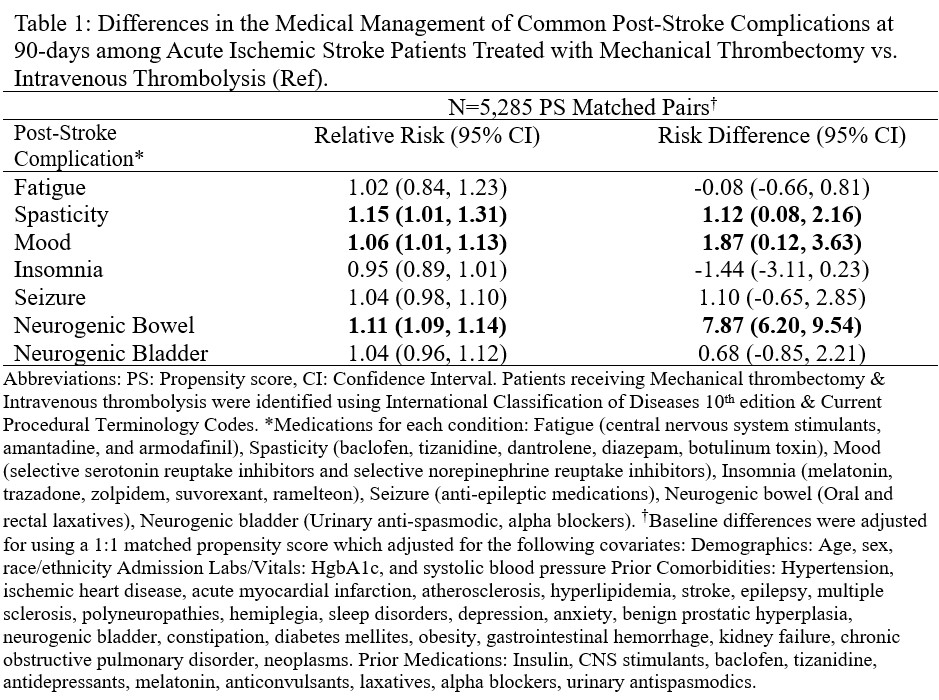
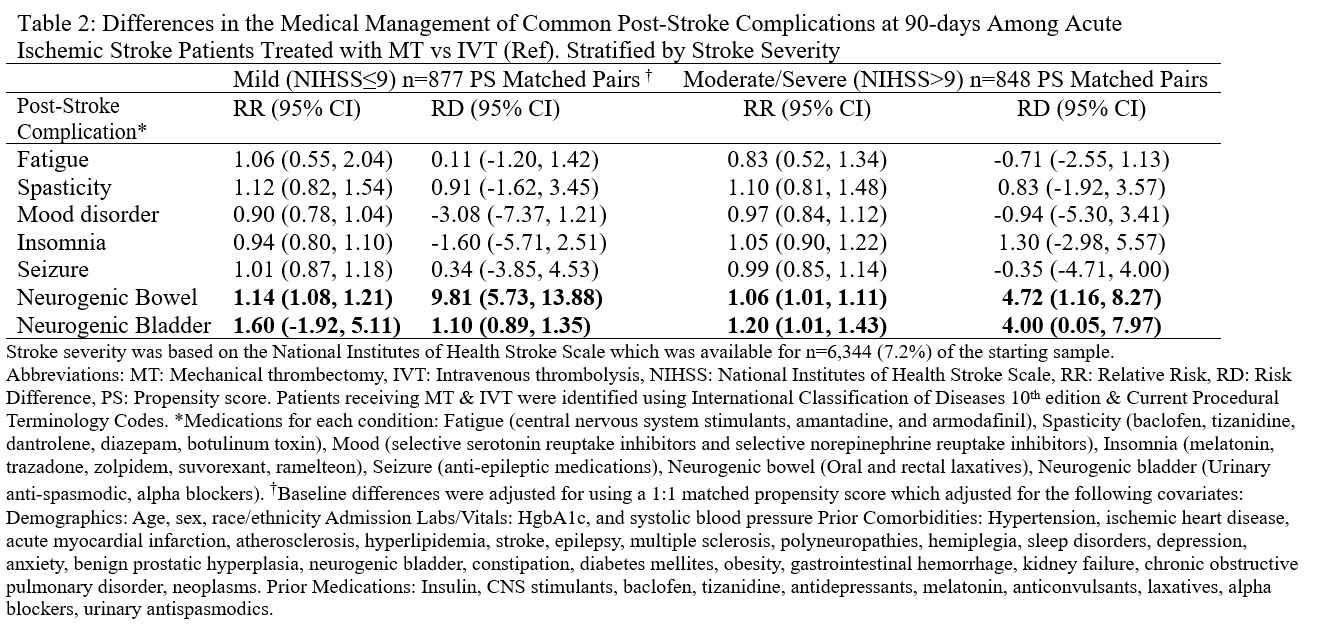
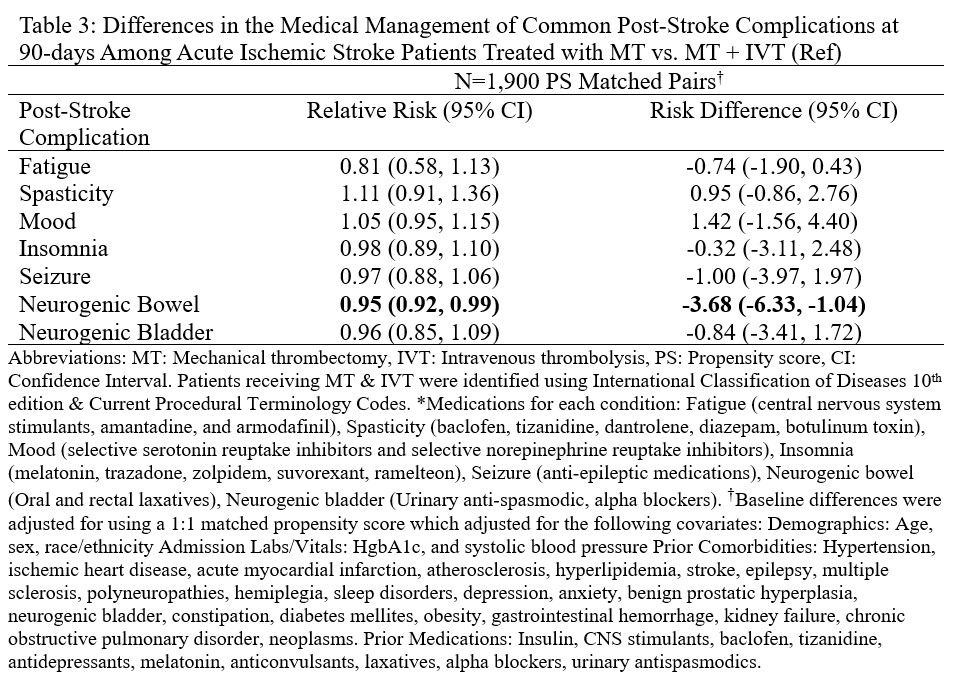
Results: The final cohort consisted of n=87,819 AIS patients treated with either IVT (n=82,534) or MT (n=5,285). PS matching resulted in 5,285 matched pairs with good balance across all baseline covariates. At 90-days, AIS patients treated with MT were more likely to receive medications for spasticity (RR: 1.15, 95%CI: 1.01, 1.31), mood (RR: 1.06, 95%CI: 1.01, 1.13) & neurogenic bowel (RR: 1.11, 95%CI: 1.09, 1.14) (Table 1). Approximately 7% (n=6,344) of AIS patients had NIHSS scores – PS matching resulted in 877 matched pairs with NIHSS ≤9 & 848 matched pairs with NIHSS>9. Following stratification, AIS patients treated with MT were significantly more likely to receive treatment of neurogenic bowel & bladder (Table 2). For the MT vs MT + IVT comparison, patients treated with MT were 5% less likely to receive treatment for neurogenic bowel RR: 0.95 (95%CI: 0.92, 0.99) among 1,900 matched pairs (Table 3).
Discussion:
Using real world data, AIS patients treated with MT (vs IVT) were more likely to receive treatment for spasticity, mood & neurogenic bowel. Among patients with documented NIHSS scores, differences remained significant for treatment of neurogenic bowel and bladder after stratifying by stroke severity. Healthcare providers should screen for these post-stroke sequelae, which substantially affect quality of life for AIS survivors.
Methods: A retrospective cohort of hospitalized AIS patients treated with IVT or MT were identified from Electronic Medical Records of 92 large healthcare organizations (01/2015-09/2024). Matched propensity scores were used to adjust for baseline differences across 36 factors. Outcomes included the use of medication(s) for the management of fatigue, spasticity, mood, sleep, seizure, neurogenic bowel & neurogenic bladder. Pre-specified subgroup analyses included differences in post-stroke sequelae management stratified by NIHSS scores of ≤9 (mild AIS) or >9 (moderate/severe AIS) & differences in post-stroke sequelae between AIS patients treated with MT vs MT + IVT.
Results: The final cohort consisted of n=87,819 AIS patients treated with either IVT (n=82,534) or MT (n=5,285). PS matching resulted in 5,285 matched pairs with good balance across all baseline covariates. At 90-days, AIS patients treated with MT were more likely to receive medications for spasticity (RR: 1.15, 95%CI: 1.01, 1.31), mood (RR: 1.06, 95%CI: 1.01, 1.13) & neurogenic bowel (RR: 1.11, 95%CI: 1.09, 1.14) (Table 1). Approximately 7% (n=6,344) of AIS patients had NIHSS scores – PS matching resulted in 877 matched pairs with NIHSS ≤9 & 848 matched pairs with NIHSS>9. Following stratification, AIS patients treated with MT were significantly more likely to receive treatment of neurogenic bowel & bladder (Table 2). For the MT vs MT + IVT comparison, patients treated with MT were 5% less likely to receive treatment for neurogenic bowel RR: 0.95 (95%CI: 0.92, 0.99) among 1,900 matched pairs (Table 3).
Discussion:
Using real world data, AIS patients treated with MT (vs IVT) were more likely to receive treatment for spasticity, mood & neurogenic bowel. Among patients with documented NIHSS scores, differences remained significant for treatment of neurogenic bowel and bladder after stratifying by stroke severity. Healthcare providers should screen for these post-stroke sequelae, which substantially affect quality of life for AIS survivors.
More abstracts on this topic:
A single-center experience of oncology rehabilitation to facilitate cardiopulmonary fitness recovery among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy.
Imboden Mary, Li Hsin Fang, Koltner Erin, Murphy Corrin, Page David, Layoun Michael
Assessing the Ability of ChatGPT to Guide the Decision for Intravenous Thrombolysis in Patients with Acute Ischemic StrokesIbrikji Sidonie, Uchino Ken, Buletko Andrew, Itrat Ahmed, Sundararajan Jayashree, Kharal Abbas, Al Banna Mona, Khawaja Zeshaun
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)