Final ID: DP22
The NOMAS-CBI Score: Development of a Risk Factor-Based Score to Detect Covert Brain Infarcts on MRI
Methods: Inclusion criteria were age > 40 years, no prior stroke or TIA, and available MRI brain scan. Exclusion criteria: missing information on risk-factor variables. We retrieved demographics and vascular risk factor information at the time-point closest to the MRI. Logistic regression modeling was used to identify variables that had strongest association with CBIs on MRI. Three models (CBI score, CBI score 1, CBI score 2) with varying number of variables were devised to identify abbreviated versions of the score. We estimated cut-offs for the three scores, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values (PPV, NPV), and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC).
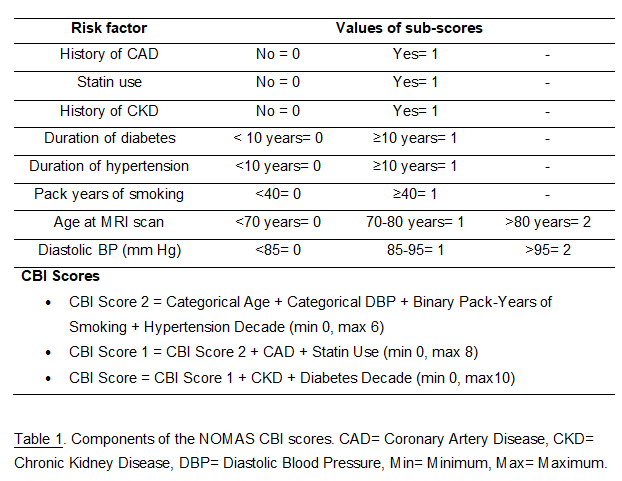
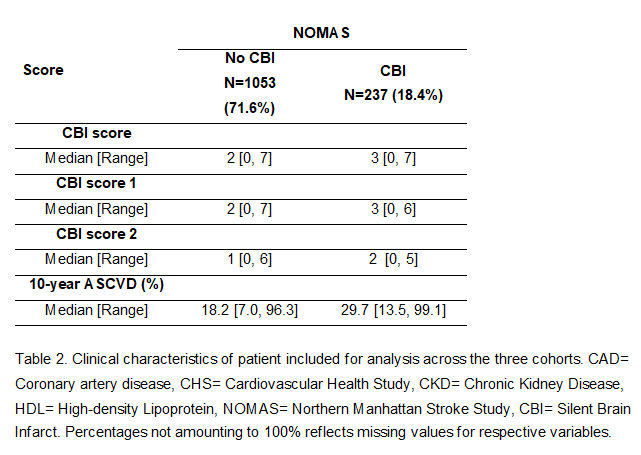
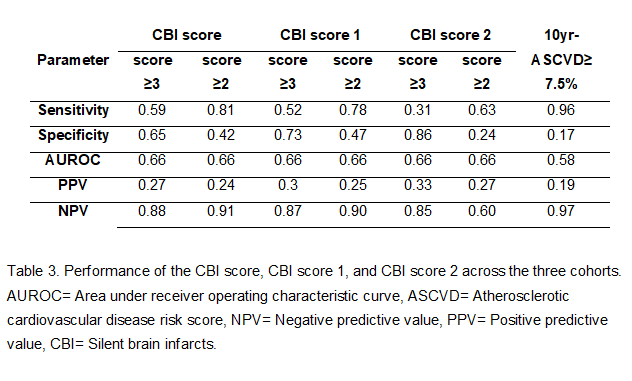
Results: Among 1,290 included patients, 237 (18.4%) had CBI. The CBI, CBI score 1, and CBI score 2 scores had 8, 6, and 4 risk-factor variables, respectively (Table 1). The median CBI score was higher in patients with CBIs compared to those without (Table 2). Two cut-offs, ≥ 2 and ≥ 3, were chosen for sensitivity analysis based on the median scores. The sensitivity of the three scores for identifying CBIs was higher at a cut-off ≥ 2 (0.81) compared to ≥ 3 (0.59) (Table 3). The AUROC indicated moderate accuracy (0.66) for predicting CBI. The Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) risk score (>7.5%) had higher sensitivity (0.96) but similar accuracy (0.66) in comparison to the CBI scores. Compared to the CBI score, the shorter CBI score 2 had lower sensitivity (0.63) and similar accuracy (0.66) at a cut-off of ≥ 2.
Conclusion: The NOMAS-CBI score uses vascular risk factor information and detects CBI on MRI with high sensitivity and moderate accuracy. A point-of-care variant, the CBI score 2, had lower sensitivity but similar accuracy. The score is comparable to the ASCVD and is easier to perform. Further analysis on the validity of the scores across other prospective cohorts is underway.
More abstracts on this topic:
Chen Zhanlin, Gordon Adam, Webster Gregory
Age-Related Differences in Aortic Valve Calcium Progression and the Risk for Aortic Stenosis: Multi-Ethnic Study of AtherosclerosisMarrero Natalie, Thanassoulis George, Rotter Jerome, Blaha Michael, Whelton Seamus, Jha Kunal, Grant Jelani, Razavi Alexander, Budoff Matthew, Shah Sanjiv, Blumenthal Roger, Post Wendy, Shaw Leslee
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.