Final ID: WP233
Minimally Invasive Surgical Evacuation Confers a Mortality Benefit in Patients With Moderate-Sized Putaminal Hemorrhages
Abstract Body: Introduction: Minimally invasive surgical (MIS) evacuation of basal ganglia hemorrhages has not demonstrated efficacy compared to medical management. Refining surgical selection criteria based on anatomic location may help to identify patients that selectively benefit from MIS evacuation. Prior study from our group has suggested that MIS evacuation of moderate-sized putaminal hemorrhages (pICH) using tubular retractors is associated with favorable functional outcomes. We hypothesized that postoperative functional outcomes were improved in patients with moderate-sized pICH compared to those of a matched cohort of medically managed patients.
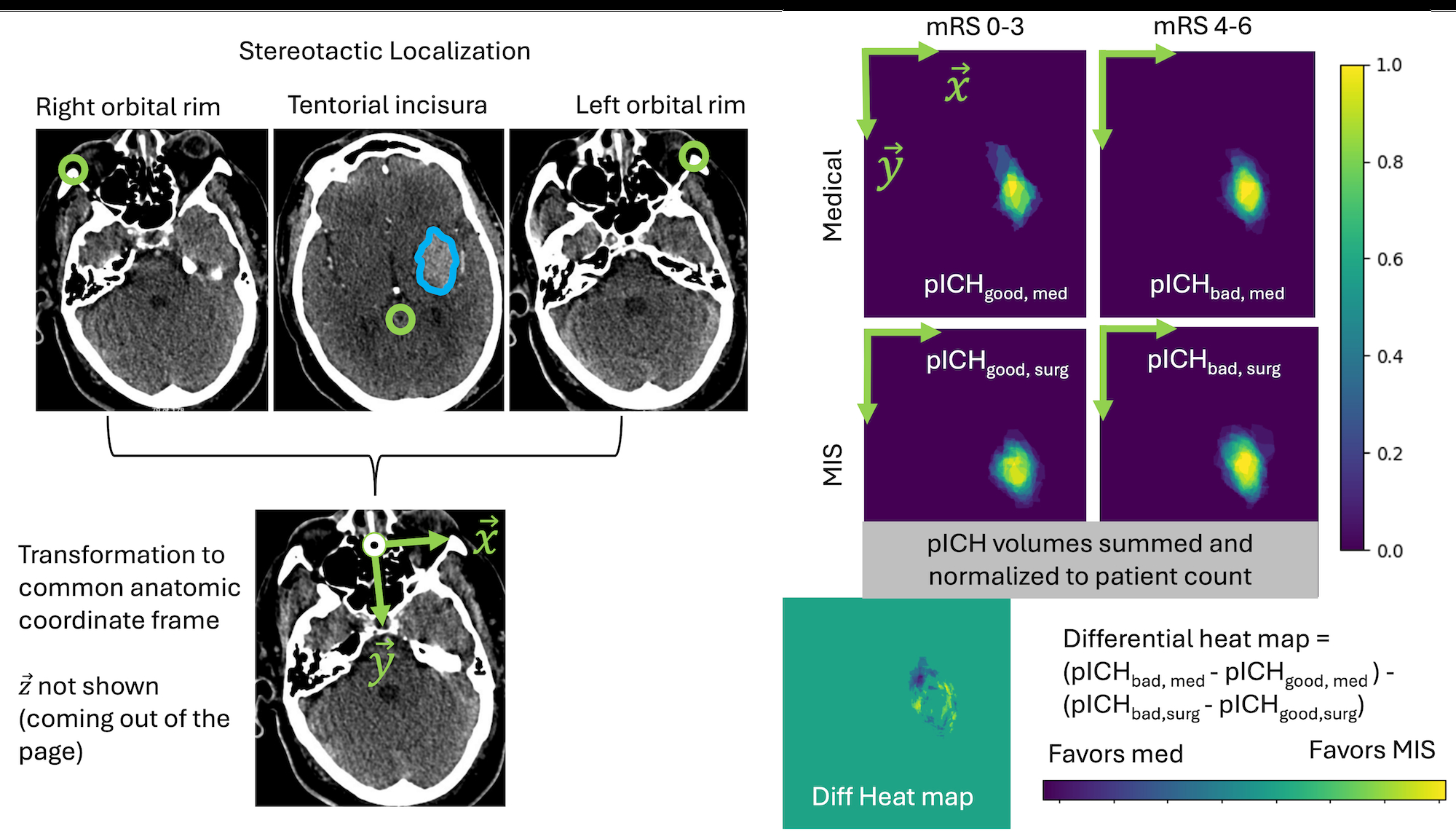
Methods: We performed a single-center retrospective review of patients admitted with spontaneous, non-lesional pICH between 10-50 mL from 2013-2024. Exclusion criteria included poor surgical candidacy based on comorbidity burden and baseline modified Rankin Scale (mRS) 4-6. Patients who underwent MIS evacuation were 1:1 matched to medically managed patients based on size and ICH score. The main outcome was mRS obtained within one year of admission. Regional pICH extension patterns were evaluated by stereotactically localizing pICH volumes in an anatomic coordinate frame (Image 1). Heat maps were constructed to illustrate pICH locations that were differentially associated with good (mRS 0-3) and poor (mRS 4-6) outcomes in surgical and medical cohorts.
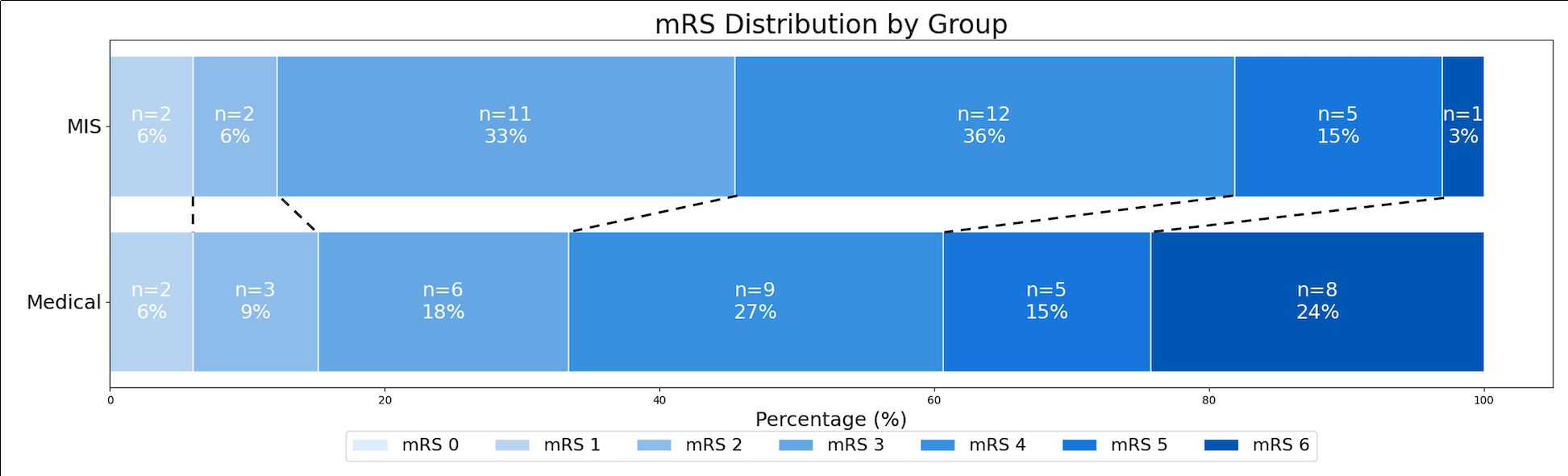
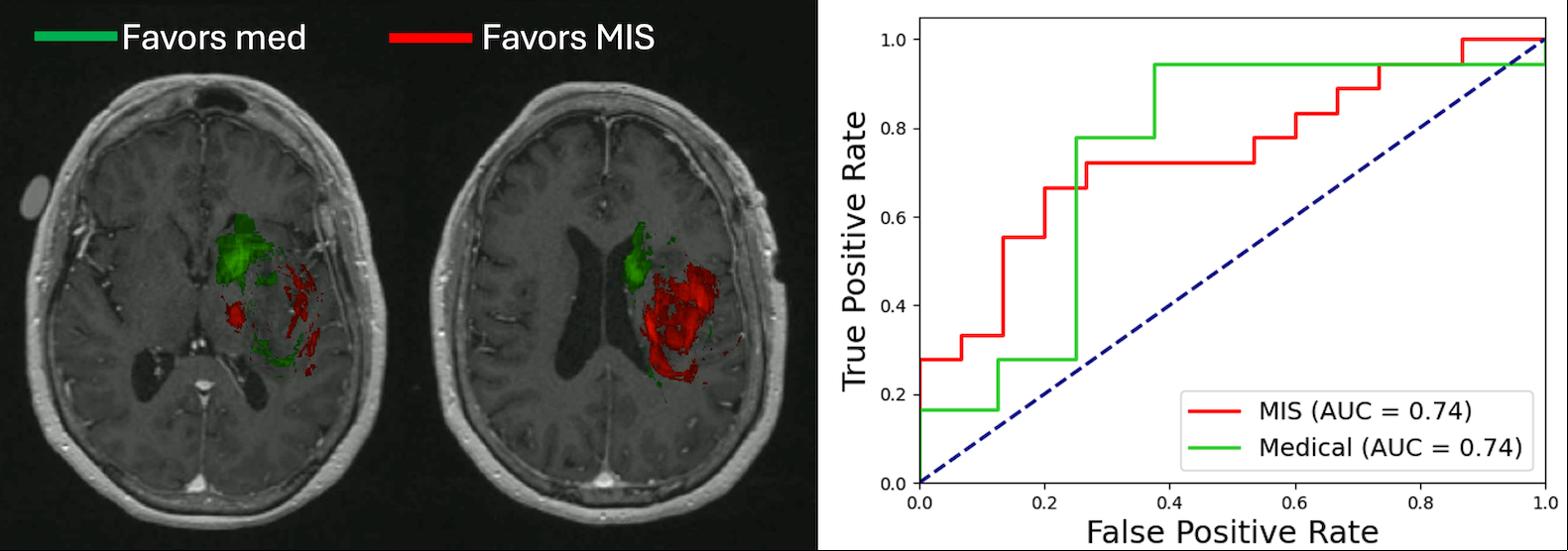
Results: Sixty-six patients (33 medical/33 surgical) were included (median age 54 years, 56% male). Groups (medical vs. surgical) were balanced according to ICH score (0-2: 91% vs. 85%, p=0.123), size (median 23 vs. 29-mL, p=0.125), Charlson Comorbidity Index (median 2 vs. 1, p=0.214), and follow-up duration (median 4.4 vs. 5.0 months, p=0.117). Rates of good functional outcome were similar between groups (42% vs. 55%, p=0.314), but mortality was higher in the medical group (24% vs. 3%, p =0.027) (Image 2). Anteromedial extension in the region of the anterior limb of the internal capsule and caudate uniquely predicted poor outcome in surgically managed patients (AUC 0.74, p=0.006), while posterior and superior extension in the region of the frontal lobe predicted poor outcome in medically managed patients (AUC 0.74, p=0.045) (Image 3).
Conclusions: MIS evacuation is associated with improved mortality rates in patients with moderate-sized pICH. Regional extension patterns can differentially predict functional outcome in medically and surgically managed patients.
Methods: We performed a single-center retrospective review of patients admitted with spontaneous, non-lesional pICH between 10-50 mL from 2013-2024. Exclusion criteria included poor surgical candidacy based on comorbidity burden and baseline modified Rankin Scale (mRS) 4-6. Patients who underwent MIS evacuation were 1:1 matched to medically managed patients based on size and ICH score. The main outcome was mRS obtained within one year of admission. Regional pICH extension patterns were evaluated by stereotactically localizing pICH volumes in an anatomic coordinate frame (Image 1). Heat maps were constructed to illustrate pICH locations that were differentially associated with good (mRS 0-3) and poor (mRS 4-6) outcomes in surgical and medical cohorts.
Results: Sixty-six patients (33 medical/33 surgical) were included (median age 54 years, 56% male). Groups (medical vs. surgical) were balanced according to ICH score (0-2: 91% vs. 85%, p=0.123), size (median 23 vs. 29-mL, p=0.125), Charlson Comorbidity Index (median 2 vs. 1, p=0.214), and follow-up duration (median 4.4 vs. 5.0 months, p=0.117). Rates of good functional outcome were similar between groups (42% vs. 55%, p=0.314), but mortality was higher in the medical group (24% vs. 3%, p =0.027) (Image 2). Anteromedial extension in the region of the anterior limb of the internal capsule and caudate uniquely predicted poor outcome in surgically managed patients (AUC 0.74, p=0.006), while posterior and superior extension in the region of the frontal lobe predicted poor outcome in medically managed patients (AUC 0.74, p=0.045) (Image 3).
Conclusions: MIS evacuation is associated with improved mortality rates in patients with moderate-sized pICH. Regional extension patterns can differentially predict functional outcome in medically and surgically managed patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel EMR-Based Algorithm with the Virtual Echocardiography Screening Tool (VEST) to Screen Patients for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Narowska Gabriela, Anand Suneesh, Gangireddy Chethan, Enevoldsen John, Keane Martin, Edmundowicz Daniel, Forfia Paul, Vaidya Anjali
AngioVac-Assisted Thrombectomy of Intracardiac Thrombi in a Patient with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease, Pulmonary Hypertension, and Intracranial HemorrhageRyad Robert, Hackney Noah, Succari Loutfi, Cohen Adam, Quimby Donald
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)