Final ID: TP210
Myelin in the Macrophage Response to Intracerebral Hemorrhage-Relevant Signals
Abstract Body: Introduction: Blood-derived macrophages become activated and contribute to a toxic environment in the brain after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). However, after three days, these macrophages become reparative and essential to tissue repair and recovery. The mechanisms by which this happens are poorly understood, but both myelin and cholesterol have been implicated in suppressing the macrophage response to different inflammatory signals. We have previously demonstrated through RNA sequencing that myelin suppresses responses to a broad range of diverse stimuli, while cholesterol only suppresses the response to lipopolysaccharides (LPS). The LXR agonist T091317 also suppressed responses, but not to the extent of myelin. We hypothesized that myelin would suppress cytokine production in the macrophage response to S100A9 and LPS.
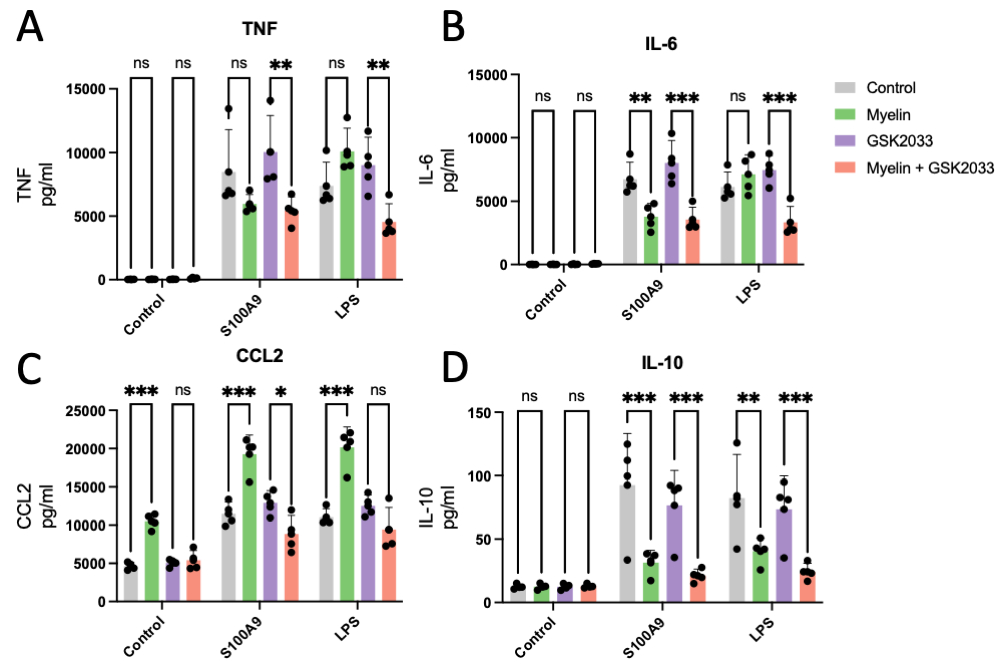
Methods and Results: Murine bone marrow-derived macrophages were pretreated with myelin for 18 hours before stimulation with S100A9 or LPS. Cytokine concentrations of TNF, IL-6, CCL2, and IL-10 were measured by cytometric bead array and analyzed by flow cytometry. Myelin seemed to have no significant effect on TNF production (Fig 1A). Myelin limited IL-6 production in response to S100A9 but not to LPS, but the LXR antagonist GSK2033 was unable to reverse this suppression (Fig 1B). Myelin increased CCL2 production in response to both stimulations in an LXR-dependent way (Fig 1C). IL-10 production was decreased in the myelin-treated conditions, and GSK2033 was unable to reverse this (Fig 1D).
Conclusions: The measurement of protein responses may be more informative than transcriptional responses and it can help validate the RNA seq. Myelin suppressed some cytokine production, but not to the extent of what was shown in the RNA seq. This suggests that myelin may play a role in the suppressive response of macrophages to ICH, but other components are involved as well.
Methods and Results: Murine bone marrow-derived macrophages were pretreated with myelin for 18 hours before stimulation with S100A9 or LPS. Cytokine concentrations of TNF, IL-6, CCL2, and IL-10 were measured by cytometric bead array and analyzed by flow cytometry. Myelin seemed to have no significant effect on TNF production (Fig 1A). Myelin limited IL-6 production in response to S100A9 but not to LPS, but the LXR antagonist GSK2033 was unable to reverse this suppression (Fig 1B). Myelin increased CCL2 production in response to both stimulations in an LXR-dependent way (Fig 1C). IL-10 production was decreased in the myelin-treated conditions, and GSK2033 was unable to reverse this (Fig 1D).
Conclusions: The measurement of protein responses may be more informative than transcriptional responses and it can help validate the RNA seq. Myelin suppressed some cytokine production, but not to the extent of what was shown in the RNA seq. This suggests that myelin may play a role in the suppressive response of macrophages to ICH, but other components are involved as well.
More abstracts on this topic:
Alzheimer’s Disease and Risk of Intracranial Hemorrhage
Zhang Cenai, Bruce Samuel, Navi Babak, Murthy Santosh, Kamel Hooman
CCL11 is a pivotal player in the brain-lung axis that mediates stroke outcomes in aged mice with intracerebral hemorrhage.Ozaki Dan, Kitamura Yuki, Bautista-garrido Jesus, Sun Guanghua, Kim Gab Seok, Aronowski Jaroslaw, Jung Joo Eun
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)