Final ID: TP329
Hospital encounters in the 7 days and 30 days before first-ever stroke: An observational study using data linkage
Up to 20% of people have a hospital encounter in the 30 days before a first ever stroke, suggesting opportunities for better primary prevention. The reasons for these healthcare encounters before stroke have been largely unexplored. We aimed to describe diagnoses in hospital encounters within 7 days and 30 days before a first-ever stroke.
Methods
We used a statewide (Tasmania, ~500,000 population) linked dataset comprising emergency department [ED] presentations, hospital admissions and deaths in Australia from 2007-2020. An 8-year look back period was used to identify first ever strokes. ICD 10-AM codes in the principal diagnosis field were used to determine diagnoses in hospital encounters before stroke. We describe the distribution of diagnosis groups for each hospital encounters, separately for ED presentations and hospital admissions, in the 7 days and 30 days before stroke.
Results
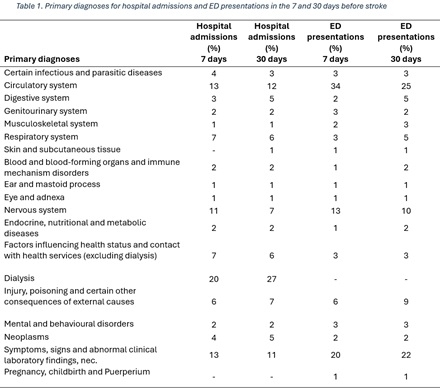
Out of 4907 first-ever stroke patients, 202 (4.12%) people had 234 hospital admissions within 7 days before stroke and 507 (10.33%) people had 724 hospital admissions within 30 days before stroke. Among 339 (7%) people, there were 351 ED presentations within the 7 days before stroke and among 676 (13.78%) people, there were 765 ED presentations in the 30 days before stroke. In event-level analyses, the most common diagnoses for hospital admissions were dialysis, diseases of circulatory system (e.g. carotid artery stenosis and unruptured cerebral aneurysm), abnormal symptoms or pathological findings (e.g. convulsions and headache), nervous system disorders (e.g. migraine) and respiratory diseases (Table 1). The most common diagnoses for ED presentations were circulatory system disorders, abnormal pathological findings and nervous system disorders in the 7 days and 30 days before stroke.
Conclusion
Hospital encounters in the period immediately before stroke are common and associated with a broad range of health conditions. These may represent potentially high-risk groups requiring more intensive primary stroke prevention interventions.
More abstracts on this topic:
Drenkova Kamelia, Lo Sicco Kristen, Berger Jeffrey, Garshick Michael, Kazatsker Filipp, Muller Matthew, Schlamp Florencia, Luttrell-williams Elliot, Liberow Sarah, Mcgirl Siobhan, Kennedy Lauren, Garelik Jessica
3-Minute Heart Health App: A Feasibility StudyAbdulkarim Iya, Metzger Joseph, Stovitz Steven, Van't Hof Jeremy
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.