Final ID: TMP95
Risk Factors, Stroke Characteristics and Outcomes in Children with Inpatient Versus Outpatient Strokes
Methods: The Stanford Pediatric Stroke Registry retrospectively and prospectively enrolled children with acute AIS who were admitted to our tertiary care pediatric hospital between 2007-2024. For this analysis we included patients who met the following criteria: 1) age 30 days-18 years old; 2) new diagnosis of AIS; 3) acute neuroimaging available for direct review. Inpatient strokes were defined as strokes that occurred while the child was hospitalized, either at our center or at an outside facility prior to transfer. Demographic, clinical and radiographic data were compared using chi-squared or Fishers Exact test for categorical variables and Mann-Whitney U test or t-test for continuous variables. Outcomes were reported using descriptive statistics due to the hypothesis-generating nature of the report.
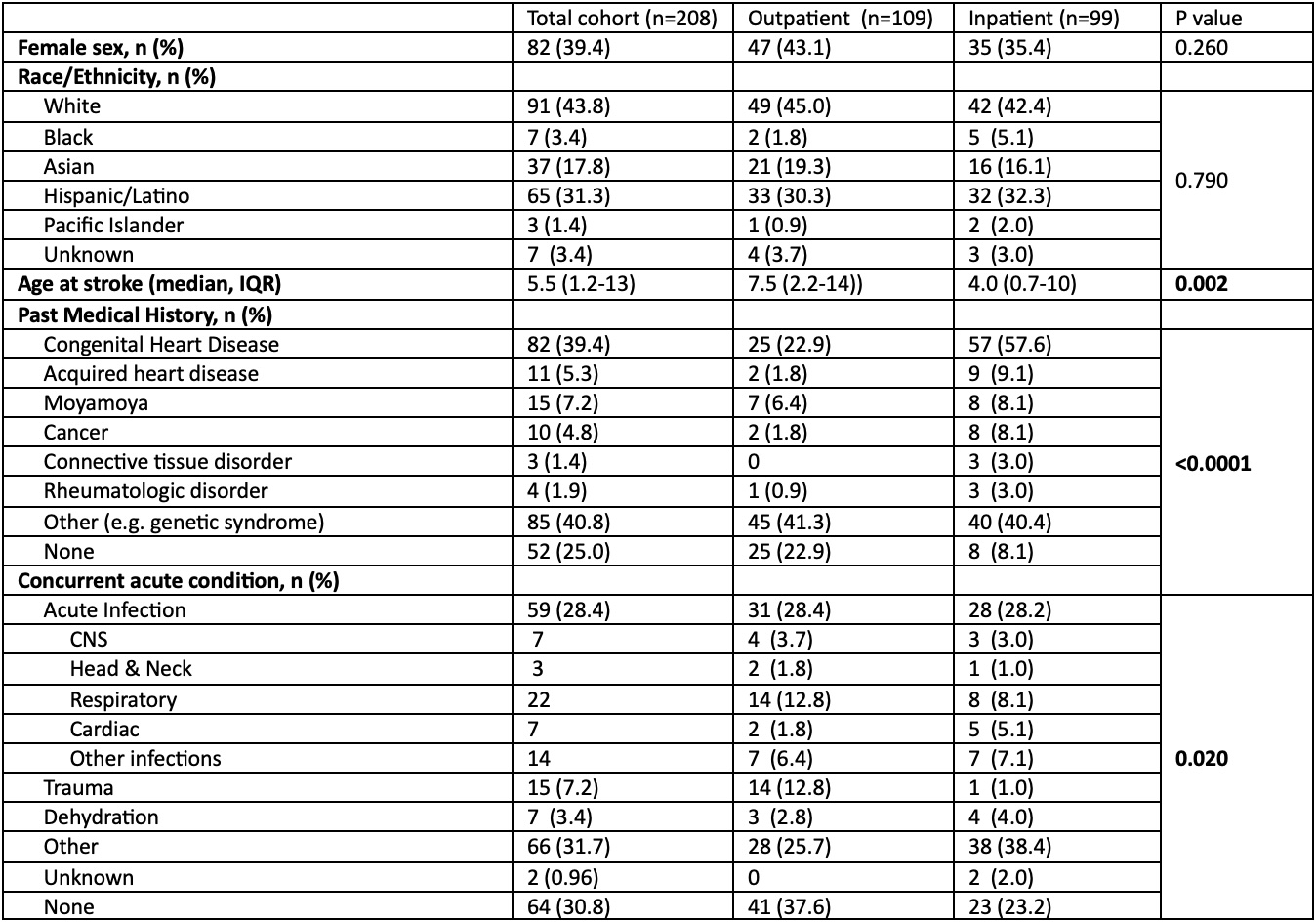
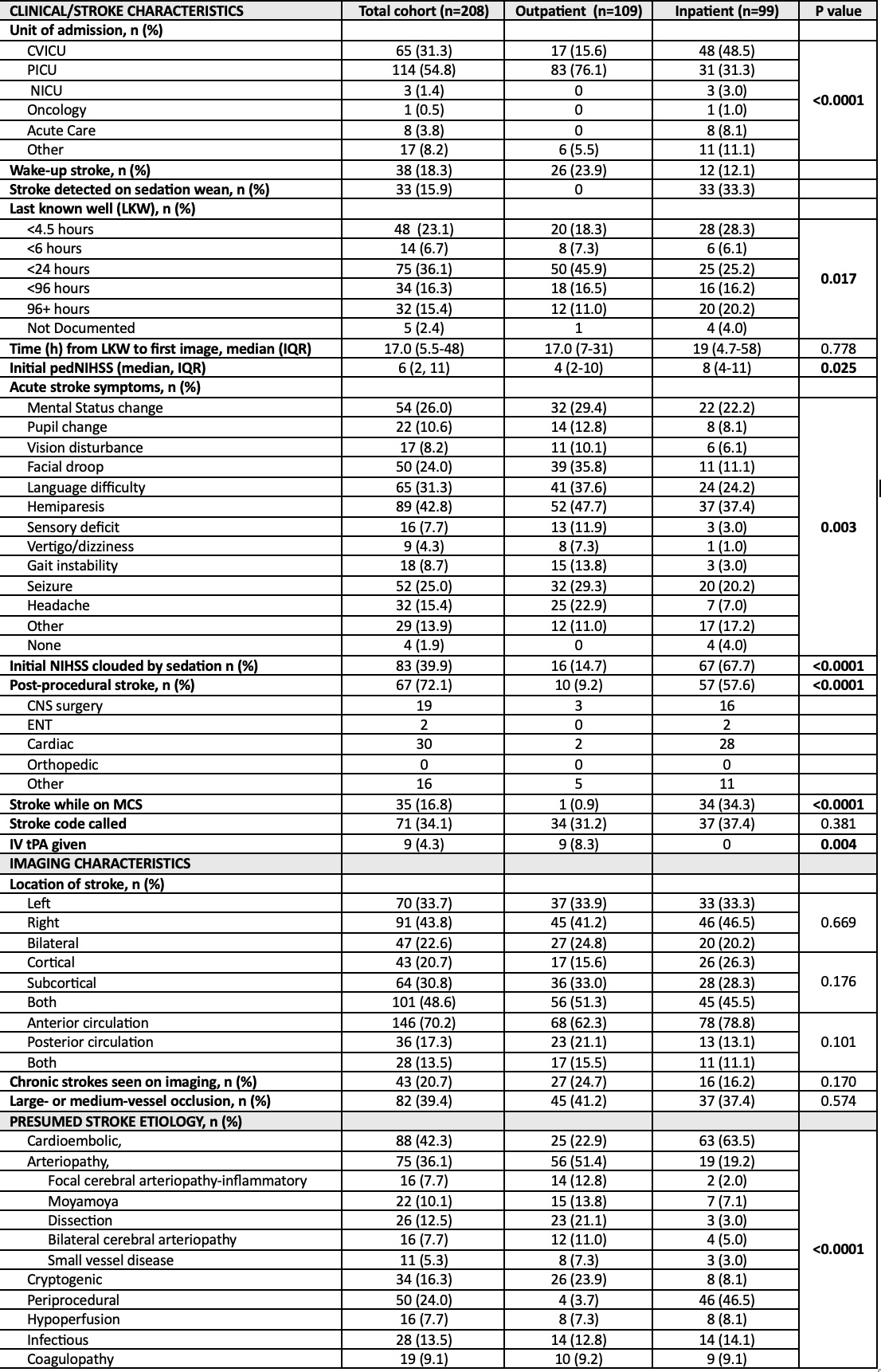
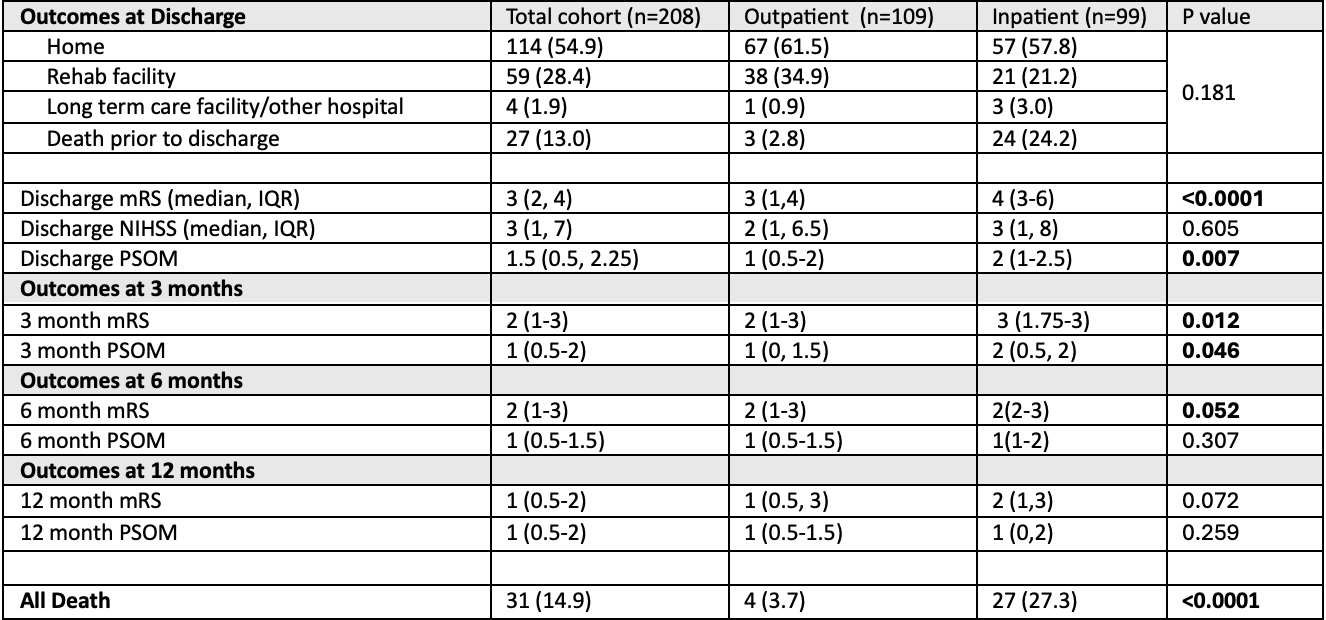
Results: A total of 208 children with acute AIS met inclusion criteria; 99 (47.6%) experienced a stroke while hospitalized. Inpatient stroke patients were overall younger and had higher rates of congenital heart diease and cancer than children with outpatient strokes, while trauma was more common in outpatient strokes (Table 1). There were no significant differences in imaging characteristics between groups. Cardioembolism and periprocedural strokes were more prevalent in inpatient strokes, whereas arteriopathy and cryptogenic stroke were the most common stroke etiologies in outpatients (Table 2). A significantly higher proportion of inpatient stroke patients died compared to outpatient strokes (27.3% vs 3.7%, p<0.0001); most patients died prior to discharge (Table 3).
Conclusions: In our pediatric AIS cohort, nearly half had a stroke while hospitalized. Our study suggests that stroke and risk factor profiles differ between inpatient and outpatient strokes in multiple domains, and that children with inpatient strokes have higher rates of death. Further prospective studies are needed to determine factors contributing to higher mortality in order to tailor appropriate prevention strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Xiong Li, Chen Xiangyan, Leung Howan, Zhu Lixia, Leung Thomas, Wong Lawrence
Mental Health Outcomes In Parents with Children with Pediatric Arterial Ischemic StrokeLehman Laura, Rafay Mubeen, Dowling Michael, Pergami Paola, Fox Christine, Beslow Lauren, Dlamini Nomazulu, Kirton Adam, Guilliams Kristin, Taylor John, Fain Daniel, Glass Hannah, Peglar Lindsay
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.