Final ID: WMP105
Multimodal Deep Learning for Ischemic Stroke Prediction by Integrating Demographic, Clinical, and Atrial Phenotypic and Genotypic Data
Abstract Body: Introduction: Accurate prediction of the risk of ischemic stroke (IS) is vital for prevention and would be aided by multimodal biomarkers integrating genetic, clinical, and functional data. The role of imaging and EKG based atrial measurements, other than atrial fibrillation (AF), in IS prediction is uncertain and many strokes remain cryptogenic despite extensive work-up. As an exploratory step to improve stroke evaluation by including atrial traits, we developed a novel multimodal deep learning model integrating demographic and clinical variables with atrial phenotypic and genotypic data.
Methods: We collected individuals from UK Biobank (UKBB) and defined ischemic stroke (IS) by the UKBB Algorithmically Defined Outcome (ADO). We developed a multimodal multi-layer perceptron with late fusion (MMLP-LF) model to predict whether a subject has IS by integrating five data modalities from UKBB: 1) MRI and EKG derived atrial traits, 2) lead genetic variants (P<5e-8) from GWAS of atrial traits, 3) patient demographics, 4) ICD codes including AF but excluding IS codes and 5) procedure codes related to cardiac valve surgery. We split the samples into 64%-16%-20% train-validation-test sets via stratified random sampling. Models were trained on the training set with 20 rounds of random initialization. The validation set was used for model selection. We used Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUROC) for performance evaluation. Shapley additive explanation (SHAP) analysis was conducted for feature importance attribution.
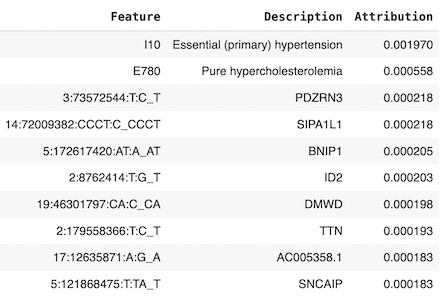
Results: Our dataset included 24,582 individuals from the UKBB, among which 100 (0.41 %) had IS. Our full MMLP-LF model including 5 modalities achieved the highest AUROC of 0.85 for predicting IS on the hold-out test set, substantially outperforming the best unimodal branch (AUROC 0.79 with ICD codes, 0.71 with demographic variables). If we excluded atrial phenotypes, the AUROC was still 0.85. If genetic traits were also removed, the AUROC declined to 0.82. SHAP analysis revealed that ICD codes for hypertension and hyperlipidemia are the most influential contributors to the full model followed by GWAS-identified lead genetic variants associated with atrial traits (Figure).
Conclusion: Our MMLP-LF model improved IS prediction over unimodal models by integrating multimodal data and identified genetic and clinical drivers predicting IS. This model establishes a new paradigm for integrating multiple modalities to predict IS outcomes.
Methods: We collected individuals from UK Biobank (UKBB) and defined ischemic stroke (IS) by the UKBB Algorithmically Defined Outcome (ADO). We developed a multimodal multi-layer perceptron with late fusion (MMLP-LF) model to predict whether a subject has IS by integrating five data modalities from UKBB: 1) MRI and EKG derived atrial traits, 2) lead genetic variants (P<5e-8) from GWAS of atrial traits, 3) patient demographics, 4) ICD codes including AF but excluding IS codes and 5) procedure codes related to cardiac valve surgery. We split the samples into 64%-16%-20% train-validation-test sets via stratified random sampling. Models were trained on the training set with 20 rounds of random initialization. The validation set was used for model selection. We used Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUROC) for performance evaluation. Shapley additive explanation (SHAP) analysis was conducted for feature importance attribution.
Results: Our dataset included 24,582 individuals from the UKBB, among which 100 (0.41 %) had IS. Our full MMLP-LF model including 5 modalities achieved the highest AUROC of 0.85 for predicting IS on the hold-out test set, substantially outperforming the best unimodal branch (AUROC 0.79 with ICD codes, 0.71 with demographic variables). If we excluded atrial phenotypes, the AUROC was still 0.85. If genetic traits were also removed, the AUROC declined to 0.82. SHAP analysis revealed that ICD codes for hypertension and hyperlipidemia are the most influential contributors to the full model followed by GWAS-identified lead genetic variants associated with atrial traits (Figure).
Conclusion: Our MMLP-LF model improved IS prediction over unimodal models by integrating multimodal data and identified genetic and clinical drivers predicting IS. This model establishes a new paradigm for integrating multiple modalities to predict IS outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Causal Association of Left Atrial Emptying Fraction With Ischemic Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis
Nguyen Kevin, Cole John, Perry James, Gaynor Brady, Bai Zilong, Wang Fei, Xu Huichun, Leifer Dana
Causal Association of Left Atrial Emptying Fraction With Ischemic Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization AnalysisNguyen Kevin, Cole John, Perry James, Gaynor Brady, Bai Zilong, Wang Fei, Xu Huichun, Leifer Dana
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)