Final ID: 35
Impact of Artificial Intelligence Imaging Decision Support Software on Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke in England
Abstract Body: Introduction
AI imaging decision support software is recommended by UK and USA stroke guidelines to facilitate identification and transfer of stroke patients eligible for endovascular therapy (EVT) but the impact on thrombectomy delivery is unclear. This prospective observational study evaluated the impact of Brainomix 360 Stroke software in four stroke networks (28 hospitals) in England’s National Health Service (NHS). The primary outcome was percentage of acute stroke patients receiving EVT (the EVT rate); door-in door-out (DIDO) times were assessed as a secondary outcome.
Methods
Data were collected prospectively from the Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme. The impact of Brainomix 360 Stroke software was assessed in two ways: comparison of EVT rates at the 28 evaluation sites and non-evaluation NHS sites before and after implementation (pre-implementation: Jan 2019-Feb 2020; post- : Jan 2022-Feb 2023); comparison of EVT rates and DIDO times at evaluation sites after implementation in patients for whom AI software was used and in those it was not. Multivariate regressions were used to evaluate whether AI use was a predictor of EVT or DIDO time, accounting for other clinical variables (e.g., age, NIHSS, day of week, time of day, time since onset).
Results
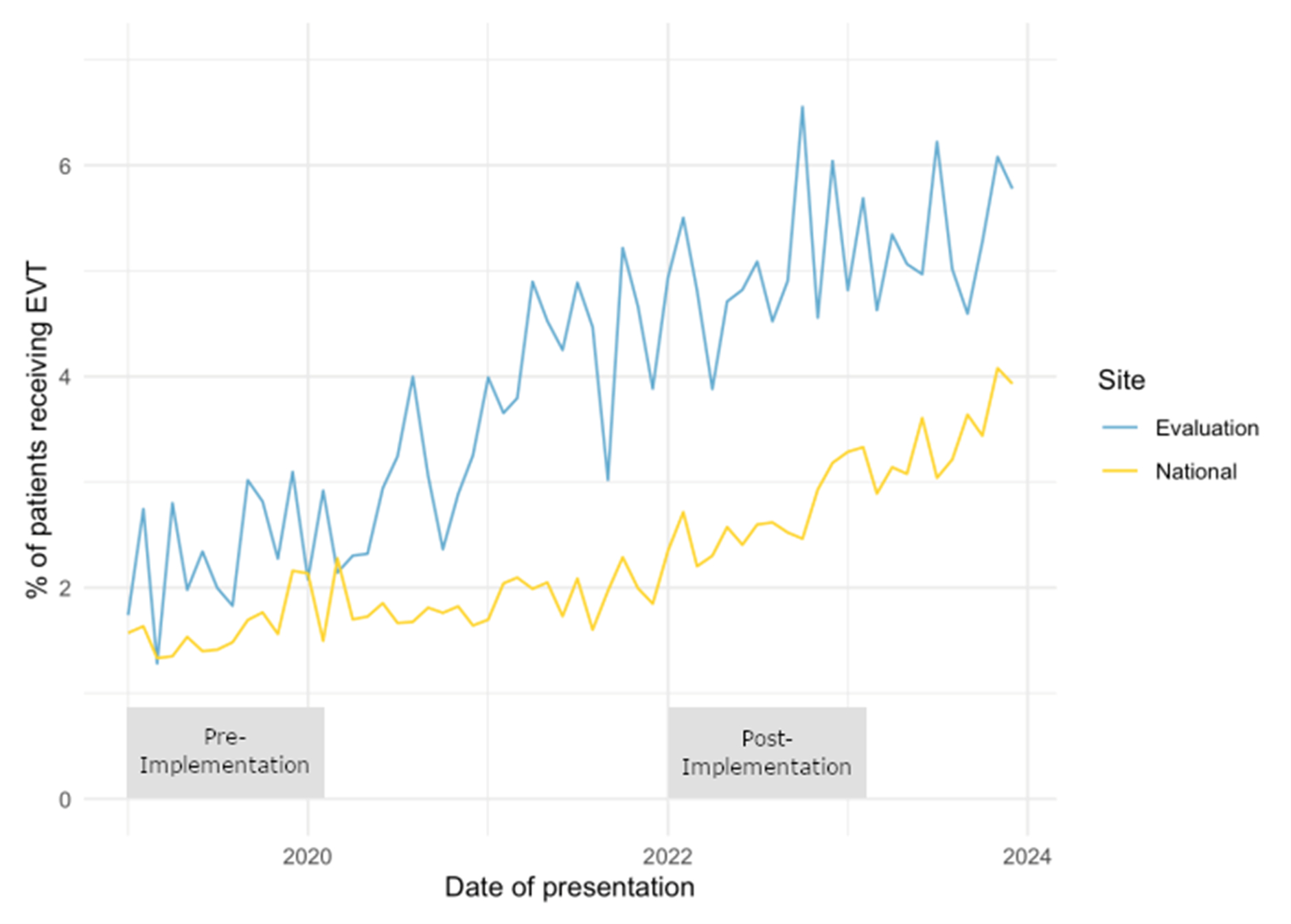
The dataset included 71,327 patients from 28 evaluation hospitals. Figure 1 shows the change in EVT rates over time in evaluation (blue) and non-evaluation sites (yellow). EVT rate at evaluation sites increased from 2.3% pre-implementation to 4.6% post-implementation (p<.0001). By contrast, EVT rate at non-evaluation sites changed from 1.6% to 2.6% (p<.0001).
After implementation, cases that were reviewed with AI software support were more likely to receive EVT (5.9% vs 3.6%; OR=1.6 [95% CI:1.3-1.9, p<.0001). When limiting the analysis to cases admitted to primary stroke centres, the EVT rate was twice as high in cases reviewed with AI software (4.7% vs 2.2%; OR=2.3 [1.8-3.1], p<.0001). DIDO times were shorter for cases reviewed with AI software (median 127 vs. 192 minutes; p<.0001).
Conclusions
This prospective study showed that use of AI imaging software was associated with a higher rate of EVT, both by comparing pre- vs. post-implementation data, as well as by comparing cases for whom AI software was versus was not used. Use of AI software was also associated with faster time to transfer. The results support guideline recommendations for AI software to be used in clinical practice.
AI imaging decision support software is recommended by UK and USA stroke guidelines to facilitate identification and transfer of stroke patients eligible for endovascular therapy (EVT) but the impact on thrombectomy delivery is unclear. This prospective observational study evaluated the impact of Brainomix 360 Stroke software in four stroke networks (28 hospitals) in England’s National Health Service (NHS). The primary outcome was percentage of acute stroke patients receiving EVT (the EVT rate); door-in door-out (DIDO) times were assessed as a secondary outcome.
Methods
Data were collected prospectively from the Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme. The impact of Brainomix 360 Stroke software was assessed in two ways: comparison of EVT rates at the 28 evaluation sites and non-evaluation NHS sites before and after implementation (pre-implementation: Jan 2019-Feb 2020; post- : Jan 2022-Feb 2023); comparison of EVT rates and DIDO times at evaluation sites after implementation in patients for whom AI software was used and in those it was not. Multivariate regressions were used to evaluate whether AI use was a predictor of EVT or DIDO time, accounting for other clinical variables (e.g., age, NIHSS, day of week, time of day, time since onset).
Results
The dataset included 71,327 patients from 28 evaluation hospitals. Figure 1 shows the change in EVT rates over time in evaluation (blue) and non-evaluation sites (yellow). EVT rate at evaluation sites increased from 2.3% pre-implementation to 4.6% post-implementation (p<.0001). By contrast, EVT rate at non-evaluation sites changed from 1.6% to 2.6% (p<.0001).
After implementation, cases that were reviewed with AI software support were more likely to receive EVT (5.9% vs 3.6%; OR=1.6 [95% CI:1.3-1.9, p<.0001). When limiting the analysis to cases admitted to primary stroke centres, the EVT rate was twice as high in cases reviewed with AI software (4.7% vs 2.2%; OR=2.3 [1.8-3.1], p<.0001). DIDO times were shorter for cases reviewed with AI software (median 127 vs. 192 minutes; p<.0001).
Conclusions
This prospective study showed that use of AI imaging software was associated with a higher rate of EVT, both by comparing pre- vs. post-implementation data, as well as by comparing cases for whom AI software was versus was not used. Use of AI software was also associated with faster time to transfer. The results support guideline recommendations for AI software to be used in clinical practice.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Hypoperfusion Intensity Ratio, Cerebral Blood Volume Index, and the CRISP2 Collateral Score with Good Outcome for Patients Transferred for Thrombectomy
Asimos Andrew, Hines Andrew, Rhoten Jeremy, Karamchandani Rahul, Yang Hongmei, Strong Dale, Teli Katelynn, Clemente Jonathan, Defilipp Gary, Bernard Joe, Stetler William, Parish Jonathan
A Retrospective Study to Determine Opportunities to Improve Earlier EMS Activation for Transport of Patients with Large Vessel Occlusion to Thrombectomy CentersMaria Shannon, Mojares Joseph, Zrelak Patricia
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)