Final ID: TP110
Impact of High-Intensity Training on Cardiopulmonary and Lipid Profiles in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Introduction: Cardiovascular comorbidities are highly prevalent in patients who suffer from cerebrovascular disease. Peak oxygen uptake (VO2 peak) is a well-established, independent predictor of cardiovascular health and premature mortality. Dyslipidemia also contributes significantly to cardiovascular disease risk. Although previous studies have demonstrated improvements in these parameters with any exercise, the evidence remains inconclusive regarding which exercise intensity offers the greatest benefit. This systematic review and meta-analysis aims to compare the effects of high-intensity training (HIT) with other exercise intensities, including moderate intensity (MIT) and usual activity (UA).
Methods: We systematically searched the PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and Scopus databases for studies comparing HIT with MIT or UA in stroke patients. We evaluated changes from baseline in VO2 peak, serum LDL, and HDL levels. Additionally, a separate analysis comparing HIT with MIT and UA was conducted for VO2 peak.
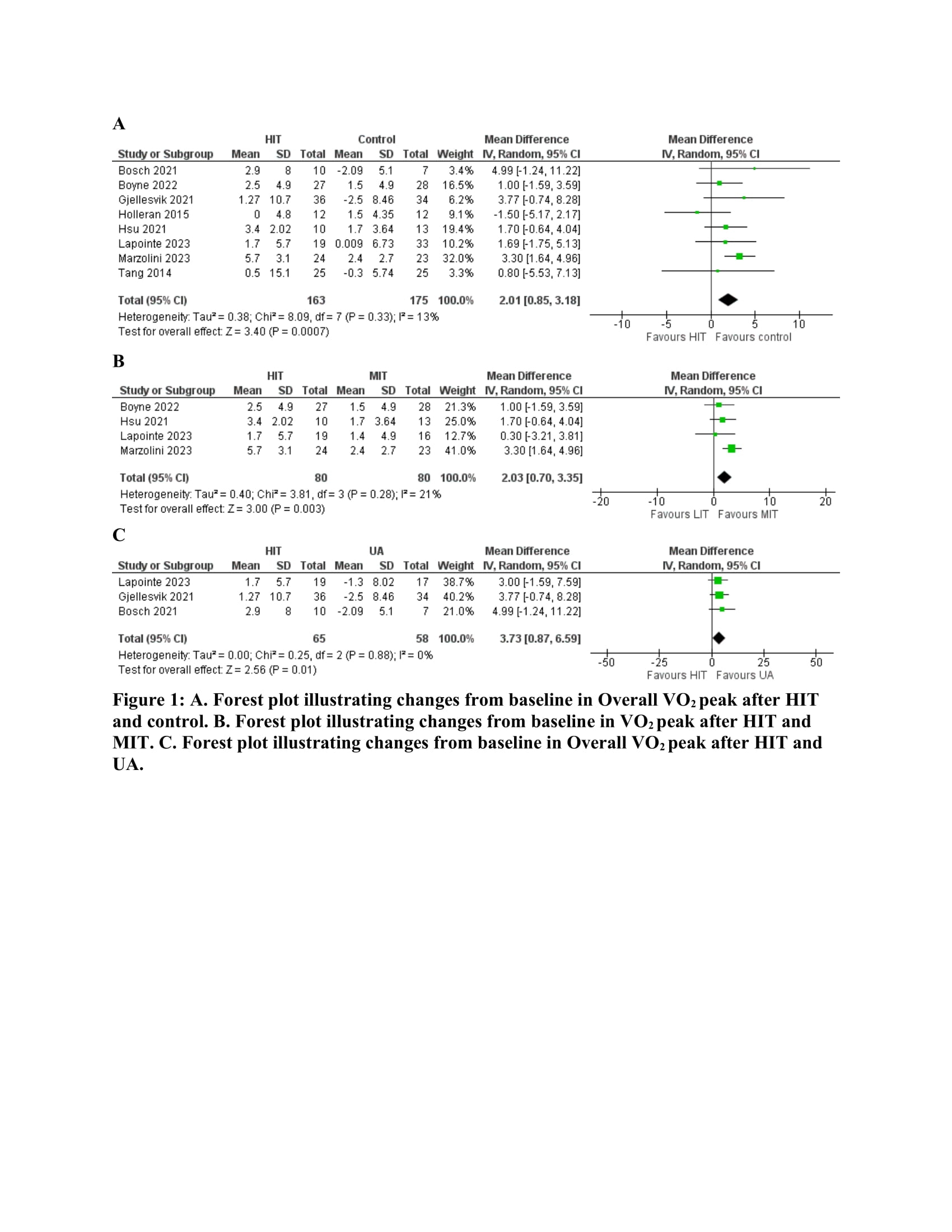
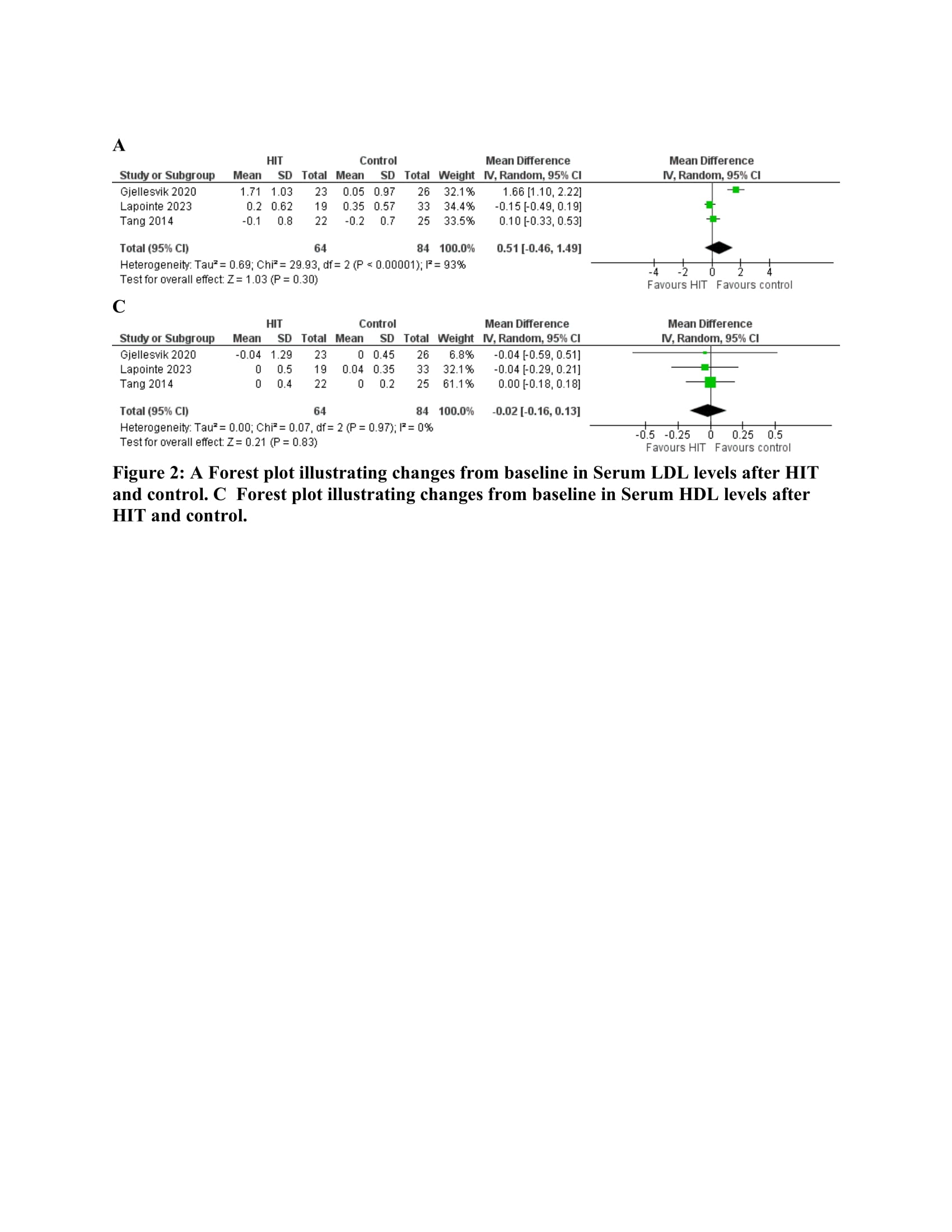
Results: A total of eight studies, involving 338 patients, were included in our analysis, with 163 (48%) of these patients undergoing HIT. The pooled analysis revealed that VO2 peak was significantly higher in the control group compared to the HIT group, with a mean difference (MD) of 2.01 ml/kg/min (95% CI: 0.85-3.18, p < 0.01). Further analysis of four studies comparing HIT with MIT and three studies comparing HIT with UA showed that VO2 peak was significantly higher following MIT (MD 2.03; 95% CI: 0.70-3.35; p < 0.01) and UA (MD 3.73; 95% CI: 0.87-6.59; p = 0.01). A separate analysis of three studies involving 148 patients showed no significant difference in serum LDL levels (MD 0.51; 95% CI: -0.46-1.49; p = 0.30) or serum HDL levels (MD -0.02; 95% CI: -0.16-0.13; p = 0.83).
Conclusion: High-intensity training, based on a moderate sized pooled sample, does not offer superior advantages in changes from baseline in cardiopulmonary parameters compared to different exercise intensities. Future well-structured randomized controlled trials are needed to evaluate different exercise intensities and durations for more definitive conclusions. Nevertheless, the early data seems to indicate that there are no differences between exercise modalities.
More abstracts on this topic:
Lytsen Rikke Mohr, Nielsen Sofie, Sillesen Anne-sophie, Axelsson Anna, Voegg Ruth Ottilia Birgitta, Kamstrup Pia, Iversen Kasper, Bundgaard Henning, Frikke-schmidt Ruth
Apolipoprotein A-I Proteoforms in Large HDL are Associated with Incident Myocardial Infarction: Observations from Dallas Heart StudyGangwar Anamika, Des Soye Benjamin, Saldanha Suzanne, Jaiswal Shailesh, Melchior John, Mcdermott Jason, Wilkins John, Rohatgi Anand
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.