Final ID: WMP17
The Role of Intracranial Arterial Calcifications in Neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology
Intracranial arterial calcifications (IAC) are considered a surrogate for intracranial large artery atherosclerosis but IAC can also represent non-atherosclerotic arterial aging. People with IAC have an increased risk of dementia. Nonetheless, the interplay between IAC, atherosclerosis, luminal stenosis and arterial stiffness as determinants of neurodegeneration remains unclear.
Methods:
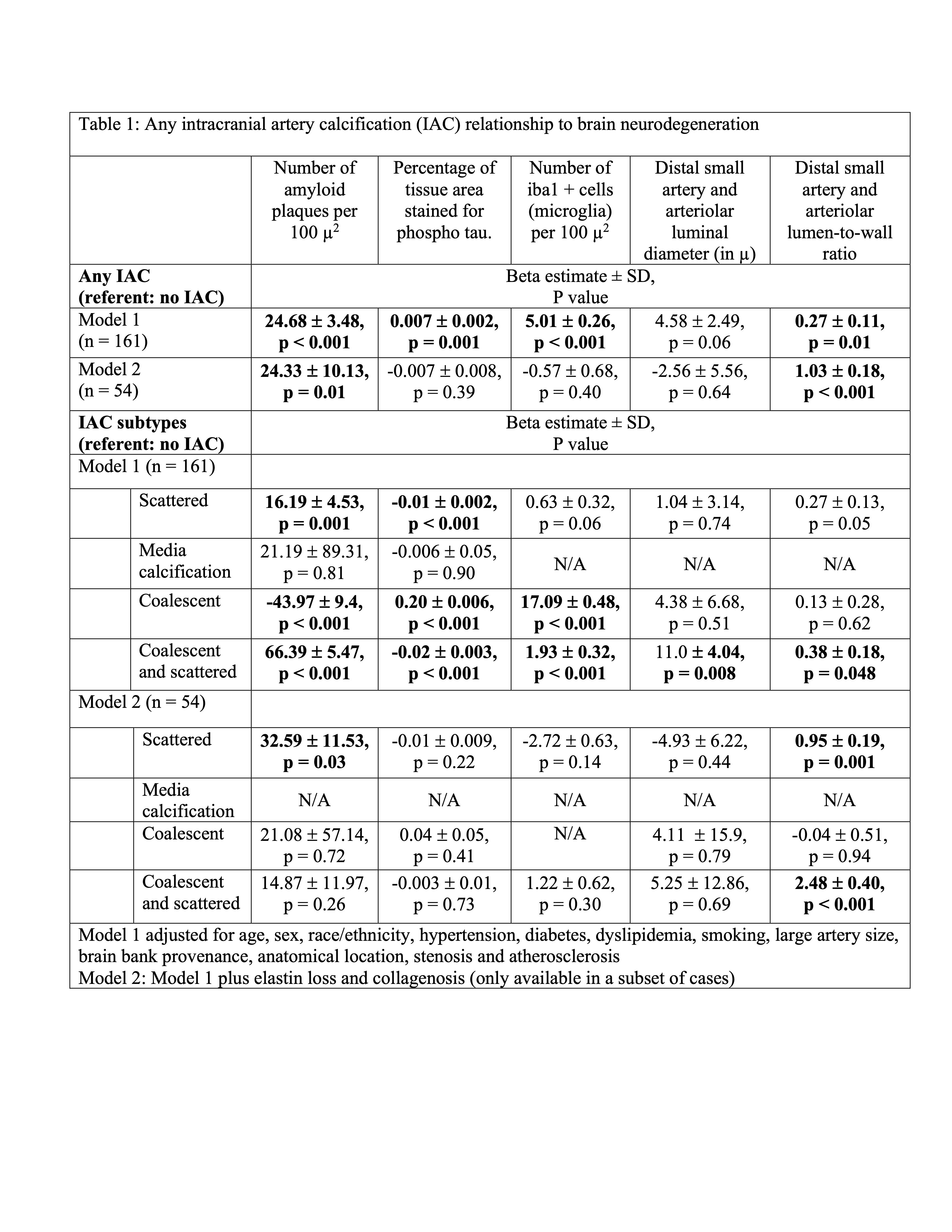
We analyzed 161 brain autopsy cases from the Brain Arterial Remodeling Study. We dissected each of the components of the circle of Willis and stained all arterial segments with H&E, elastic van-Gieson (to semi-quantify elastin content) and trichrome (to semi-quantify collagen content) stains. We rated calcification using H&E as present or absent and classified calcifications as scattered, media calcifications, coalescent or a combination of the above. We obtained ipsilateral brain cuts and stained with H&E to measure the arteriolar wall thickness and lumen. We used immunohistochemistry to stain for beta amyloid, phospho-tau and Iba1, a measure of activated microglia. Each stained slide was processed automatically to quantify the number of amyloid plaques and microglial (Iba1+) cells per 100u2 and percentage of tissue area stained positive by phospho-tau. We related calcification in the circle of Willis to parenchymal measure of neurodegeneration using mixed hierarchical models, adjusting for age, demographics and vascular risks.
Results:
Among 161 cases (mean age 81±16 years), 52% were female, 78% non-Hispanic white, 52% had hypertension, 11% diabetes, and 54% died with diagnosed dementia. Presence of any calcification was associated with increased number of Aβ plaques per 100 µ2, greater percentage of tissue area stained by phospho-tau, higher number of microglial cells and higher lumen to wall ratio (Table 1). The results were most consistent for IAC that had combined scattered and coalescent calcifications. The association between IAC and neurodegeneration markers attenuated after adjusting for elastin loss and collagenosis, both markers of arterial stiffness, but not after adjusting for atherosclerosis or luminal stenosis.
Conclusion:
IAC are associated with pathology markers of neurodegeneration, specifically Alzheimer’s disease. The association was independent of atherosclerosis and luminal stenosis, but attenuated partially after adjusting for markers of arterial stiffness. Hemodynamic studies in living persons are needed to replicate these associations.
More abstracts on this topic:
Ishikawa Hirotoshi, Kasayuki Noriaki, Fukuda Daiju, Otsuka Kenichiro, Sugiyama Takatoshi, Yamaura Hiroki, Hojo Kana, Kawa Yoshinori, Shintani Ako, Ito Asahiro, Yamazaki Takanori
Advanced Diffusion and Functional MRI Measures Are Associated with Microstructural Morphology and Cognitive Function in Subacute Ischemic Cerebellar StrokeUrday Sebastian, Clements Rebecca, Kurani Ajay, Montero Miguel, Grafman Jordan H., Harvey Richard, Ingo Carson
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.