Final ID: WP197
Detection and segmentation of hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign on non-contrast CT using artificial intelligence
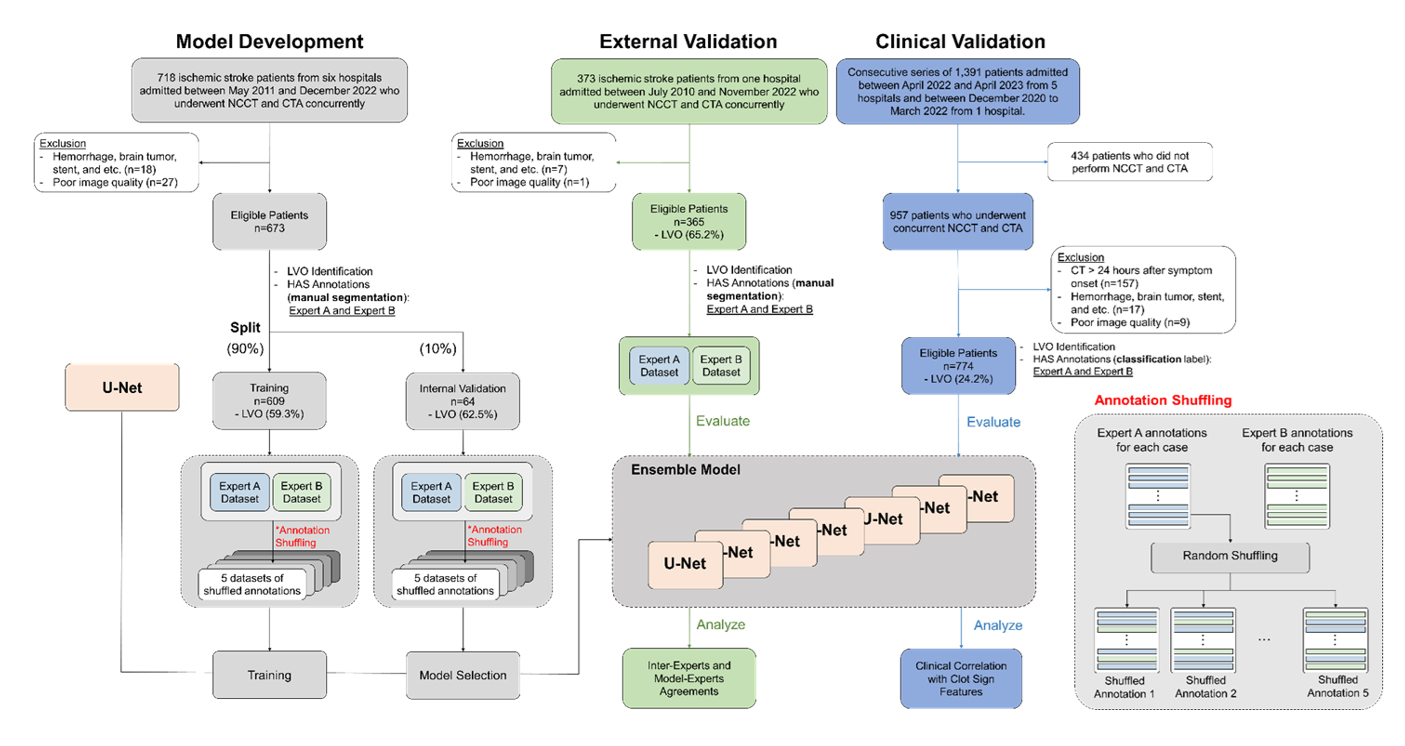
Methods: For the training dataset, we included patients with ischemic stroke undergoing concurrent NCCT and CT angiography between May 2011 and December 2022 from six stroke centers. The model was externally validated using a dataset from one stroke center. For the clinical validation dataset, a consecutive series of patients admitted within 24 hours of symptom onset were included between December 2020 and April 2023 from six stroke centers. The model was trained using a 2D U-Net algorithm with manual segmentation by two experts. We constructed models trained on datasets annotated individually by each expert, and an ensemble model using shuffled annotations from both experts. The performance of the models was compared using area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUROC), sensitivity, and specificity.
Results: A total of 673, 365, and 774 patients were included in the training, external validation, and clinical validation datasets, respectively, with mean (SD) ages of 68.8 (13.2), 67.6 (13.4), and 68.8 (13.6) years and male frequencies of 55.0%, 59.5%, and 57.6%. The ensemble model achieved higher AUROC and sensitivity compared to the models trained on annotations from a single expert in the external validation dataset. In the clinical validation dataset, the ensemble model exhibited an AUROC of 0.846 (95% CI, 0.819–0.871), sensitivity of 76.8% (65.1–86.1%), and specificity of 88.5% (85.9–90.8%). The predicted volume of the clot was significantly correlated with infarct volume on follow-up diffusion-weighted imaging (r=0.42; p<0.001).
Conclusion: Our algorithm promptly and accurately identifies HAS, facilitating the screening of potential patients who may require intervention.
More abstracts on this topic:
Al-alusi Mostafa, Khurshid Shaan, Sanborn Danita, Picard Michael, Ho Jennifer, Maddah Mahnaz, Ellinor Patrick, Lau Emily, Small Aeron, Reeder Christopher, Shnitzer Dery Tal, Andrews Carl, Kany Shinwan, Ramo Joel, Haimovich Julian
A large-scale multi-view deep learning-based assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction in echocardiographyJing Linyuan, Metser Gil, Mawson Thomas, Tat Emily, Jiang Nona, Duffy Eamon, Hahn Rebecca, Homma Shunichi, Haggerty Christopher, Poterucha Timothy, Elias Pierre, Long Aaron, Vanmaanen David, Rocha Daniel, Hartzel Dustin, Kelsey Christopher, Ruhl Jeffrey, Beecy Ashley, Elnabawi Youssef
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.