Final ID: WMP84
The impact of large language models on stroke management: A literature review and proposing a practical model for the future stroke care
Abstract Body: Introduction: Despite notable advancements in diagnostic tools and treatment strategies in stroke care, finding an optimal management approach that delivers the best outcomes remains elusive.The introduction of artificial intelligence(AI),particularly Large Language Models(LLMs),has brought new perspectives to stroke management.Here,we explore the potential applications of LLMs in stroke care and propose a practical model for their future integration into stroke management.
Method: We conducted a comprehensive literature review on PubMed,Scopus and web of science databases up to May 2024 to identify existing applications of LLMs in healthcare,specifically stroke management.
Results: Our results revealed several applications of LLMs in healthcare,including personalized rehabilitation programs,mental health support,and enhanced physician-patient interactions,which could be effectively integrated into stroke care.Based on these findings, we proposed a framework that incorporates Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning techniques,rasoning frameworks,and ensemble methods to address common limitations of LLMs identified in the literature.
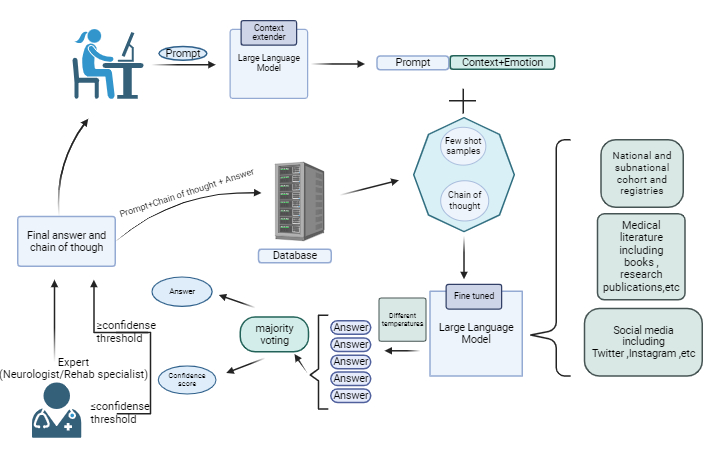
In the proposed framework (Figure1),the process begins with the patient or their caretaker inputting data or questions into the“context extractor” LLM .
The context extractor analyzes the input for key points and assesses the emotional state of the patient or caretaker.The System will then search for relevant examples and reasoning’s stored in a pre-existing database,integrating this information into the decision-making process to provide a more personalized and contextually appropriate response.
In the next step a fine-tuned language model, trained on various stroke-related data sources will process the data. The model's settings are adjusted using strategies such as varying the temperature of responses to ensure data validity and minimize errors .The outputs are then evaluated through a majority voting system.If the output scores above a predetermined threshold, it is accepted as the final outcome;If it falls below the threshold,specialist opinions are sought to verify accuracy.Once validated,the final results are presented to the patient and caregiver and stored in the database for future reference.
Conclusion: Our framework demonstrates how integrating LLMs with expert validation can enhance stroke care by providing accurate, personalized support.With further development,this approach could revolutionize AI-driven stroke management.
Method: We conducted a comprehensive literature review on PubMed,Scopus and web of science databases up to May 2024 to identify existing applications of LLMs in healthcare,specifically stroke management.
Results: Our results revealed several applications of LLMs in healthcare,including personalized rehabilitation programs,mental health support,and enhanced physician-patient interactions,which could be effectively integrated into stroke care.Based on these findings, we proposed a framework that incorporates Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning techniques,rasoning frameworks,and ensemble methods to address common limitations of LLMs identified in the literature.
In the proposed framework (Figure1),the process begins with the patient or their caretaker inputting data or questions into the“context extractor” LLM .
The context extractor analyzes the input for key points and assesses the emotional state of the patient or caretaker.The System will then search for relevant examples and reasoning’s stored in a pre-existing database,integrating this information into the decision-making process to provide a more personalized and contextually appropriate response.
In the next step a fine-tuned language model, trained on various stroke-related data sources will process the data. The model's settings are adjusted using strategies such as varying the temperature of responses to ensure data validity and minimize errors .The outputs are then evaluated through a majority voting system.If the output scores above a predetermined threshold, it is accepted as the final outcome;If it falls below the threshold,specialist opinions are sought to verify accuracy.Once validated,the final results are presented to the patient and caregiver and stored in the database for future reference.
Conclusion: Our framework demonstrates how integrating LLMs with expert validation can enhance stroke care by providing accurate, personalized support.With further development,this approach could revolutionize AI-driven stroke management.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Cross-scale Causal Machine Learning Framework Pinpoints Mgl2+ Macrophage Orchestrators of Balanced Arterial Growth
Han Jonghyeuk, Kong Dasom, Schwarz Erica, Takaesu Felipe, Humphrey Jay, Park Hyun-ji, Davis Michael E
A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Critical Illness and Signs of Myocardial InjuryMueller Joshua, Stepanova Daria, Chidambaram Vignesh, Nakarmi Ukash, Al'aref Subhi
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)