Final ID: TP173
Automated Vessel Landmark Detection and AIF/VOF Validation for Enhanced CTP Analysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke
Methods: We used a dataset of 499 stroke patient CT cases from 2021 to 2023, with vessel landmarks manually annotated by radiologists. Of these, 50 cases were for testing, and 449 were used for training. Our system includes two components: (1) an AI model for ROIs detection and (2) an ML model for ROIs intensity validation. The AI model, based on a Unet with ResNet as the encoder, detects eight ROIs from 4D CTP images. It is optimized using mean squared error (MSE) loss to reduce the difference between predicted and ground truth (GT) landmarks. The second component, an ML model, differentiates AIF from VOF landmarks and checks intensity normality. We used XGBoost to evaluate intensity validity and a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) to verify consistency with predicted landmarks. Both models were trained using radiologist-verified data, and data augmentation was applied to improve robustness.
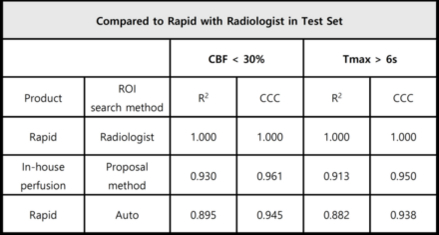
Results: The AI model showed an average Euclidean distance error of 4.37 mm on the test set, indicating accurate vessel localization. The ML model achieved 0.815 accuracy, 0.92 sensitivity, and 0.725 specificity in distinguishing AIF from VOF. Our method also correlated strongly with manual radiologist segmentation, with Pearson R2 scores of 0.93 for CBF < 30% and 0.913 for Tmax > 6 seconds.
Conclusion: In this study, we propose a novel AI and ML-based framework for optimizing ROI selection for AIF/VOF in CTP analysis. Our approach improves vessel localization and intensity validation while producing CTP maps closely aligned with manual expert review. This method offers a promising alternative to conventional techniques, enhancing perfusion analysis precision and supporting better clinical decision-making in acute ischemic stroke management.
More abstracts on this topic:
Kesten Jamie, Mlynash Michael, Yuen Nicole, Seners Pierre, Wouters Anke, Schwartz Maya, Lansberg Maarten, Albers Gregory, Heit Jeremy
A First-in-Class Humanized Antibody Fragment Targeting Platelet Glycoprotein Ibα: A Comprehensive Preclinical Study of CA1001 for the Treatment of Acute Ischemic StrokeXu Xiaohong, Preeti Preeti, Yu Ruoying, Shaykhalishahi Hamed, Zhang Cheng, Shen Chuanbin, Li Bei, Tang Naping, Chang Yan, Xiang Qian, Cui Yimin, Lei Xi, Ni Heyu, Zhu Guangheng, Liu Zhenze, Hu Xudong, Slavkovic Sladjana, Neves Miguel, Ma Wenjing, Xie Huifang
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.