Final ID: TP177
Characterization of Clot Composition with Radiomics
Approximately 30% of strokes are cryptogenic. Radiomics is a non-invasive imaging tool to analyze images at a voxel-by-voxel level. We correlated the histology of clots from patients with LVO with specific radiomic features, for a better determination of clot composition.
Methods
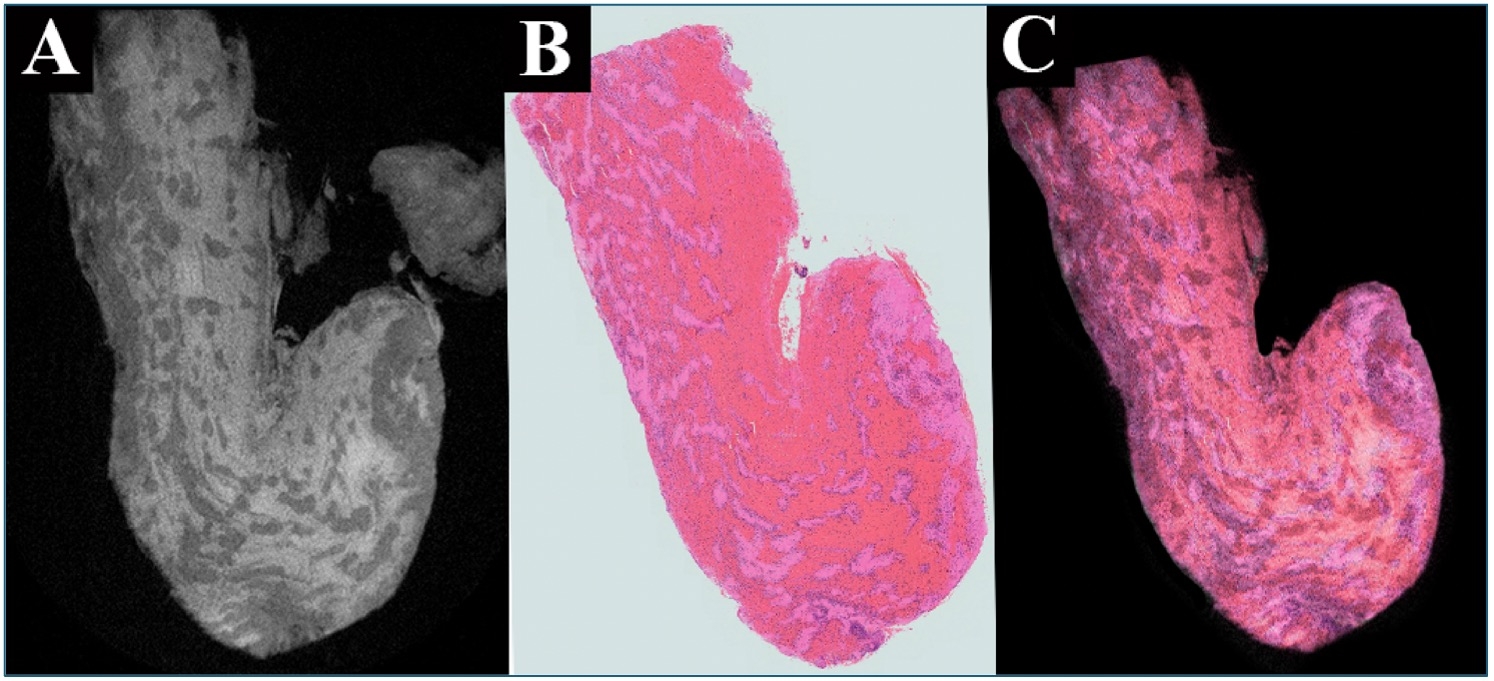
Patients diagnosed with AIS due to LVO between 2019 to 2024 were analyzed. Ten clots retrieved from mechanical thrombectomy were imaged with micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) and histologically analyzed. Radiomic features (RFs) from each clot were extracted and correlated with different clot components. NCCT images were co-registered with the corresponding slices obtained from histology. A larger cohort of 426 patients with NCCT scans obtained at presentation was subsequently analyzed. Clots displaying a hyperdense sign on NCCT were included. Stroke etiology was adjudicated based on the TOAST classification.
Results
The analysis of micro-CT showed that total energy (TE), joint average (JA) and large dependence high gray level emphasis (LDHGLE) were specific for red blood cells (RBCs, p<0.001, p 0.003, and p<0.002, respectively). Fibrin’s RFs included minimum (MI) and 10 percentile (p .005, and p<0.001, respectively), and calcium RF’s difference variance (DV, p 0.05).TE, JA and LDHGLE were correlated with clots that had at least 70% RBCs (Rho 0.654 and 0.652, respectively). MI was correlated (Rho 0.795) with clots that had at least >80% of fibrin. The RFs of the NCCT segmentations of these clots revealed strong correlation with corresponding micro-CT values of TE (Rho 0.687) JA (0.809) and LDHGLE (rho 0.657). TE (AUC 0.800, sensitivity 0.750, specificity 0.800, cutoff 38244.3089) and LDHGLE (AUC 0.750, sensitivity 0.750, specificity 0.800, cutoff: 52.64) had significant accuracy for determining clots with higher RBC composition in NCCT. MI (AUC: 0.350, sensitivity: 0.500, specificity: 0.400, cutoff: 32.3) did not have accuracy in the identification of fibrin. A total of 145 of 426 patients had optimal clot visualization on NCCT. Fifty patients had a cardioembolic stroke, 45 LAA and 50 were cryptogenic. RFs for identification of RBCs (> 70%) were present in 60% of cardioembolic, 27% of LAA and 42% cryptogenic strokes.
Conclusion
RFs are sensitive and specific to determine clots rich in RBC composition. Cardioembolic clots have higher RBCs compared with LAA and cryptogenic. Radiomic analysis is a novel non-invasive tool of determining stroke etiology.
More abstracts on this topic:
Wong Ka-ho, Krothapalli Neeharika, Littig Lauren, Champagne Alison, Majersik Jennifer, Reddy Vivek, De Havenon Adam
A distinct clot transcriptomic signature is associated with atrial fibrillation-derived ischemic stroke in the INSIGHT RegistrySeah Carina, Rivet Dennis, Fraser Justin, Kellner Christopher, Devarajan Alex, Vicari James, Dabney Alan, Baltan Selva, Sohrabji Farida, Pennypacker Keith, Nanda Ashish, Woodward Britton
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.