Final ID: WP287
Impact of Multiple Social Determinants of Health on Blood Pressure Reduction Post Stroke: Analysis of Sex Differences
Abstract Body: Introduction: Effective blood pressure (BP) control post-stroke is a critical secondary prevention strategy. Research shows that social determinants of health (SDOH) may influence this process by addressing underlying factors contributing to health disparities. We conducted a secondary analysis using data from the Discharge Educational Strategies for Reduction of Vascular Events (DESERVE) study to investigate the cumulative effect of multiple SDOH domains on BP reduction in stroke survivors, with a particular focus on sex-specific outcomes.
Methods: We applied the Healthy People 2020 framework to identify SDOH across the following domains: economic factors, education, social context, healthcare access, and neighborhood characteristics. Stroke survivors in the DESERVE skill-based intervention study completed a 6-month follow-up (n=361) and were classified into two groups based on the number of negative factors: <3 and ≥3 SDOH. The primary outcome was the reduction in systolic BP (RSBP) from baseline to the follow-up. We utilized t-test and ANOVA for initial comparisons, followed by multivariable linear regression models to examine the relationship between multiple SDOH and RSBP, adjusted for potential confounding variables, stratified men versus women.
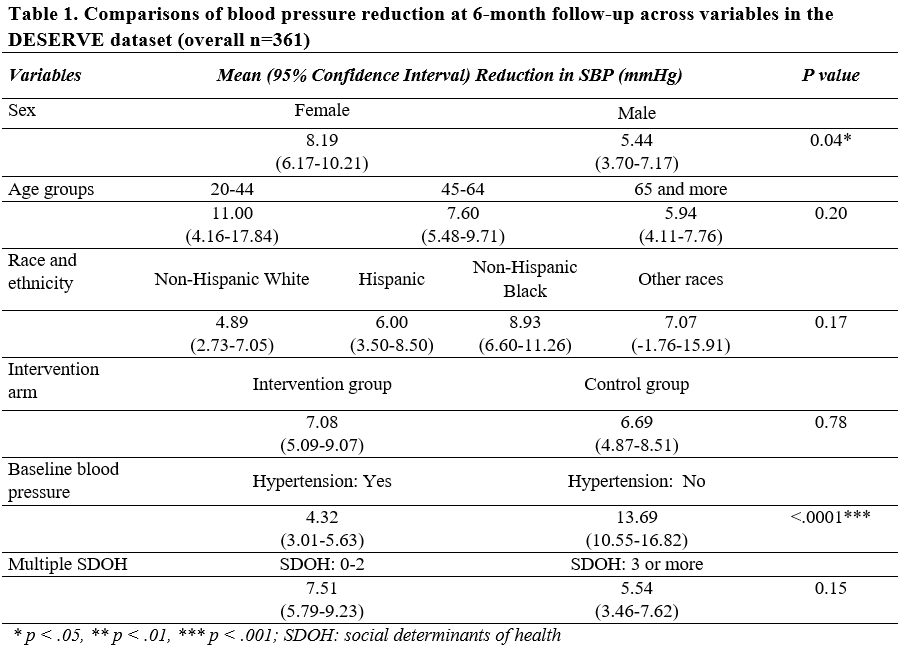
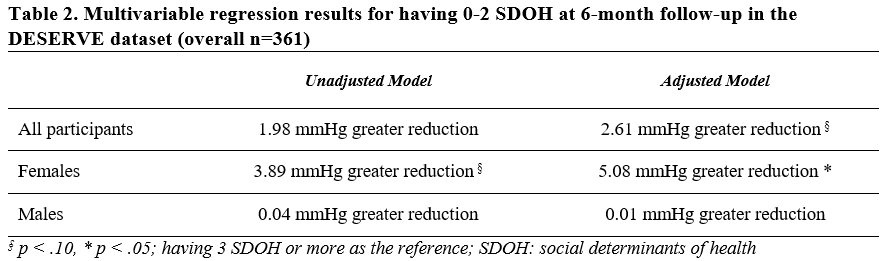
Results: Participants had a mean age of 64.5 years, with 52.6% female. There were 27.7% non-Hispanic whites, 28.8% Hispanics, and 39.3% non-Hispanic Blacks. About 72.6% of participants had hypertension at baseline, and 31.6% experienced ≥3 SDOH. There was an averaged 6.9 mmHg RSBP over the 6 months with significant variations across different subgroups, as women showed a significantly greater average RSBP compared to men (8.19 mmHg vs. 5.44 mmHg, p=0.04). RSBP was greater among participants with fewer SDOH than multiple (7.51 mmHg for <3 SDOH vs. 5.54 mmHg for ≥3 SDOH, p=0.15) (Table 1). The adjusted regression models revealed having <3 SDOH was associated with a 2.61 mmHg greater RSBP compared to ≥3 SDOH (p<0.1), which was statistically significant among females (5.08 mmHg greater reduction, p<0.05), while negligible in males (Table 2).
Conclusion: Our findings underscore the complex interplay between SDOH and post-stroke SBP management, revealing a disproportionate impact on female stroke survivors. The cumulative burden of multiple SDOH hinders effective RSBP, especially in females. Integrating SDOH considerations into stroke care is crucial to address health disparities and unique challenges faced by women.
Methods: We applied the Healthy People 2020 framework to identify SDOH across the following domains: economic factors, education, social context, healthcare access, and neighborhood characteristics. Stroke survivors in the DESERVE skill-based intervention study completed a 6-month follow-up (n=361) and were classified into two groups based on the number of negative factors: <3 and ≥3 SDOH. The primary outcome was the reduction in systolic BP (RSBP) from baseline to the follow-up. We utilized t-test and ANOVA for initial comparisons, followed by multivariable linear regression models to examine the relationship between multiple SDOH and RSBP, adjusted for potential confounding variables, stratified men versus women.
Results: Participants had a mean age of 64.5 years, with 52.6% female. There were 27.7% non-Hispanic whites, 28.8% Hispanics, and 39.3% non-Hispanic Blacks. About 72.6% of participants had hypertension at baseline, and 31.6% experienced ≥3 SDOH. There was an averaged 6.9 mmHg RSBP over the 6 months with significant variations across different subgroups, as women showed a significantly greater average RSBP compared to men (8.19 mmHg vs. 5.44 mmHg, p=0.04). RSBP was greater among participants with fewer SDOH than multiple (7.51 mmHg for <3 SDOH vs. 5.54 mmHg for ≥3 SDOH, p=0.15) (Table 1). The adjusted regression models revealed having <3 SDOH was associated with a 2.61 mmHg greater RSBP compared to ≥3 SDOH (p<0.1), which was statistically significant among females (5.08 mmHg greater reduction, p<0.05), while negligible in males (Table 2).
Conclusion: Our findings underscore the complex interplay between SDOH and post-stroke SBP management, revealing a disproportionate impact on female stroke survivors. The cumulative burden of multiple SDOH hinders effective RSBP, especially in females. Integrating SDOH considerations into stroke care is crucial to address health disparities and unique challenges faced by women.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Community Outreach Program Focused on Hypertension Awareness Reaches 600+ People in Rural Georgia and Works to Build the Next Generation of Biomedical Scientists
Dent Elena, Ilatovskaya Daria, Pinkerton Brittany, Crider Emily, Ryan Michael, Sullivan Jennifer
Age at Menarche Associated with Longitudinal Increases in Blood Pressure in Postmenopausal Indian Women: Data from the Centre for Cardiometabolic Risk Reduction in South-Asia (CARRS) studyQuarpong Wilhemina, Chandrasekaran Suchitra, Mehta Puja, Narayan K, Tandon Nikhil, Ramakrishnan Usha, Patel Shivani
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)