Final ID: WP366
Escape of Kdm6a from X Chromosome is Detrimental to Ischemic Brains via IRF5 Signaling
Abstract Body: Introduction
The fundamental roles of chromatin biology and epigenetics in progression of diseases have been increasingly recognized. Some genes escaping from X chromosome inactivation (XCI) impact neuroinflammation through epigenetic regulation. Our previous studies have suggested that the X escapee genes Kdm6a and Kdm5c were involved in microglial activation after stroke in aged mice. However, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that Kdm6a/5c demethylate H3K27Me3/H3K4Me3 in microglia respectively, and mediate the transcription of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) and IRF4, leading to microglial pro-inflammatory responses and exacerbated stroke injury.
Methods
Aged (17–20 months) Kdm6a/5c microglial conditional knockout (CKO) female mice (one allele of the gene) were subjected to a 60-min middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Gene floxed females (two alleles) and males (one allele) were included as controls. Infarct volume and behavioral deficits were quantified 3 days after stroke. Immune responses including microglial activation and infiltration of peripheral leukocytes in the ischemic brain were assessed by flow cytometry. Epigenetic modification of IRF5/4 by Kdm6a/5c were investigated by CUT&RUN ChIP assay.
Results
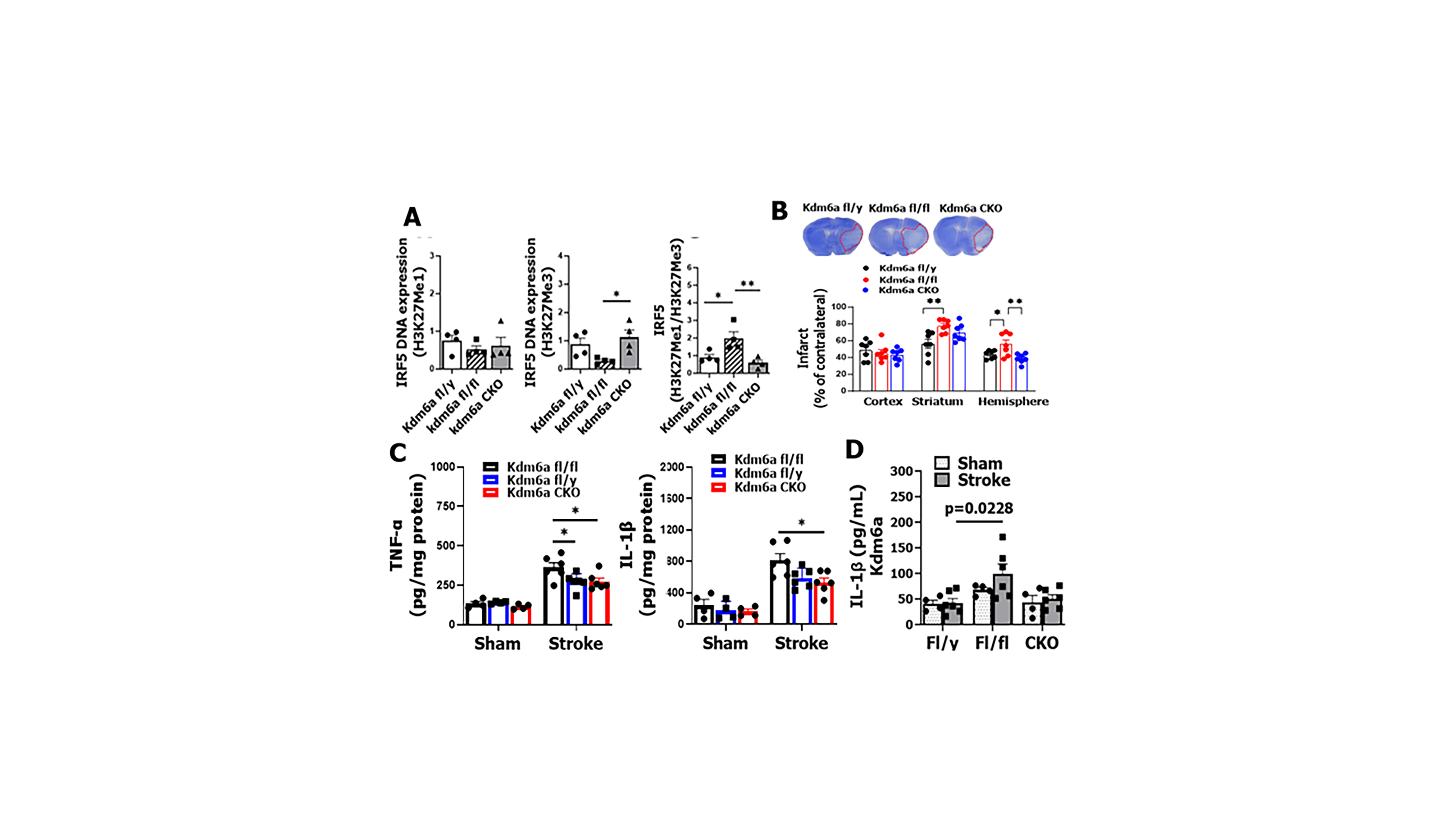
The demethylation of H3K27Me3 by Kdm6a, increased IRF5 transcription; meanwhile Kdm5c demethylated H3K4Me3 to repress IRF5 (IRF5 ratio H3K27Me1/H3K27Me3 in fl/y vs. fl/fl, p = 0.0331; fl/fl vs. CKO, p = 0.0082, Figure 1A). Both Kdm6afl/fl and Kdm5cfl/fl mice had worse stroke outcomes compared to fl/y and CKO mice (Figure 1B). Gene floxed females showed more robust expression of CD68 in microglia (Kdm6a fl/y vs. fl/fl, p < 0.0001), elevated brain and plasma levels of IL-1β or TNF-α, after stroke (Figure 1C, 1D).
Conclusion
We concluded that IRF5 signaling plays a critical role in mediating the deleterious effect of Kdm6a; whereas Kdm5c’s effect is independent of IRF5.
Keywords: Stroke, Aging, Kdm6a/5c, Microglia, Epigenetics, Ischemia, IRF
The fundamental roles of chromatin biology and epigenetics in progression of diseases have been increasingly recognized. Some genes escaping from X chromosome inactivation (XCI) impact neuroinflammation through epigenetic regulation. Our previous studies have suggested that the X escapee genes Kdm6a and Kdm5c were involved in microglial activation after stroke in aged mice. However, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that Kdm6a/5c demethylate H3K27Me3/H3K4Me3 in microglia respectively, and mediate the transcription of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) and IRF4, leading to microglial pro-inflammatory responses and exacerbated stroke injury.
Methods
Aged (17–20 months) Kdm6a/5c microglial conditional knockout (CKO) female mice (one allele of the gene) were subjected to a 60-min middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Gene floxed females (two alleles) and males (one allele) were included as controls. Infarct volume and behavioral deficits were quantified 3 days after stroke. Immune responses including microglial activation and infiltration of peripheral leukocytes in the ischemic brain were assessed by flow cytometry. Epigenetic modification of IRF5/4 by Kdm6a/5c were investigated by CUT&RUN ChIP assay.
Results
The demethylation of H3K27Me3 by Kdm6a, increased IRF5 transcription; meanwhile Kdm5c demethylated H3K4Me3 to repress IRF5 (IRF5 ratio H3K27Me1/H3K27Me3 in fl/y vs. fl/fl, p = 0.0331; fl/fl vs. CKO, p = 0.0082, Figure 1A). Both Kdm6afl/fl and Kdm5cfl/fl mice had worse stroke outcomes compared to fl/y and CKO mice (Figure 1B). Gene floxed females showed more robust expression of CD68 in microglia (Kdm6a fl/y vs. fl/fl, p < 0.0001), elevated brain and plasma levels of IL-1β or TNF-α, after stroke (Figure 1C, 1D).
Conclusion
We concluded that IRF5 signaling plays a critical role in mediating the deleterious effect of Kdm6a; whereas Kdm5c’s effect is independent of IRF5.
Keywords: Stroke, Aging, Kdm6a/5c, Microglia, Epigenetics, Ischemia, IRF
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Role for Lipoprotein(a) in Potentiating Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation
Mouawad Sahar, Boffa Michael, Koschinsky Marlys
Advanced Age Increases Susceptibility to Ischemic Myopathy after Murine Hindlimb IschemiaKulkarni Deepali, Massie Pierce, Justus Matthew, Mazloumibakhshayesh Milad, Coffman Brittany, Pace Carolyn, Clark Ross
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)