Final ID: WP179
Initial Core Volume Assessment-based Machine Learning on Non-Contrast CT could Discriminate Outcomes According to ASPECTS score and Stroke Elapsed Time in Reperfusion Treatment Patients
In reperfusion treatment, advanced neuroimaging can be used to indicate treatment or forecasting outcomes, however immediate access is not widely available. This study aims to explore the assessment of initial core volume (ICV) measured on NCCT by a machine learning-based algorithm on outcomes in overall and according to ASPECTS and stroke elapsed time.
Methods
Consecutive patients who received reperfusion treatment were studied in two stroke-centers (Jan-2021 to Dec-2023). On admission, ICV was defined on NCCT (aICV) by an algorithm trained using UNet architecture with ResNet 34 encoder. Favorable ASPECTS was defined as score 9-10. Elapsed time from symptoms onset to admission was stratified as early (<240 min) and late (>240 min) temporal window. Good clinical outcome was defined as mRS 0-2 at 90 days. A statistical analysis was performed to evaluate the relation between aICV and clinical outcome in overall and pre-defined groups.
Results
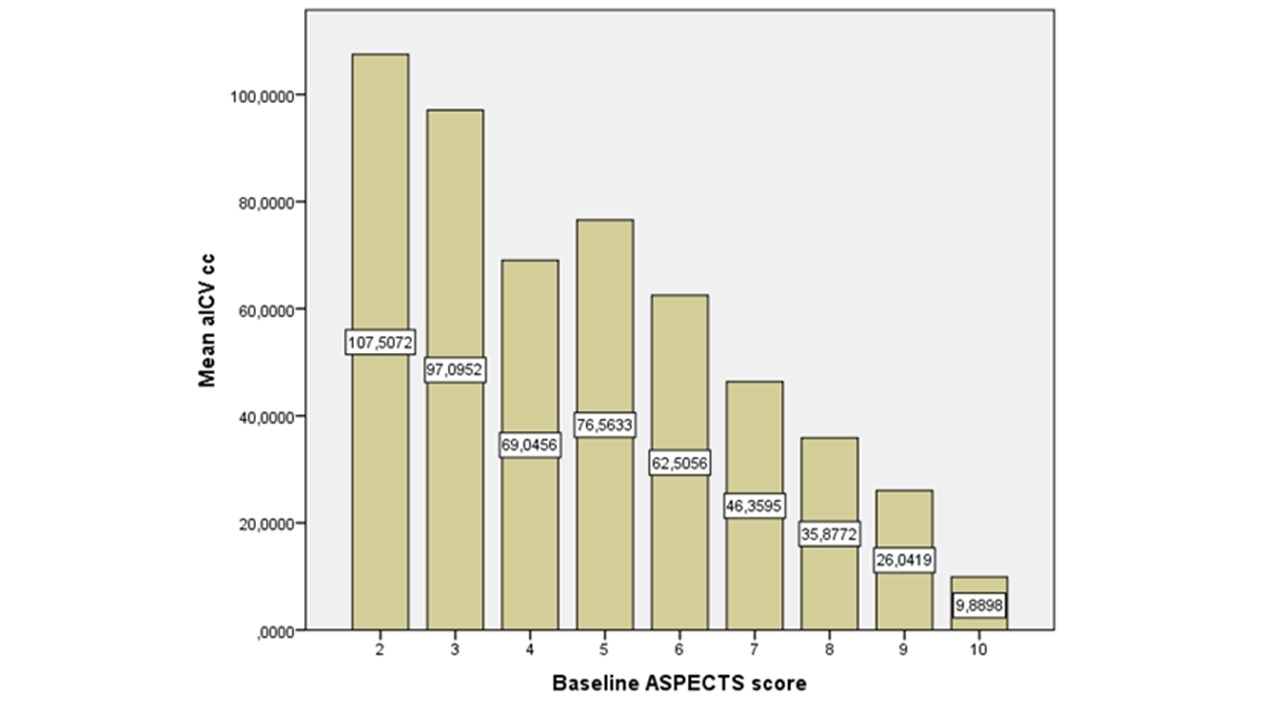
Among 595 consecutive patients included, mean age was 73.5(SD±14.4) and median baseline NIHSS 13(IQR:7-19). Mean aICV presented an inverse (r=-0.580, p<0.001) and direct (r=0.152, p=0.001) relation with ASPECTS and elapsed time respectively (figure 1).
In overall, lower aICV was associated with good outcome (13.7 SD±23.4 vs 34.2 SD±25.6, p< 0.001). A logistic regression showed that lower aICV (OR:0.982, CI95%:0.931-0.974, p=0.001), baseline NIHSS and younger age were predictors of good outcome.
In favorable ASPECTS patients, lower aICV was associated with good outcome (10.2 SD±18.8 vs 17.4 SD±25.6, p=0.002). A logistic regression showed that lower aICV (OR:0.984, CI95%:0.970-0.999, p=0.043), baseline NIHSS and younger age were predictors of good outcome.
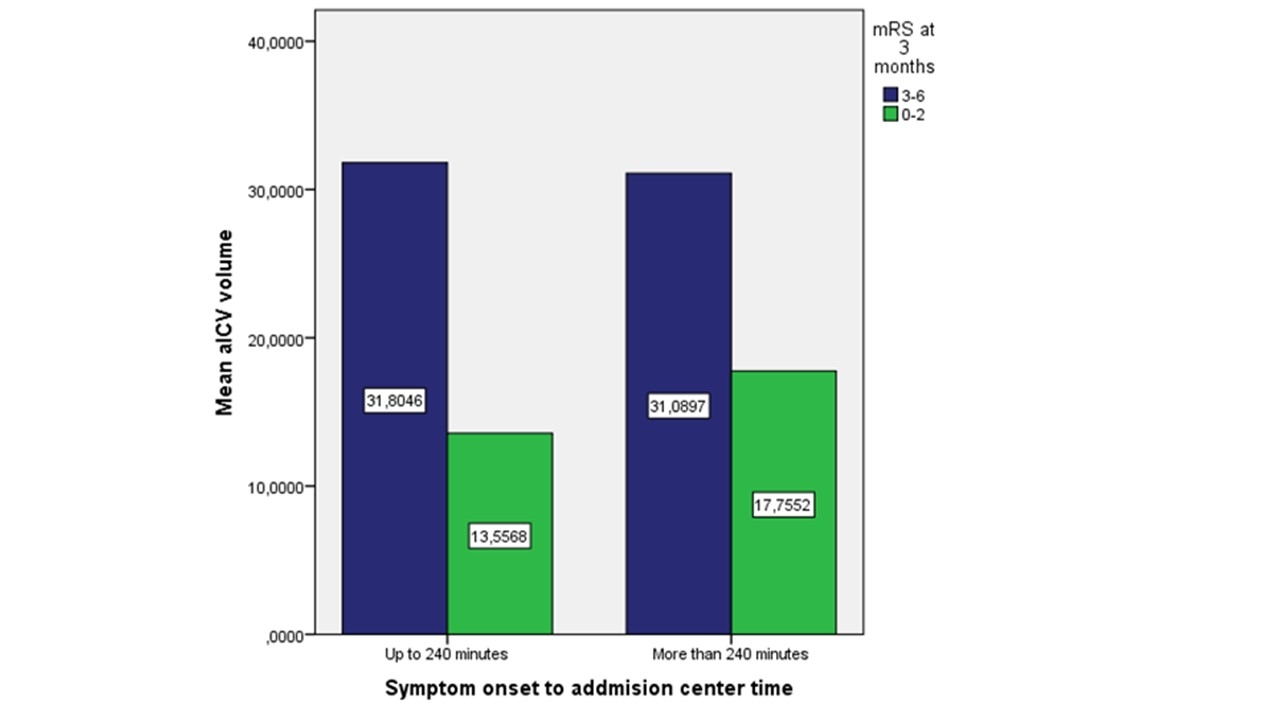
Lower aICV was associated with good outcome in both; early and late temporal window (figure 2). Adjusted logistic regression showed that lower aICV (OR: 0.983, CI95%: 0.968-0.998, p=0.03) and age were predictors of good outcome in the early window. In the late window; aICV (OR: 0.977, CI95%: 0.960-0.994, p=0.007) and age were also predictors of good outcome.
Conclusion
Among reperfusion treatment patients, ICV assessment-based machine learning logarithm on NCCT is capable to predict a favorable outcome even in patients with a favorable ASPECTS score and in both, the early and late time window. Furthers studies will determine the potential role of aICV to safely expand the indication of reperfusion treatments based on NCCT in different settings
More abstracts on this topic:
Xu Xiaohong, Preeti Preeti, Yu Ruoying, Shaykhalishahi Hamed, Zhang Cheng, Shen Chuanbin, Li Bei, Tang Naping, Chang Yan, Xiang Qian, Cui Yimin, Lei Xi, Ni Heyu, Zhu Guangheng, Liu Zhenze, Hu Xudong, Slavkovic Sladjana, Neves Miguel, Ma Wenjing, Xie Huifang
A Case Report: Outpatient Diagnosis of Venous Stent Migration - Avoiding Catastrophic OutcomesBasnyat Anouksha, Pamganamamula Madhu, Naidu Raja, Pamganamamula Teja, Manchiraju Srinidhi, Gaddam Srilakshmi, Panganamamula Lalitha
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.