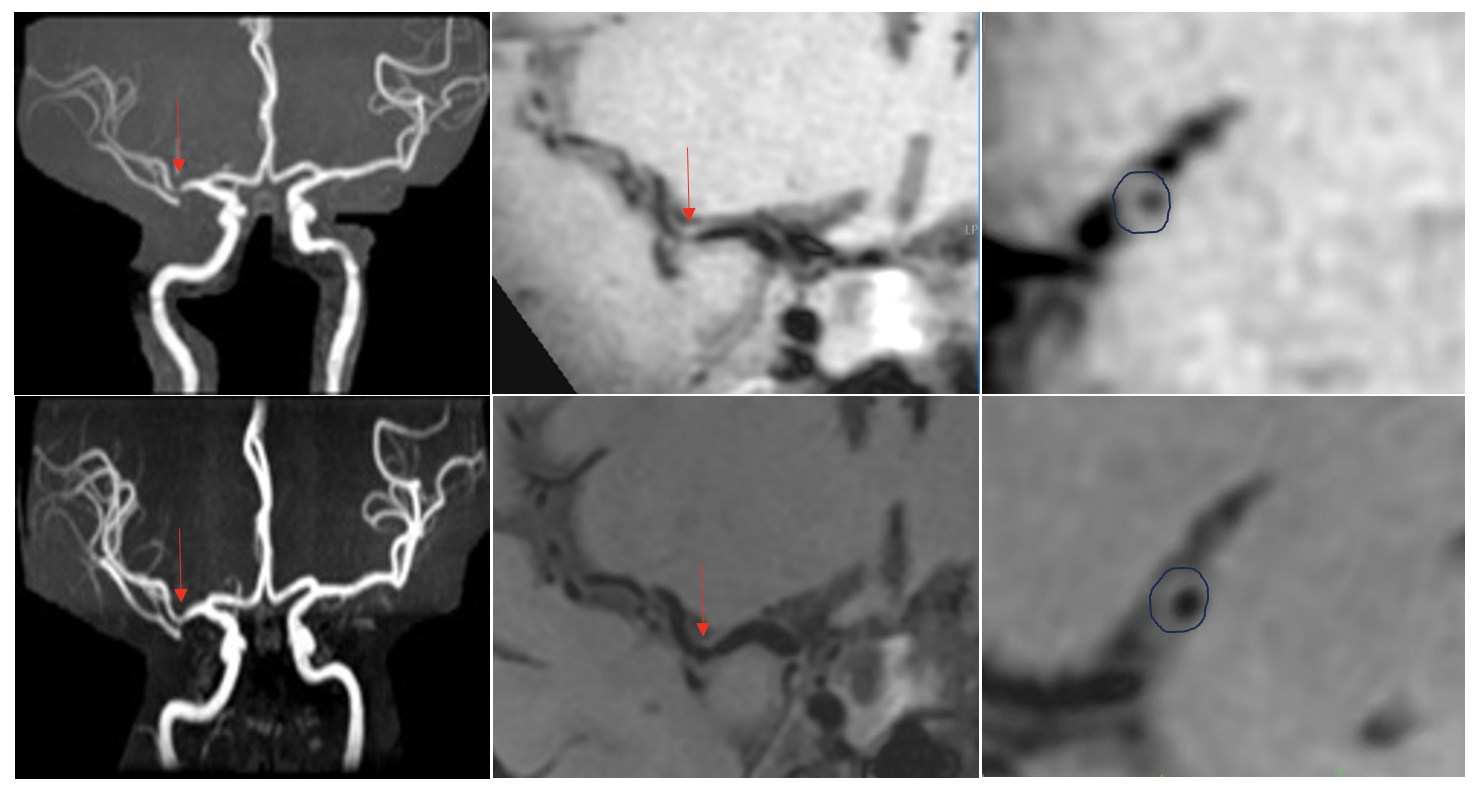
Final ID: 38
Evolocumab added to statin is superior to statin alone in reversing symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis
Methods: From a prospectively established high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (HR-MRI) database, consecutive ICAS (>50%) patients with two detections of HR-MRI over six months were included in this study. The patients were divided into two groups: those with (evolucomab+) or without (evolocumab-) evolocumab add-on therapy. The primary outcomes were the percentage change in plaque burden and plaque response (plaque regression >5%) rate. The second outcome was the percentage change in stenosis degree. Cox regression analysis was used to estimate the association between evolocumab add-on therapy and the above outcomes in both general and subgroup (intensive statin vs. non-intensive statin) analysis.
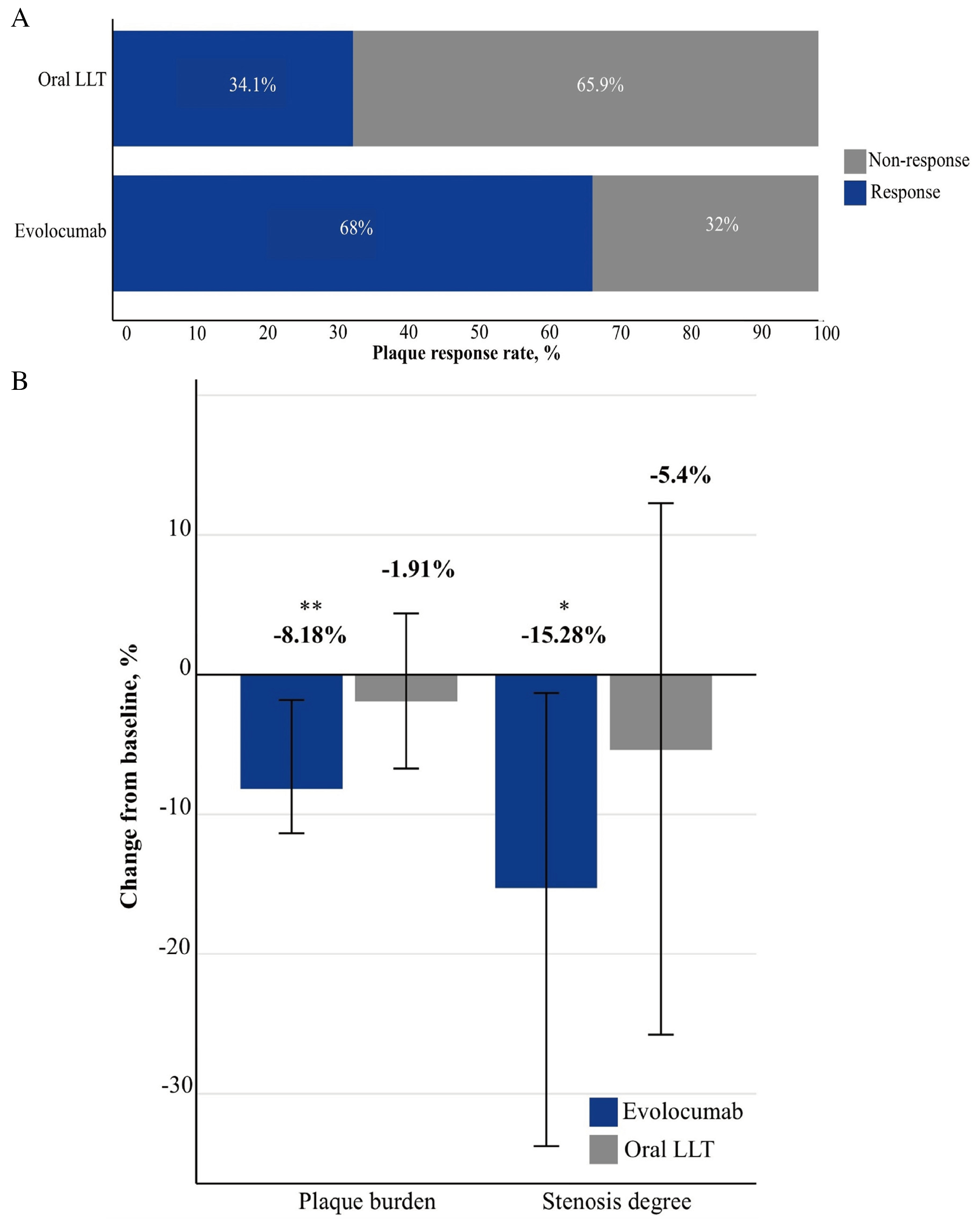
Results: The data of 179 patients receiving statins and/or ezetimibe, 50 of which with evolucumab and 129 without, were analyzed. Evolocumab add-on therapy over six months showed a significant reduction in the percentage change of plaque burden (evolocumab+, median [IQR]: 0.08 [0.02-0.11] vs. evolocumab-: 0.02 [0.04-0.07]), increase in plague response rate (evolocumab+: 68.0% vs. evolocumab-: 34.1%), and reduction in the percentage change of stenosis degree (evolocumab+: 0.15 [0.01-0.34] vs. evolucumab-: 0.05 [-0.12-0.26]). After adjusting for potential confounders, evolocumab was significantly associated with the percentage reduction in plaque burden (estimate [95% CI], 0.074 [0.029-0.119]), the increase in plague response rate (6.70 [2.81-16.99]), and the percentage reduction in stenosis degree (0.198 [0.074-0.321]). In both intensive and non-intensive statin groups, evolocumab add-on therapy was still significantly associated with better outcomes in the percentage reduction in plague burden (intensive: 0.063 [0.004-0.121], P < 0.05; non-intensive: 0.126 [0.045-0.208], P < 0.01), the increase in plaque response rate (intensive: 3.75 [1.09-14.10], P < 0.05; non-intensive: 11.60 [2.55 – 52.82], P < 0.01), and the percentage reduction in stenosis degree (intensive: 0.148 [-0.015-0.312], P = 0.075; non-intensive: 0.331 [0.118-0.544], P < 0.01).
Conclusions: Evolocumab add-on therapy over six months is superior to statin alone in reversing symptomatic ICAS.
More abstracts on this topic:
Ma Yan, Wang Tao, Wang Haibo, Yang Yifan, Wang Jie, Derdeyn Colin, Gu Yuxiang, Jiao Liqun
A Novel CRISPR based Epigenetic Silencer Potently, Durably, and Safely Reduces LDLc in Non-Human Primates at Therapeutically Relevant DosesDuncan-lewis Christopher, Narsineni Lokesh, Karmarkar Maitreyee, Li Yuexuan, Krupa Oleh, Bucher Simon, Sharma Neel, Chang Han, Schulwach Keith, Ripley-phipps Sterling, Tran Vanessa, Fernandes Jason, Goh Natalie, Deiter Fred, Reimer Kirsten, Mrak Anna, Eggers Michelle, Sze Christie, Mirotsou Maria, Oresic Bender Kristina, Bardai Farah, Denny Sarah, Charles Emeric, Khakoo Aarif, Oakes Benjamin, Keller Steven, Alcantara-lee Raniel, Santamaria Carlos, Bale Shyam Sundhar, Kozy Heather, Corbo Lana
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.