Final ID: TP181
Advanced Diffusion and Functional MRI Measures Are Associated with Microstructural Morphology and Cognitive Function in Subacute Ischemic Cerebellar Stroke
Abstract Body: Introduction: The mechanisms of cognitive dysfunction following ischemic cerebellar stroke (CS) are not well understood. Furthermore, traditional clinical stroke MRI protocols often cannot identify subtle and early changes in normal appearing tissue of the cerebellum. We aimed to implement an advanced MRI protocol in subacute CS patients to better understand outcomes.
Hypothesis: The MRI markers for tissue microstructure and cerebrovascular function (CVF) in the cerebellum will provide mechanistic insight into post-stroke cognitive dysfunction.
Methods: After 4 weeks of stroke onset, 13 first-time subacute mildly-impaired ischemic stroke participants (PPT) were imaged on a 3T Siemens Prisma MRI scanner with an advanced multi-shell diffusion-weighted protocol to map of Non-Gaussian Diffusion (NGD) and a multi-echo resting-state functional protocol with a breath-hold task (rs+BH-fMRI) to map CVF. PPT demographics: 62.6(11.44) years, sex (11 males), race (1 Latino, 2 Asian, 4 black, 6 white), NIHSS median = 1 (IQR 0-3), Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) median = 25 (IQR 21-28). 3 PPTs were diagnosed with right cerebellar stroke (CS), and 10 PPTs were diagnosed with non-cerebellar subcortical stroke (NCS). Statistical analyses were performed to: 1) identify the group differences between the CS PPTs versus the NCS PPTs for both NGD and rs+BH-fMRI metrics in the normal appearing white and gray matter of the infarcted cerebellum, and 2) for all PPTs, correlate the NGD metrics in the left 'unaffected' cerebellum white matter versus MoCA score.
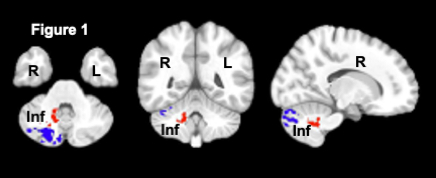
Results: Fig. 1 shows the group comparison for significantly increased NGD (p<0.05) in the infarcted hemisphere of CS PPTs versus NCS PPTs. Classical fractional anisotropy (FA) did not reach significance. Fig. 2 shows the individual rs+BH-fMRI data (Fig. 2), where the amplitude of the CVF response was significantly decreased for the CS PPTs versus NCS PPTs in the infarcted cerebellum (p=0.043). Fig. 3 shows the correlational analysis in the 'unaffected' left cerebellar hemisphere with significantly increased NGD (r=0.473, p=0.038) with respect to MoCA scores. Classical FA did not reach significance.
Conclusions: Using advanced MRI protocols we demonstrated that novel NGD metrics and breath-hold based fMRI measures are sensitive to cerebellar morphology post-stroke and correlate with cognitive function. These measures can be used to identify trajectories for recovery and accelerated cognitive impairment after ischemic CS.
Hypothesis: The MRI markers for tissue microstructure and cerebrovascular function (CVF) in the cerebellum will provide mechanistic insight into post-stroke cognitive dysfunction.
Methods: After 4 weeks of stroke onset, 13 first-time subacute mildly-impaired ischemic stroke participants (PPT) were imaged on a 3T Siemens Prisma MRI scanner with an advanced multi-shell diffusion-weighted protocol to map of Non-Gaussian Diffusion (NGD) and a multi-echo resting-state functional protocol with a breath-hold task (rs+BH-fMRI) to map CVF. PPT demographics: 62.6(11.44) years, sex (11 males), race (1 Latino, 2 Asian, 4 black, 6 white), NIHSS median = 1 (IQR 0-3), Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) median = 25 (IQR 21-28). 3 PPTs were diagnosed with right cerebellar stroke (CS), and 10 PPTs were diagnosed with non-cerebellar subcortical stroke (NCS). Statistical analyses were performed to: 1) identify the group differences between the CS PPTs versus the NCS PPTs for both NGD and rs+BH-fMRI metrics in the normal appearing white and gray matter of the infarcted cerebellum, and 2) for all PPTs, correlate the NGD metrics in the left 'unaffected' cerebellum white matter versus MoCA score.
Results: Fig. 1 shows the group comparison for significantly increased NGD (p<0.05) in the infarcted hemisphere of CS PPTs versus NCS PPTs. Classical fractional anisotropy (FA) did not reach significance. Fig. 2 shows the individual rs+BH-fMRI data (Fig. 2), where the amplitude of the CVF response was significantly decreased for the CS PPTs versus NCS PPTs in the infarcted cerebellum (p=0.043). Fig. 3 shows the correlational analysis in the 'unaffected' left cerebellar hemisphere with significantly increased NGD (r=0.473, p=0.038) with respect to MoCA scores. Classical FA did not reach significance.
Conclusions: Using advanced MRI protocols we demonstrated that novel NGD metrics and breath-hold based fMRI measures are sensitive to cerebellar morphology post-stroke and correlate with cognitive function. These measures can be used to identify trajectories for recovery and accelerated cognitive impairment after ischemic CS.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Randomized, Double Blinded, Phase 2B Clinical Trial to Compare the Safety and Efficacy of Sodium Chloride and Sodium Acetate Combination Intravenous Fluids in Acute Stroke Patients
Wasay Muhammad, Suri Fareed, Saleem Shafaq, Qureshi Adnan
A machine learning approach to classifying ischemic stroke etiology using variables available in the Get-with-the-Guidelines Stroke RegistryLee Ho-joon, Schwamm Lee, Turner Ashby, De Havenon Adam, Kamel Hooman, Brandt Cynthia, Zhao Hongyu, Krumholz Harlan, Sharma Richa
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)