Final ID: WMP26
Clinical Characteristic-Driven Machine Learning Models for the Prediction of Stroke Subtypes and Eligibility of Endovascular Thrombectomy
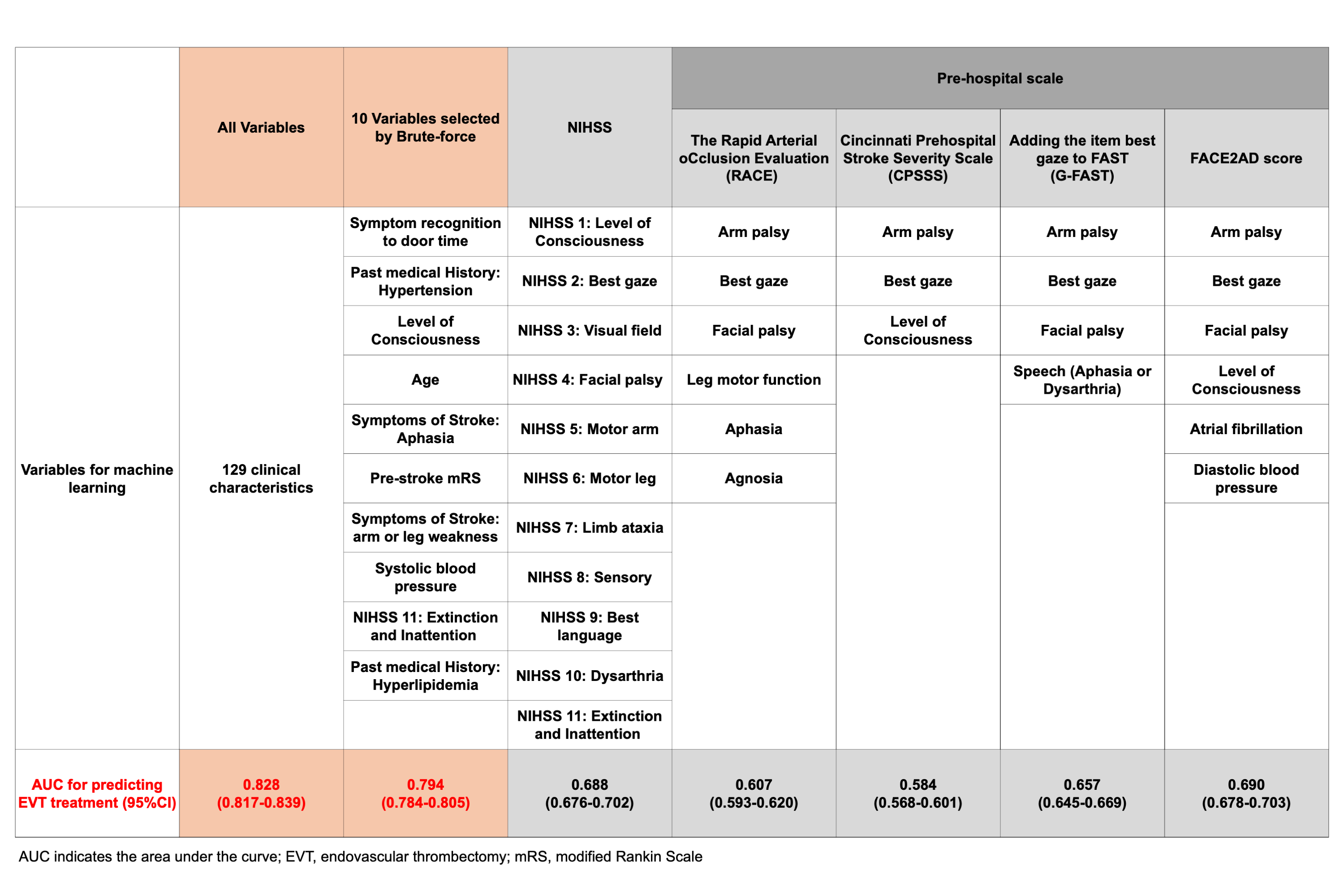
Methods: We conducted an analysis using data from the Japan Stroke Data Bank, a nationwide acute stroke registry. Patients with ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, or subarachnoid hemorrhage who were hospitalized between 2016 and 2020 were included in this study. We developed two ML models: (1) a model to predict patients who received EVT, and (2) to predict stroke categories (ischemic stroke treated with EVT, ischemic stroke treated with tPA, ischemic stroke without EVT or tPA, intracerebral hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage). Patient data were divided into the derivation cohort (data from 2016 to 2019) and the validation cohort (data in 2020). The input variables for the ML models consisted of 129 clinical characteristics, including past medical history and neurological examination findings. Imaging and laboratory data were not utilized in the ML process. We initially developed the ML models using LightGBM algorithm with all 129 variables. Subsequently, we selected the top 10 variables for model development by the feature importance and Brute-force method, comparing commonly used pre-hospital scales to predict patients with EVT.
Results: Of the 62,588 patients included in the study, 4,353 were treated with EVT, 3,001 with tPA, 39,710 had ischemic stroke treated without EVT or tPA, 12,498 had intracerebral hemorrhage, and 3,028 had subarachnoid hemorrhage. The area under the curve (AUC) for predicting patients treated with EVT was 0.828 (95% CI 0.817-0.839). For predicting the five stroke categories, the multiclass AUC was 0.848, and the micro-average F1 score was 0.705. Using the brute-force algorithm to select 10 variables, the ML model for predicting EVT treatment achieved an AUC of 0.794 (95% CI 0.784-0.805), outperforming commonly used pre-hospital scales (AUC 0.584-0.690).
Conclusions: The ML models utilizing only clinical characteristics can accurately predict stroke subtypes and EVT eligibility, offering a potential improvement over current pre-hospital scales.
More abstracts on this topic:
Shvilkin Alexei, Zlatic Natasa, Atanasoski Vladimir, Grujovic Zdolsek Sanja, Popovic Maneski Lana, Miletic Marjan, Vukcevic Vladan
A Machine Learning Approach to Simplify Risk Stratification of Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseLi Hsin Fang, Gluckman Ty, Nute Andrew, Weerasinghe Roshanthi, Wendt Staci, Wilson Eleni, Sidelnikov Eduard, Kathe Niranjan, Swihart Charissa, Jones Laney
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.