Final ID: WMP24
Heart-Brain Connection: White Matter Hyperintensity Associated with Low Heart Rate Variability
Abstract Body: Background: Cerebral autonomic regulation is measurable through heart rate variability (HRV). Low HRV (L-HRV) is linked to an increased risk for ischemic stroke. White Matter Hyperintensities (WMH) is a measure of cerebral small vessel disease (cSVD) which is associated with lacunar ischemic stroke. However, limited studies have investigated the link between L-HRV and WMH. This study aimed to investigate the association between L-HRV and WMH.
Methods: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study measured HRV using 2-minute readings in middle-aged adults at visit 4 conducted between 1996-1998 and conducted MRI scans during visit 5 between 2011-2013. Subjects on medications that influence HRV were excluded. HRV indicators were calculated using the standard deviation of normal-to-normal (SDNN), mean of RR intervals (mean RR), and root mean square of successive differences (RMSSD). cSVD was accounted for by WMH as a percent of total intracranial volume. All HRV metrics and WMH were not normally distributed, hence stratified into quartiles. An ordinal regression model was used to estimate the relationship between the lowest quartile of HRV measure and the highest quartile of WMH volume, adjusted for age, race, sex, body mass index, hypertension, and diabetes.
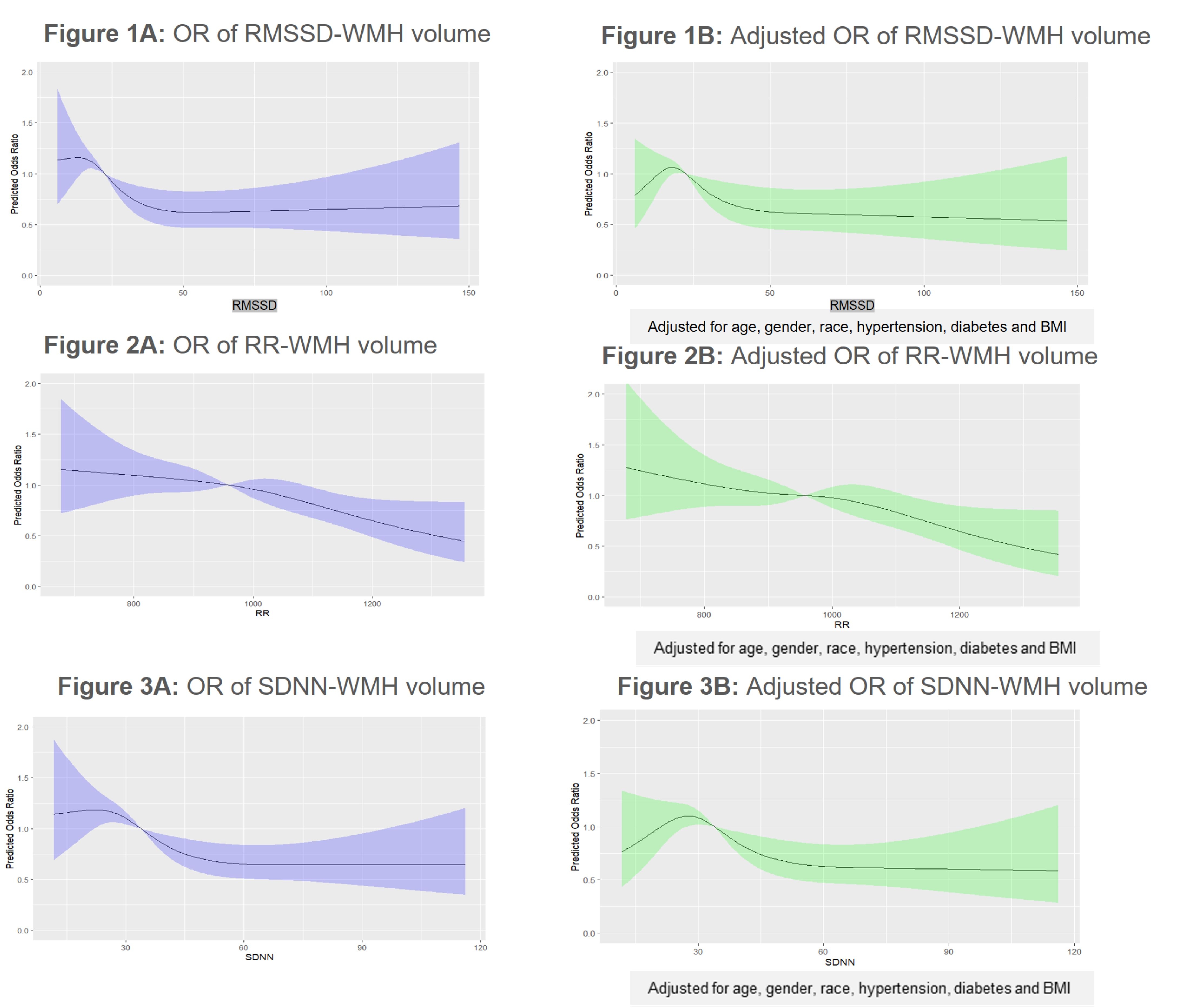
Results: Spline graphs depicting the crude and adjusted odds ratio (OR) representing the association between WMH and HRV metrics (N = 1353, mean age 76 ± 5, 72% white and 59% female) shown in figures 1A through 3B. The lowest quartile of RMSSD was significantly related to the highest quartile of WMH (OR = 1.82, CI = 1.38 – 2.39). The relationship remained significant after the adjustment (OR = 1.49, CI = 1.12 – 1.97). The lowest quartile of mean RR was significant with the highest quartile of WMH (OR = 1.52, CI = 1.16 – 1.99). The association remained significant after the adjustment (OR = 1.45, CI = 1.08 - 1.94). The lowest quartile of SDNN was associated with the highest quartile of WMH (OR = 1.57, CI = 1.20 - 2.06). The association remained borderline significant after the adjustment (OR = 1.27, CI = 0.95 – 1.68).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that L-HRV is associated with the highest quartile of WMH volume. Previously L-HRV has been suggested to associate with atrial fibrillation, a harbinger of cardioembolic stroke. Our results raise the possibility of its association with cSVD, a harbinger of lacunar stroke and vascular cognitive impairment.
Methods: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study measured HRV using 2-minute readings in middle-aged adults at visit 4 conducted between 1996-1998 and conducted MRI scans during visit 5 between 2011-2013. Subjects on medications that influence HRV were excluded. HRV indicators were calculated using the standard deviation of normal-to-normal (SDNN), mean of RR intervals (mean RR), and root mean square of successive differences (RMSSD). cSVD was accounted for by WMH as a percent of total intracranial volume. All HRV metrics and WMH were not normally distributed, hence stratified into quartiles. An ordinal regression model was used to estimate the relationship between the lowest quartile of HRV measure and the highest quartile of WMH volume, adjusted for age, race, sex, body mass index, hypertension, and diabetes.
Results: Spline graphs depicting the crude and adjusted odds ratio (OR) representing the association between WMH and HRV metrics (N = 1353, mean age 76 ± 5, 72% white and 59% female) shown in figures 1A through 3B. The lowest quartile of RMSSD was significantly related to the highest quartile of WMH (OR = 1.82, CI = 1.38 – 2.39). The relationship remained significant after the adjustment (OR = 1.49, CI = 1.12 – 1.97). The lowest quartile of mean RR was significant with the highest quartile of WMH (OR = 1.52, CI = 1.16 – 1.99). The association remained significant after the adjustment (OR = 1.45, CI = 1.08 - 1.94). The lowest quartile of SDNN was associated with the highest quartile of WMH (OR = 1.57, CI = 1.20 - 2.06). The association remained borderline significant after the adjustment (OR = 1.27, CI = 0.95 – 1.68).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that L-HRV is associated with the highest quartile of WMH volume. Previously L-HRV has been suggested to associate with atrial fibrillation, a harbinger of cardioembolic stroke. Our results raise the possibility of its association with cSVD, a harbinger of lacunar stroke and vascular cognitive impairment.
More abstracts on this topic:
Infrequent Cognitive Assessments in CABG Trials (from 2005-2023) Highlight Need for Improved Strategies for Cognitive Screening post-coronary bypass grafting (CABG) surgery
Srivatsa Shantanu, Sujanthan Sajeevan, Nino De Rivera Stephanie, Masterson Creber Ruth, Swartz Richard
Cardiac Injury Potentially Contributes to Neuroinflammation via Extracellular VesiclesLi Qingxuan, Dhyani Neha, Gao Lie, Rudebush Tara, Zucker Irving, Tian Changhai
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)