Final ID: 126
In-bed robot-guided ankle sensory-motor rehabilitation in early subacute stroke survivors: a preliminary clinical trial
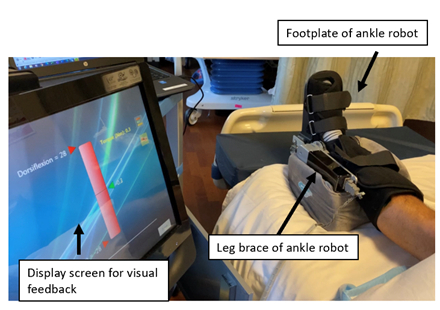
Abstract Body: Introduction: The most commonly observed motor impairment associated with stroke is the weakness of ankle muscles and stiffness of the ankle joint, which severely restricts gait and balance function and limits the performance of many activities of daily living. Stroke survivors have the most potential for motor recovery in their acute and subacute stages. An intensive in-bed robot-guided ankle training may aid in promoting motor recovery in early sub-acute stroke survivors. The purpose of the study was to investigate the feasibility and efficacy of in-bed robot-guided ankle movement training in early subacute stroke survivors.
Method: This was a controlled trial. The initial 8 patients were assigned to the study group and the rest patients were randomized to the study and control groups. In total, 44 stroke survivors at the early subacute stage were assigned to either a study group (n=26) or a control group (n=18) during their hospital stay. Individuals in the study group received 45-minutes of in-bed robot-guided ankle movement training, including passive stretching and game-based active movement training; while the control group used the same ankle robot and received passive ankle movement in the mid-range of motion and attempted active ankle movement without robotic assistance. Biomechanical and clinical outcome measures were obtained before and after the intervention.
Results: After the training (sessions: 11.3 ± 4.2 sessions), the study group had a significantly larger increase in ankle active range of motion (p=0.002, eta2=0.213), maximal voluntary contraction in plantar flexion (p=0.016,eta2=0.131) and dorsiflexion (p=0.035,eta2=0.102), compared with the control group. Patients in both groups showed a significant increase in Fugl-Meyer assessment lower limb motor score (p<0.001, eta2=0.560), Berg Balance Scale (p<0.001, eta2=0.503), and a decrease in Modified Ashworth Scale in plantar flexors (p<0.001, eta2=0.291), without significant group differences.
Conclusions: In-bed robot-guided ankle training is feasible in patients at the early subacute stage. The robotic training including passive stretching and active movement helped the recovery of ankle voluntary muscle contraction and active range of motion. Incorporating an early in-bed robotic ankle rehabilitation is a feasible intervention technique that may help facilitate the ankle volitional control.
Method: This was a controlled trial. The initial 8 patients were assigned to the study group and the rest patients were randomized to the study and control groups. In total, 44 stroke survivors at the early subacute stage were assigned to either a study group (n=26) or a control group (n=18) during their hospital stay. Individuals in the study group received 45-minutes of in-bed robot-guided ankle movement training, including passive stretching and game-based active movement training; while the control group used the same ankle robot and received passive ankle movement in the mid-range of motion and attempted active ankle movement without robotic assistance. Biomechanical and clinical outcome measures were obtained before and after the intervention.
Results: After the training (sessions: 11.3 ± 4.2 sessions), the study group had a significantly larger increase in ankle active range of motion (p=0.002, eta2=0.213), maximal voluntary contraction in plantar flexion (p=0.016,eta2=0.131) and dorsiflexion (p=0.035,eta2=0.102), compared with the control group. Patients in both groups showed a significant increase in Fugl-Meyer assessment lower limb motor score (p<0.001, eta2=0.560), Berg Balance Scale (p<0.001, eta2=0.503), and a decrease in Modified Ashworth Scale in plantar flexors (p<0.001, eta2=0.291), without significant group differences.
Conclusions: In-bed robot-guided ankle training is feasible in patients at the early subacute stage. The robotic training including passive stretching and active movement helped the recovery of ankle voluntary muscle contraction and active range of motion. Incorporating an early in-bed robotic ankle rehabilitation is a feasible intervention technique that may help facilitate the ankle volitional control.
More abstracts on this topic:
Combined Measures of Socioeconomic Status Associated with Cognitive Symptoms Following Acute Ischemic Stroke
Siegel Matthew, Corlin Laura, Miller James, Cote Kathryn, Leung Lester
A Novel Approach of Monitoring Stroke Recovery: Contactless Sensor for Gait Speed and Fugl-Meyer Action Duration EstimationGu Zhuangzhuang, Titus Ryan, Regmi Hem, Tavasoli Reza, Sur Sanjib, Sen Souvik
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)