Final ID: 82
Effect Of Chronic Nicotine Exposure On Long-term Outcomes Following Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Hypothesis: Prior chronic nicotine exposure will result in more significant brain damage following an autologous blood injection-induced sICH.
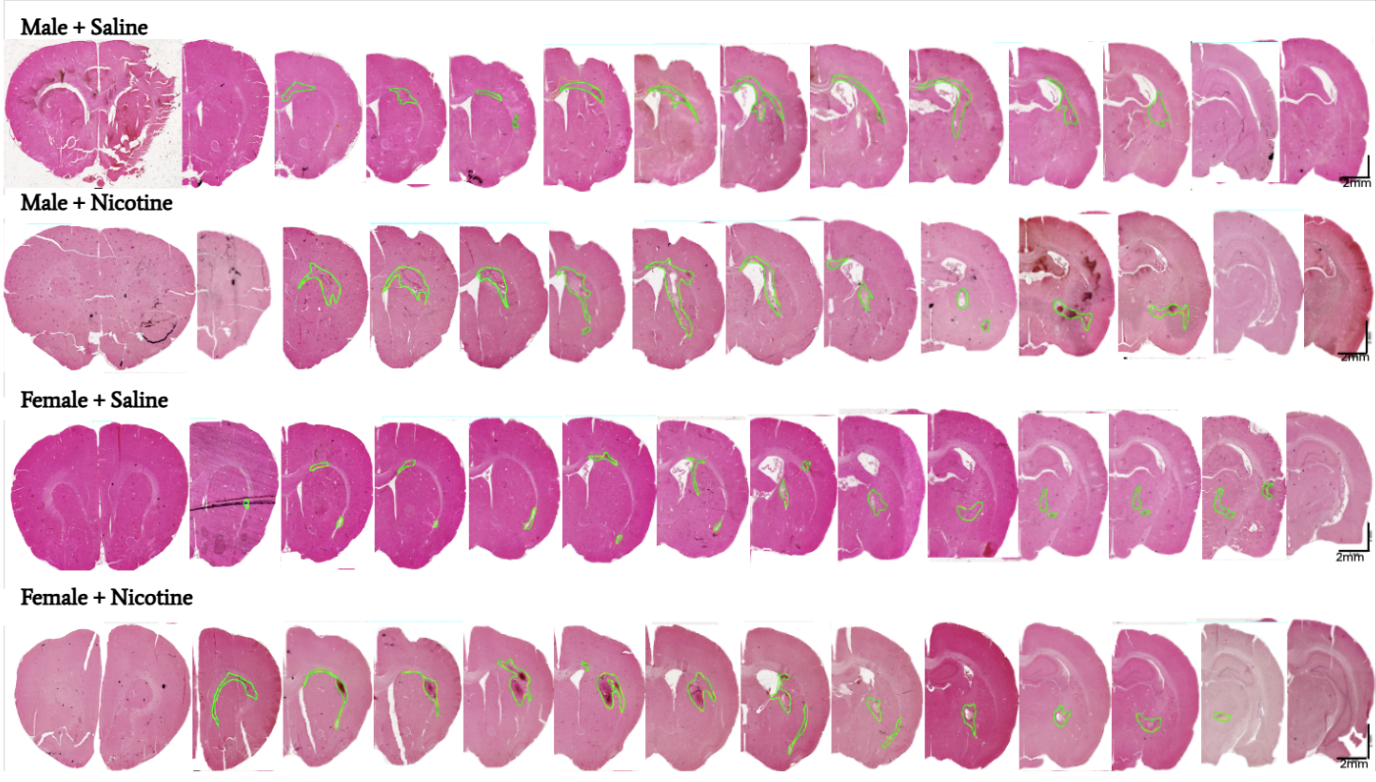
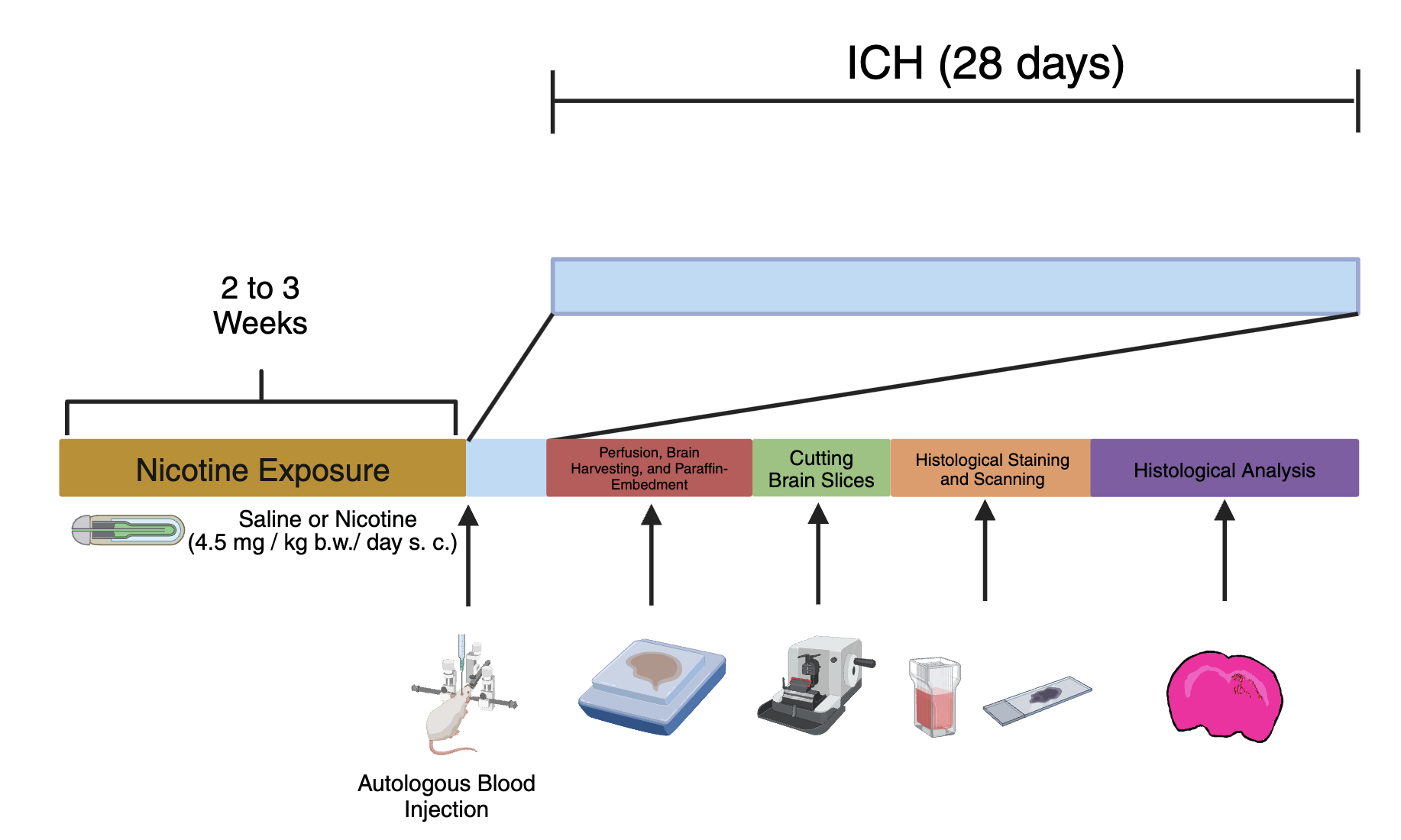
Methods: Young male and female (estrous matched) rats were randomly assigned to a saline (control) or nicotine-exposed group. Rats received nicotine or saline via. osmotic pumps for 2-3 weeks. The pump was removed before the induction of sICH by the stereotaxic injection of autologous blood into the striatum. The autologous blood injection-induced sICH model was used to obtain equal hematoma volume in all experimental groups. Rats then underwent perfusion fixation, and brains were harvested for histopathological analysis. Paraffin-embedded brain blocks were cut into 10 µm coronal sections between bregma -2.0 to +2.0, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, scanned with a high-resolution scanner, and analyzed using ImageJ to measure lesion area. Student’s t-test was used to determine significant differences in mean lesion volume between treatment groups. Two-way ANOVA was used to assess the interaction effect between sex and lesion volume.
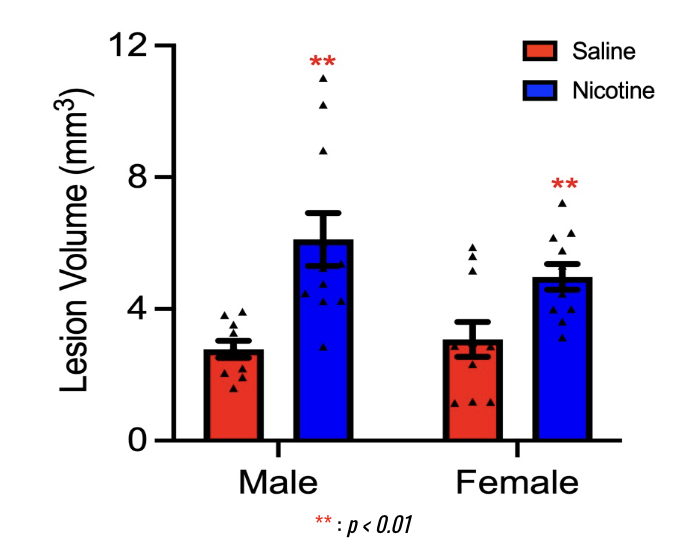
Results: For the male group, the brain lesion volume in nicotine-exposed rats was significantly (p<0.01) larger by 121% (6.11± 0.81 mm3) when compared to the lesion volume in saline-exposed rats (2.77± 0.26 mm3). For the female group, the brain lesion volume of the nicotine group was significantly (p<0.01) larger by 62% (4.98±0.39 mm3) when compared to the lesion volume of the saline group (3.07± 0.53 mm3). Sex had no significant effect on mean lesion volume.
Conclusion: Chronic nicotine exposure worsens long-term outcomes post-sICH in young rats of both sexes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Eperjesi Sarah, Yutrzenka Kayla, Marginean Horia, Crawford Erin, Lesko Alexandra, Clark Diane
Association of Intensity of E-cigarette Use with Heart Rate in Daily Life in Young Adults using a Text-Messaging Partnered with Mobile Health Monitoring PlatformJavanmardi Elmira, Hamburg Naomi, Kadel Rabindra, Barger Kathryn, Minetti Erika, Hoover Rachel, Gallagher Jacqueline, Manoochehri Arash Niusha, Weisbrod Robert, Keith Rachel
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.