Final ID: TP15
Argatroban Among Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Methods: We systematically searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane CENTRAL databases from their inception to July 2024 for randomized controlled trials of argatroban. The primary outcome was excellent functional outcome, as defined by a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 0-1 at 90 days. The secondary endpoints were favorable functional outcome, defined by a mRS score of 0-2 at 90 days, and repeat stroke or other vascular events within 90 days. Safety endpoints included symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage and parenchymal hematoma at 90 days. Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool (RoB 2). Random-effects meta-analytic models were used to estimate pooled risk ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Our protocol was preregistered on Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/tygwx/).
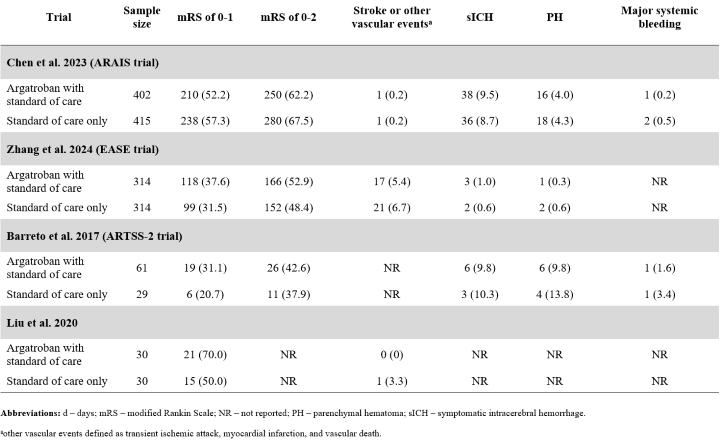
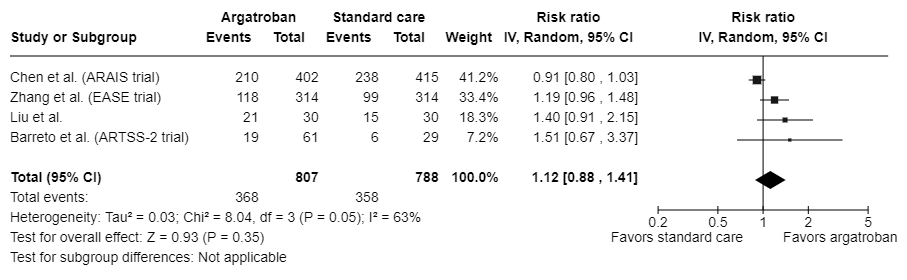
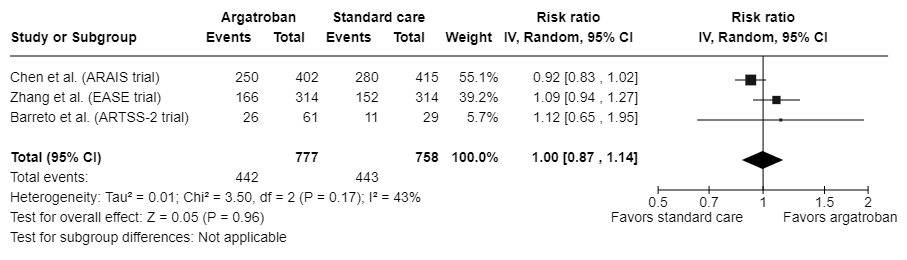
Results: Four randomized controlled trials were included. A total of 1,595 participants were randomized to receive either argatroban with standard of care (n=807) or standard of care alone (n=788). Participants were mostly male (67.1%), and their median/mean age ranged from 57 to 69 years. When data were pooled across trials, the impact of argatroban on the likelihood to have a mRS score of 0-1 was inconclusive due to a wide CI (RR: 1.12; 95% CI: 0.88-1.41; I2: 63%) (Figure 1). Similar trends were observed for the other predefined outcomes. The RRs were 1.00 (95% CI: 0.87-1.14) for a mRS score of 0-2 (Figure 2) and 0.79 (95% CI: 0.44-1.44) for stroke or other vascular events. The pooled RRs for symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage and parenchymal hematoma were 1.09 (95% CI: 0.73-1.63) and 0.84 (95% CI: 0.48-1.47), respectively.
Conclusions: Results were inconclusive due to small sample sizes. Currently, there is insufficient data to support the addition of argatroban to standard of care for the treatment of AIS. Evidence from available trials in this area supports the conduct of larger trials to determine the clinical value of argatroban.
More abstracts on this topic:
Xu Xiaohong, Preeti Preeti, Yu Ruoying, Shaykhalishahi Hamed, Zhang Cheng, Shen Chuanbin, Li Bei, Tang Naping, Chang Yan, Xiang Qian, Cui Yimin, Lei Xi, Ni Heyu, Zhu Guangheng, Liu Zhenze, Hu Xudong, Slavkovic Sladjana, Neves Miguel, Ma Wenjing, Xie Huifang
A Fecal-Derived Commensal Bacterium BM109 Reduces Infarct Size and Neurological Deficits in an Ischemic Stroke Rat ModelYoon Chung Eun, Kim You Bin, Nam Hyo Suk
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.