Final ID: TP31
Intranasal treatment targeting the brain endothelin system attenuates cognitive decline in diabetic rats after ischemic injury
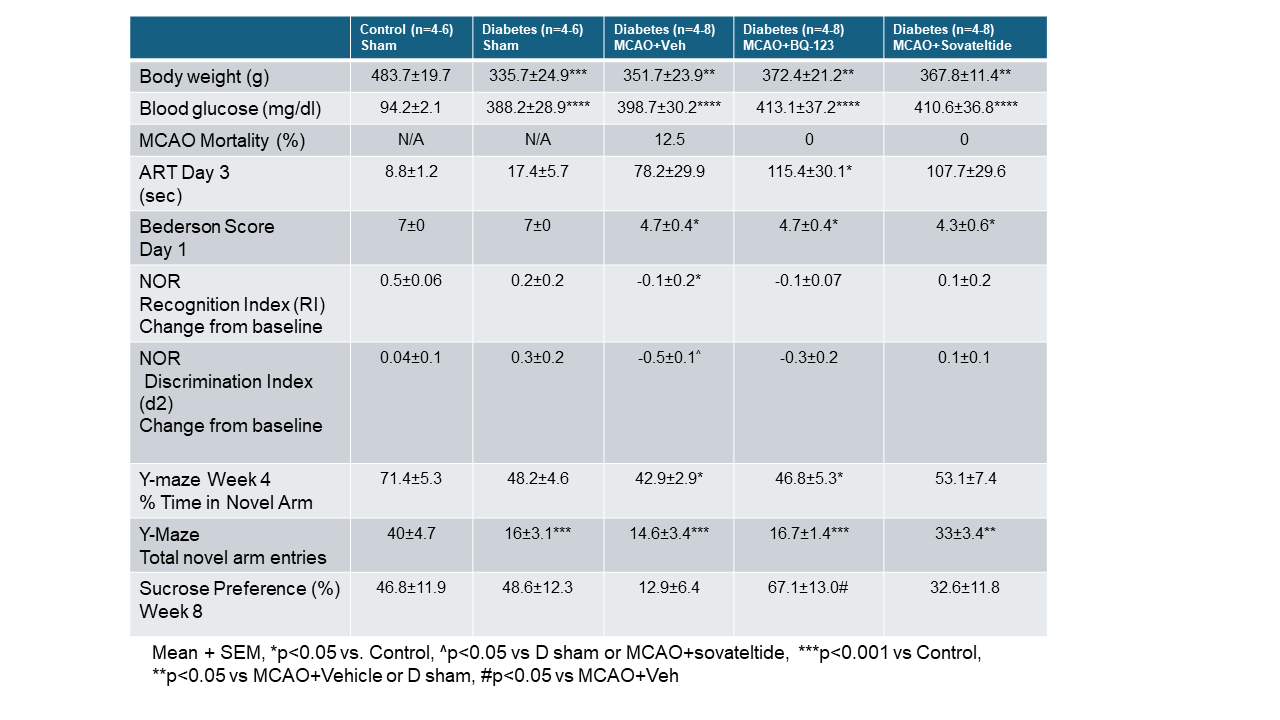
Abstract Body: Diabetes increases the risk of Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Impairment & Dementia (VCID) and stroke further amplifies this effect. Diabetes also dysregulates the Endothelin (ET) system. Elevated brain ET-1 levels correlate with tissue perfusion status and disease severity in patients with ADRD. There is emerging evidence that ETB receptor agonism improves outcomes in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke, but long-term effects, especially in diabetes, are unknown. Therefore, we hypothesized that intranasal treatment with ETA antagonist or ETB agonist will improve sensorimotor/cognitive outcomes in diabetic animals after ischemic stroke. Methods: We used a post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) model of VCID. Male rats underwent 60-min middle cerebral artery occlusion surgery (MCAO) 8 weeks after diabetes onset. Rats that met the preset inclusion criteria (adhesive removal time > 35 sec. and either a modified Bederson score <= 6 on Day 1 or weight loss > 10% on Day 3) were randomized to ETA antagonist BQ-123 (3 µg/100 µl PBS), ETB agonist Sovateltide (5 µg/kg), or vehicle intranasal treatment for 3 days per week until 8 weeks post-stroke (n=6-8). Sensorimotor and cognitive outcomes were monitored for 8 weeks. Results (Table 1): Behavior indices from the novel object recognition (NOR) test and Y-Maze test showed that diabetic rats developed cognitive deficits even in the sham group. Sovateltide improved both recognition memory and working spatial memory after stroke. BQ-123 partially prevented the decline in recognition memory. Animals treated with BQ-123 showed an improvement in depressive symptoms after stroke. Conclusions: These results suggest that intranasal stimulation of brain ETB receptors or ETA receptor inhibition can prevent the development of progressive cognitive decline after stroke. While further studies are required to better understand how the brain ET system impacts stroke recovery in diabetes, our findings provide novel insights into potential neuroprotective therapies for VCID.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acetylation of Electron Transfer Flavoprotein Alpha Is a Possible Regulatory Mechanism of Fatty Acid Oxidation in Diabetic Hearts
Tatekoshi Yuki, Yano Masaki, Hosoda Ryusuke, Saga Yukika, Kuno Atsushi
Neuronal Degradation Biomarkers Are Associated with Neurocognitive Decline and Recovery After Cardiac SurgeryKaushik Himanshu, Kanuparthy Meghamsh, Mozaffarian Dariush, Marchioli Roberto, Sellke Frank
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)