Final ID: TP49
Establishing a Cell Type-Specific Extracellular Vesicle Isolation Workflow For Improved Biomarker Discovery
Abstract Body: Background
Small vessel cerebral vascular disease (sCVD) is common to older individuals, often asymptomatic, but associated with incident stroke and future mortality. Multiple mechanisms for sCVD have been postulated, all of which include injury to the neurovascular unit. Analysis of extracellular vesicles (EVs), important constituents of the intercellular communication pathway, may offer new ways to evaluate pathological processes of sCVD as well as serve as novel biomarkers or identify new avenues for therapy. This abstract summarizes work by our group to subtype EVs and measure cargo proteins from the various cell types of the neurovascular unit from a group of cognitively normal individuals with a spectrum of sCVD.
Method
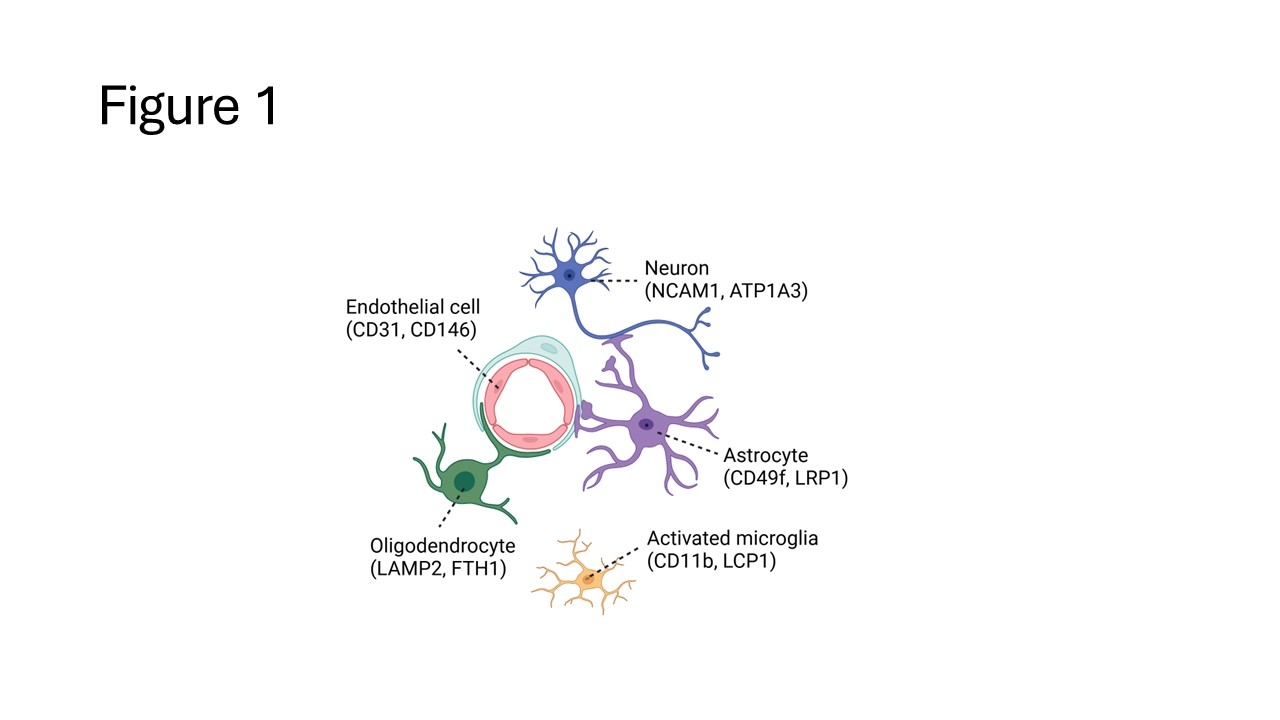
Study participants consisted of 14 individuals, 50 % female, 76 + 7 years of age, having 17.6 + 1.9 years of education. White matter hyperintensities varied from 0.73 – 38.8 cc. EV isolation used an Exodus ultrafiltration system on platelet depleted plasma. EVs were further fractionated into EV subtypes with resin-conjugated antibodies against cell type-specific markers. Five EV subtypes were isolated by two rounds of immunoprecipitation with the following markers: NCAM1/ATP1A3 (excitatory neuron EV), CD49f/LRP1 (astrocyte EV), CD11b/LCP1 (activated microglia EV), LAMP2/FTH1 (oligodendrocyte EV), CD31/CD146 (activated endothelial EV). Following isolation of EV subtypes, samples were characterized for purity and yield by nanoparticle tracking analysis, imaged for protein expression by super resolution microscopy, and sequenced for biomarker identification by quantitative proteomics.
Results
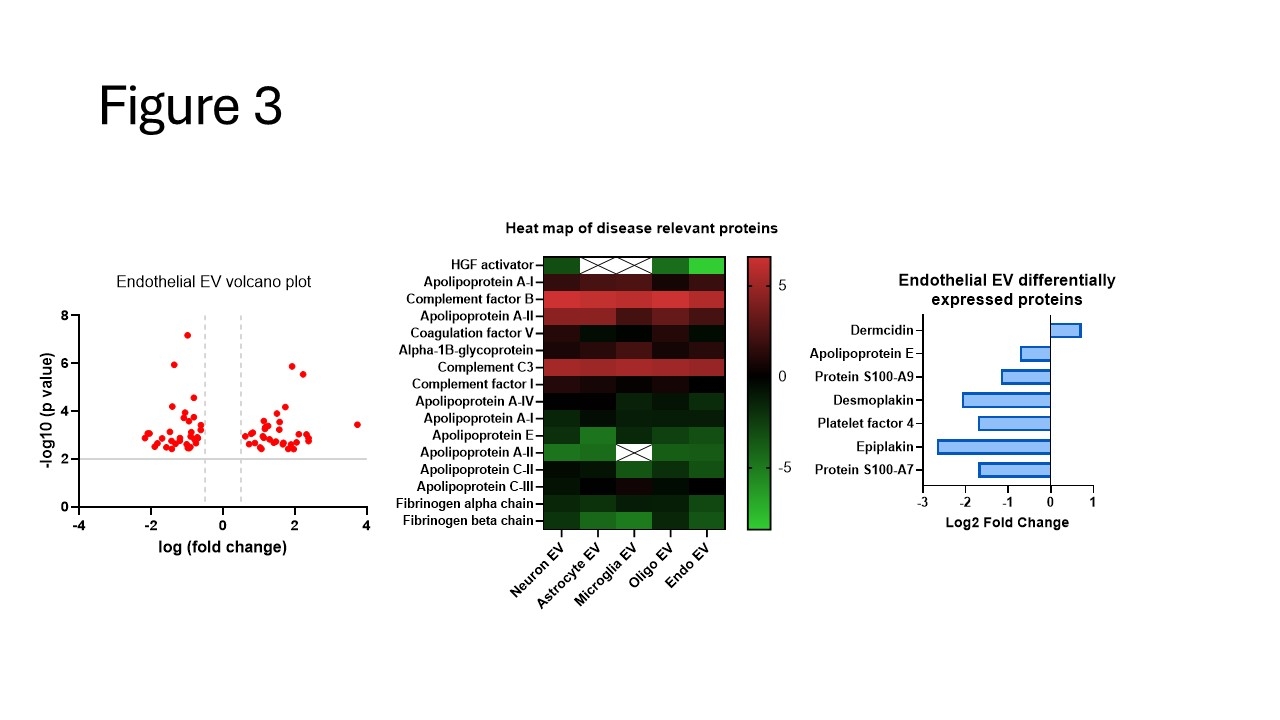
Nanoparticle tracking analysis confirmed high yields of all 5 EV subtypes, > 2E9 EVs/mL, along with identical size and surface charge profiles. Super resolution microscopy showed consistent canonical EV marker distributions on all EVs while EV subtypes expressed unique markers based off their cell type of origin. Quantitative proteomics identified 400 unique and differentially expressed proteins present amongst the various EV subtypes as compared to mean plasma EVs concentrations. Protein abundance varied widely across EV subpopulations, indicating distinct protein profiles.
Conclusion:
Preliminary results confirm the potential for biomarker discovery from novel EV subpopulations through identification of differentially expressed cargo proteins from the neurovascular unit. Future work will associate these findings with sCVD phenotypes.
Small vessel cerebral vascular disease (sCVD) is common to older individuals, often asymptomatic, but associated with incident stroke and future mortality. Multiple mechanisms for sCVD have been postulated, all of which include injury to the neurovascular unit. Analysis of extracellular vesicles (EVs), important constituents of the intercellular communication pathway, may offer new ways to evaluate pathological processes of sCVD as well as serve as novel biomarkers or identify new avenues for therapy. This abstract summarizes work by our group to subtype EVs and measure cargo proteins from the various cell types of the neurovascular unit from a group of cognitively normal individuals with a spectrum of sCVD.
Method
Study participants consisted of 14 individuals, 50 % female, 76 + 7 years of age, having 17.6 + 1.9 years of education. White matter hyperintensities varied from 0.73 – 38.8 cc. EV isolation used an Exodus ultrafiltration system on platelet depleted plasma. EVs were further fractionated into EV subtypes with resin-conjugated antibodies against cell type-specific markers. Five EV subtypes were isolated by two rounds of immunoprecipitation with the following markers: NCAM1/ATP1A3 (excitatory neuron EV), CD49f/LRP1 (astrocyte EV), CD11b/LCP1 (activated microglia EV), LAMP2/FTH1 (oligodendrocyte EV), CD31/CD146 (activated endothelial EV). Following isolation of EV subtypes, samples were characterized for purity and yield by nanoparticle tracking analysis, imaged for protein expression by super resolution microscopy, and sequenced for biomarker identification by quantitative proteomics.
Results
Nanoparticle tracking analysis confirmed high yields of all 5 EV subtypes, > 2E9 EVs/mL, along with identical size and surface charge profiles. Super resolution microscopy showed consistent canonical EV marker distributions on all EVs while EV subtypes expressed unique markers based off their cell type of origin. Quantitative proteomics identified 400 unique and differentially expressed proteins present amongst the various EV subtypes as compared to mean plasma EVs concentrations. Protein abundance varied widely across EV subpopulations, indicating distinct protein profiles.
Conclusion:
Preliminary results confirm the potential for biomarker discovery from novel EV subpopulations through identification of differentially expressed cargo proteins from the neurovascular unit. Future work will associate these findings with sCVD phenotypes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Signature of Advanced Cardiac and Vascular Aging Defines Elevated Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
Perera Sudheesha, Biswas Dhruva, Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Coppi Andreas, Khera Rohan
AHA Life's essential 8 and ideal cardiovascular health among adult swimmersTiozzo Eduard, Henley Cynthia, Jones Caroline, Perry Fredrick, Viscovich Isabella, Johnson Giana, Gardener Hannah, Yu Kerstin
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)