Final ID: 106
Streptococcus anginosus Enrichment in the Gut is a Feature of Stroke and a Predictor of Poor Prognosis
Several cross-sectional studies have implicated gut dysbiosis caused by an abundance of oral commensals in cardiovascular diseases. However, no previous studies have identified oral pathobiont in the gut of acute stroke patients and longitudinally investigated their clinical relevance.
Objective
This study aims to identify key oral pathobionts that induce gut dysbiosis in stroke patients and longitudinally assess the relationship between oral pathobionts in the gut and poor prognosis following stroke.
Methods
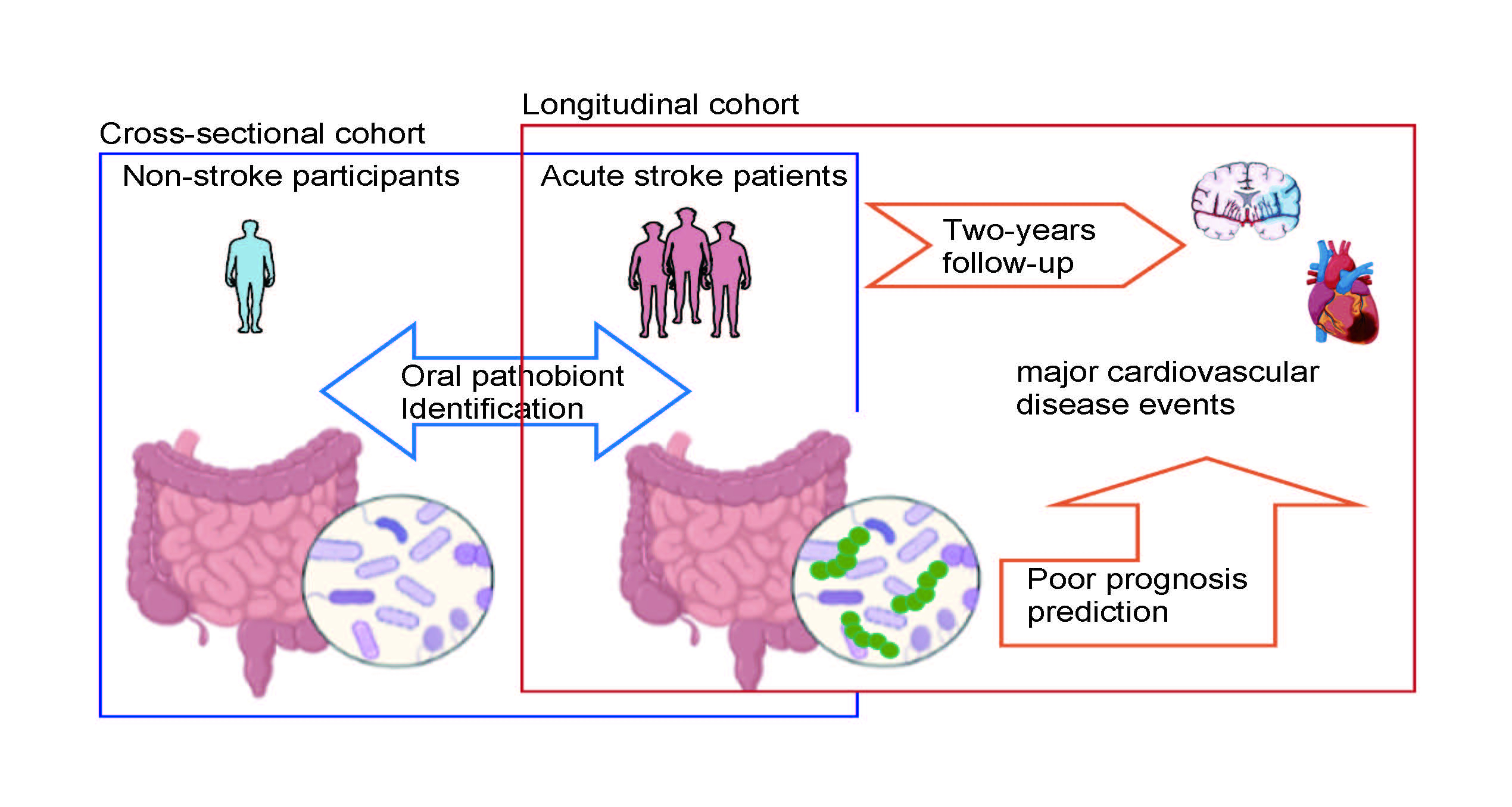
We comprehensively analyzed the 364 salivary and gut microbiomes from 189 acute stroke patients and 55 non-stroke participants from July 2020 to July 2021. Furthermore, we prospectively observed composite outcomes of mortality and cardiovascular events over a 2-year follow-up period.
Results
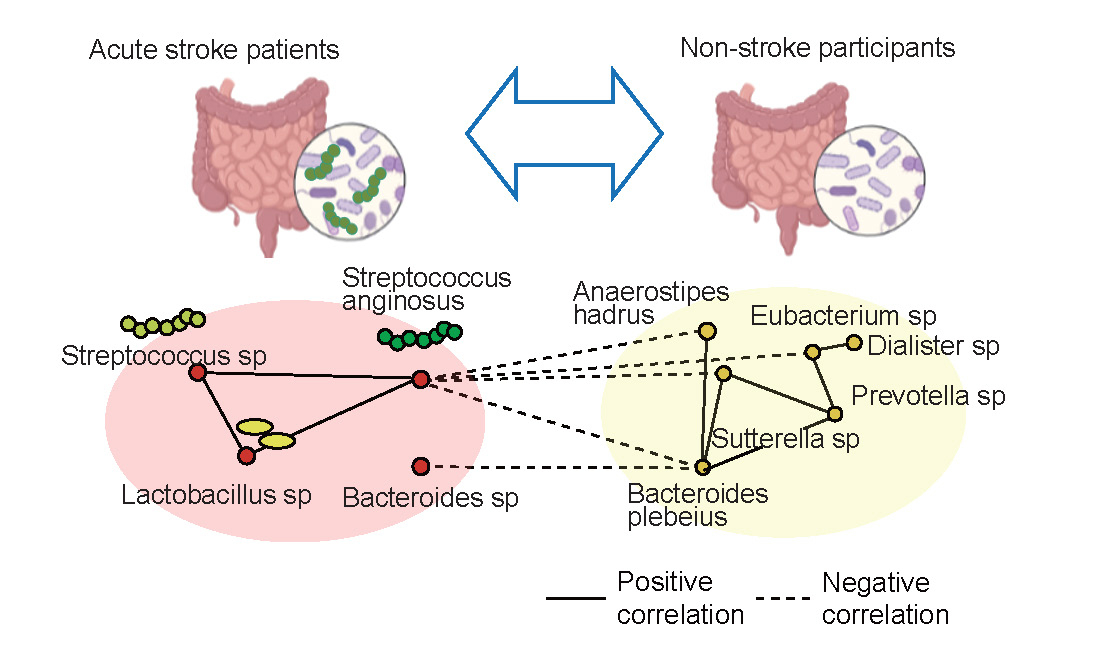
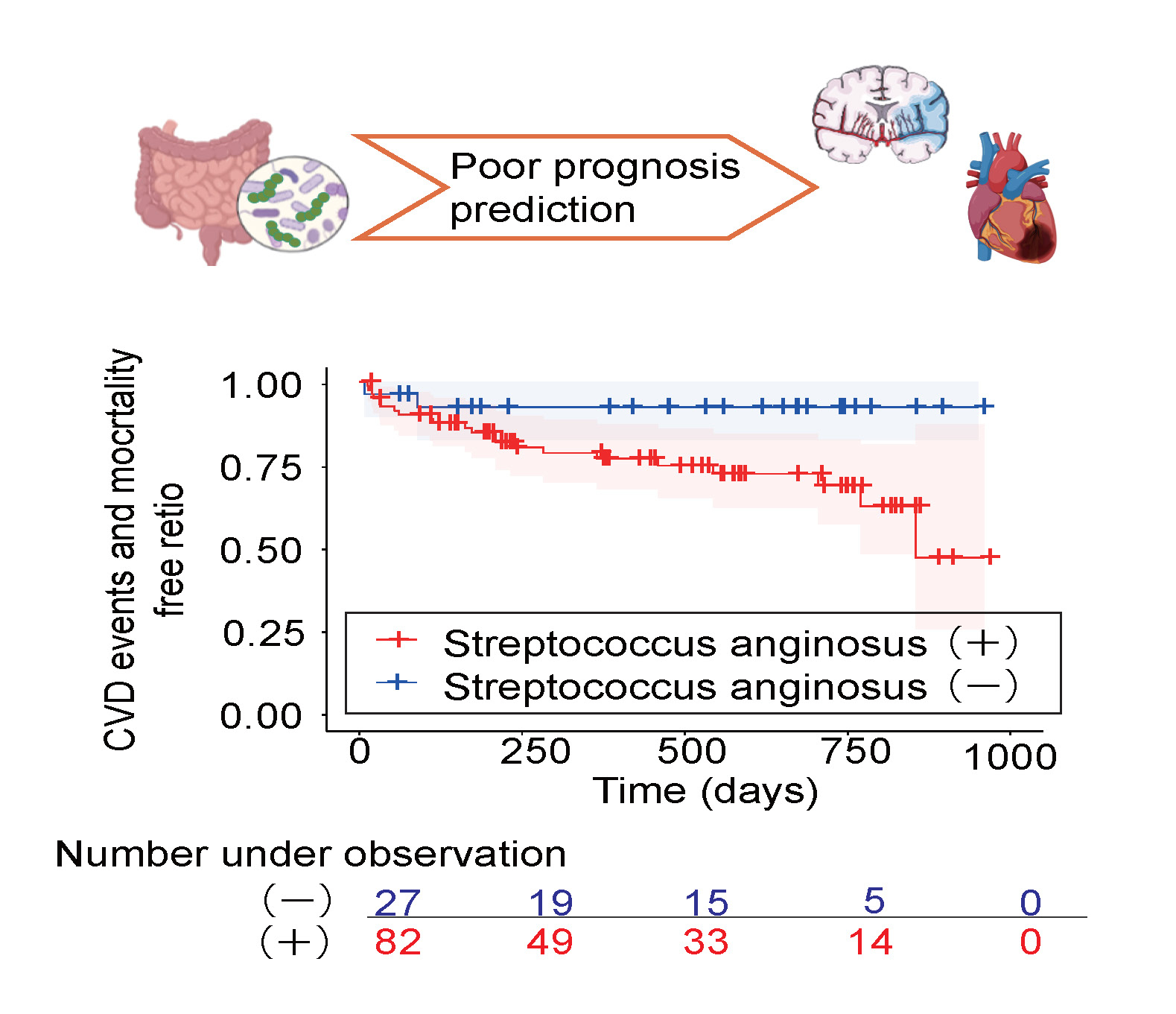
Streptococcus anginosus was significantly more abundant in both the saliva (median [IQR], 0.01 [0.00–0.14] vs. 0.00 [0.00–0.03], p=0.02) and gut (0.09 [0.00–0.28] vs. 0.00 [0.00–0.02], p<0.001) in stroke compared to non-stroke counterparts. Microbial co-occurrence network analysis revealed that Streptococcus anginosus is a central hub in gut dysbiosis. After adjusting for vascular risks, Streptococcus anginosus (odds ratio 1.20, 95% confidence interval 1.06–1.36, p<0.01), Anaerostipes hadrus (0.82, [0.73–0.93], p<0.01), and Bacteroides plebeius (0.86, [0.86–0.93], p=0.01) in the gut were independent predictors of stroke. Longitudinally, Streptococcus anginosus in the gut was significantly associated with increased mortality and major cardiovascular events (p=0.04; log-rank test), whereas Anaerostipes hadrus and Bacteroides plebeius were not (p=0.45 and p=0.19).
Conclusions:
Streptococcus anginosus in the gut was identified as an oral pathobiont in gut dysbiosis and was independently associated with a higher risk of mortality and major cardiovascular events in stroke patients. Our findings suggest that Streptococcus anginosus may serve as a novel biomarker for predicting stroke and poor outcomes following stroke, highlighting its potential as a target for therapeutic intervention.
More abstracts on this topic:
Nishioka Norihiro, Kiguchi Takeyuki, Makino Yuto, Ninomiya Kouhei, Kamo Wataru, Kamada Tsuyoshi, Maeda Hideki, Iwami Taku
A machine learning approach to classifying ischemic stroke etiology using variables available in the Get-with-the-Guidelines Stroke RegistryLee Ho-joon, Schwamm Lee, Turner Ashby, De Havenon Adam, Kamel Hooman, Brandt Cynthia, Zhao Hongyu, Krumholz Harlan, Sharma Richa
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.