Final ID: WMP13
Cardiac Injury Potentially Contributes to Neuroinflammation via Extracellular Vesicles
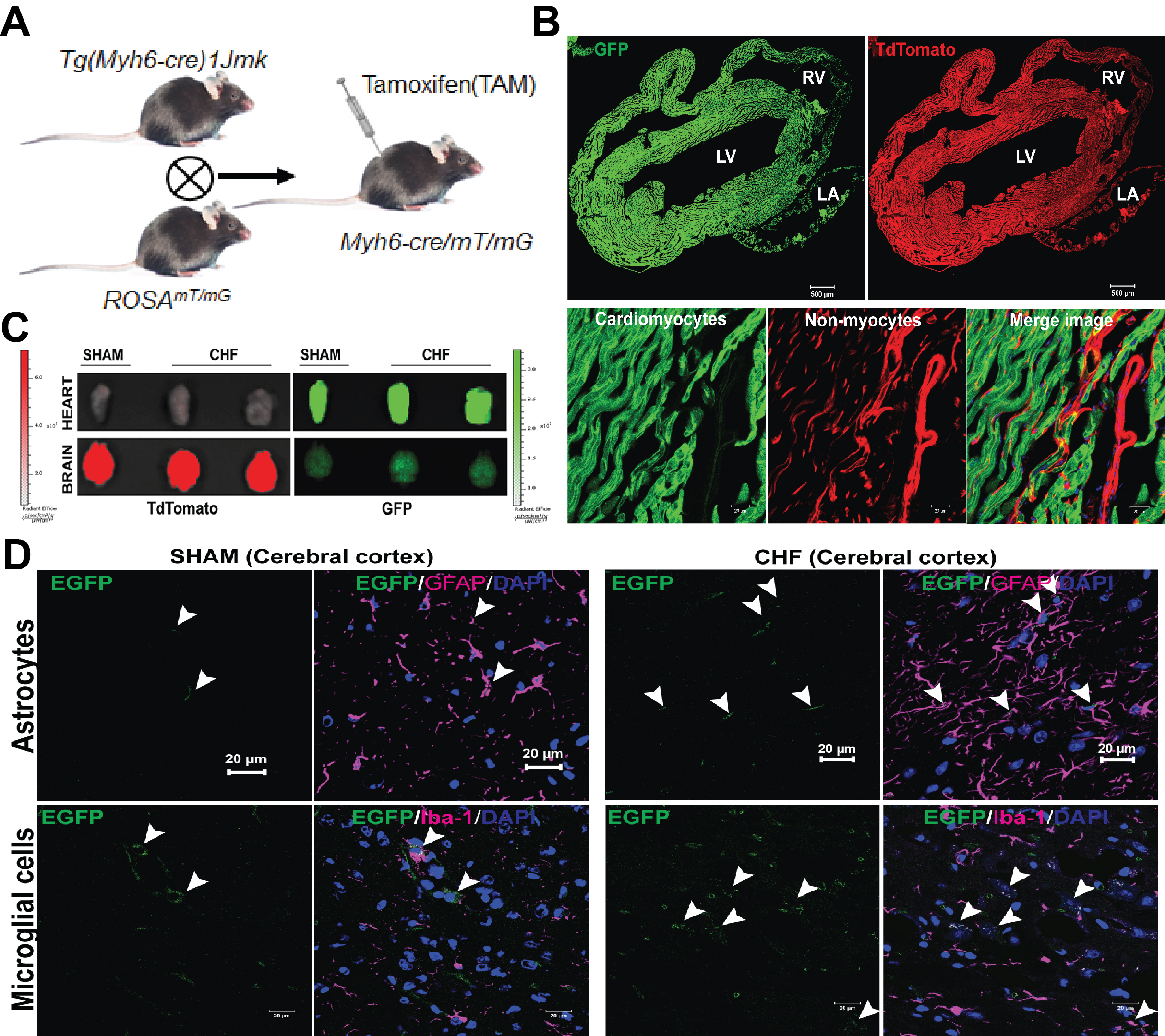
To elucidate the potential effects of myocardial injury on the CGI and the underlying mechanism by which cardiac damage regulates brain dysfunction, we employed a rodent model of myocardial infarction (MI) generated by left coronary artery ligation and a cardiac-specific GFP+ Tg reporter mouse model to track the brain distribution of cardiac extracellular vesicles (EVs), combining in vitro imaging, cellular and molecular techniques. Here we demonstrate crosstalk between heart and brain via EVs, and glial cell uptake of GFP+ cardiac EVs (See Figure). Importantly, myocardial injury not only promotes the brain distribution of cardiac EVs, but also elicits a neuroinflammatory response in vitro and in vivo. Further molecular studies suggests that cardiac EVs are abundant with miR-21-5p, which was selectively upregulated in cardiac cells in the post-MI model and transported by EVs. We also confirmed that miR-21-5p overexpression in vitro caused a pro-inflammatory response in brain microglia.
Taken together these observations indicate that weeks following MI, cardiac-secreted EVs abundant with miRNAs communicate with the brain and are associated with microglial activation, which may be responsible for neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity leading to cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Myocardial injury; Cardiogenic dementia; Neuroinflammation; Extracellular vesicles; microRNAs
Funding source: This work was supported by the National Institution of Health R01HL153176 (IZ/CT); American Heart Association (AHA) Career Development Award (19CDA34520004) and AHA Transformational Program Award (https://doi.org/10.58275/AHA.24TPA1300008.pc.gr.198448) to CT.
More abstracts on this topic:
Zarate Sara, Vissa Udaykiran, Santner Ava, Kelly Olivia, Reasonover Samantha, Santisteban Monica
Association between Age and the Change in Cognition after Stroke- A Pooled Cohort Analysis of ARIC, REGARDS, and FOSSpringer Mellanie, Gottesman Rebecca, Hayward Rodney, Howard Virginia, Koton Silvia, Lazar Ronald, Sussman Jeremy, Ye Wen, Levine Deborah, Chen Bingxin, Whitney Rachael, Briceno Emily, Gross Alden, Aparicio Hugo, Beiser Alexa, Burke James, Giordani Bruno
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.