Final ID: 51
Efficacy of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Prevention of Stroke among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Heart Failure, or Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of 12 Randomized Controlled Trials.
Background
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have shown a reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, its efficacy on cerebrovascular events is yet to be well established, with conflicting results to date.
Objective
We sought to evaluate the efficacy of GLP-1 RAs on stroke risk among its different types in patients with T2DM, heart failure, or obesity.
Methods
We performed a systematic literature search on PubMed, EMBASE, and ClinicalTrials.gov for relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs) from inspection until June 30th, 2024, without any language restrictions. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were pooled using a random-effect model, and a p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
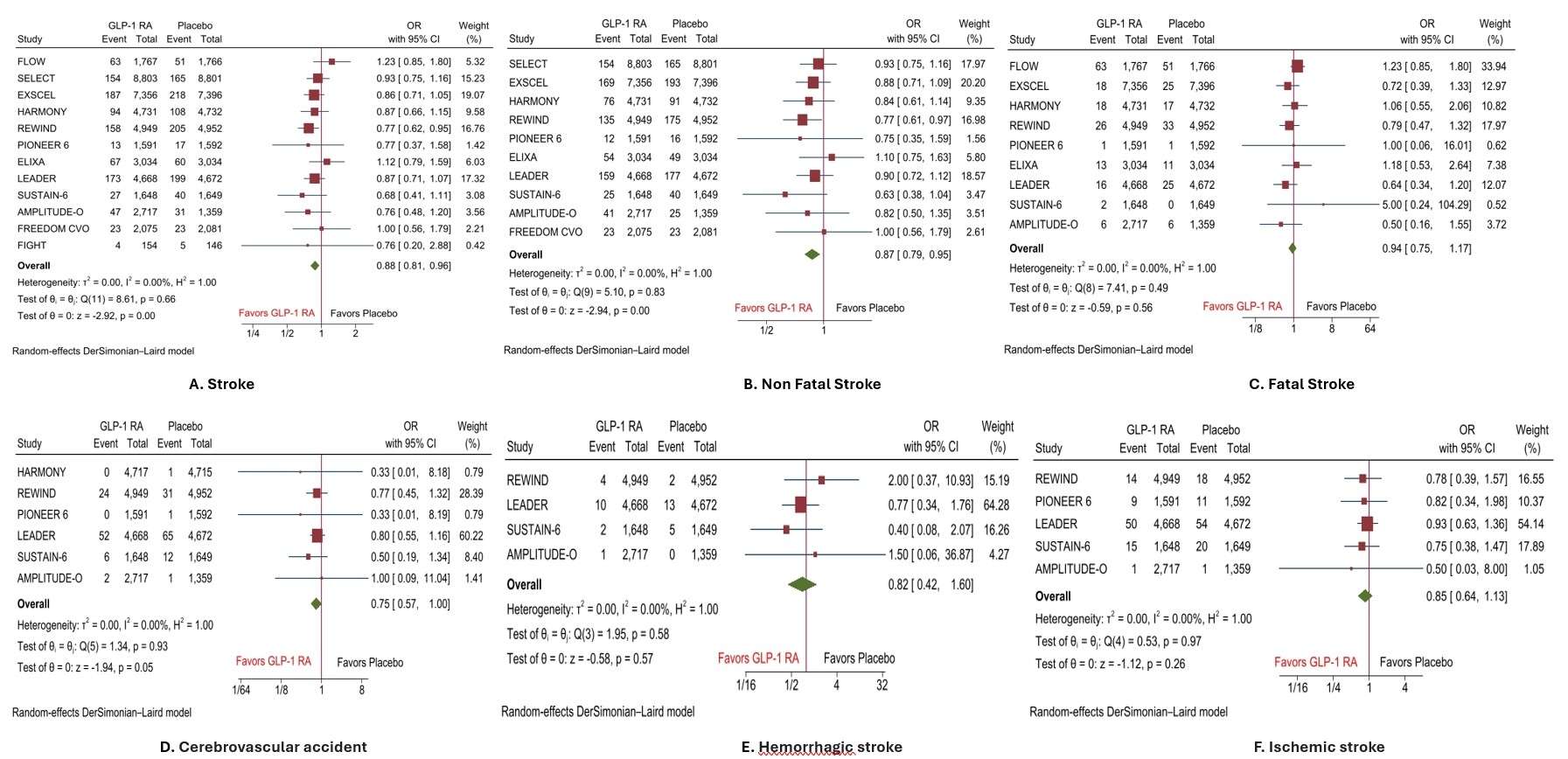
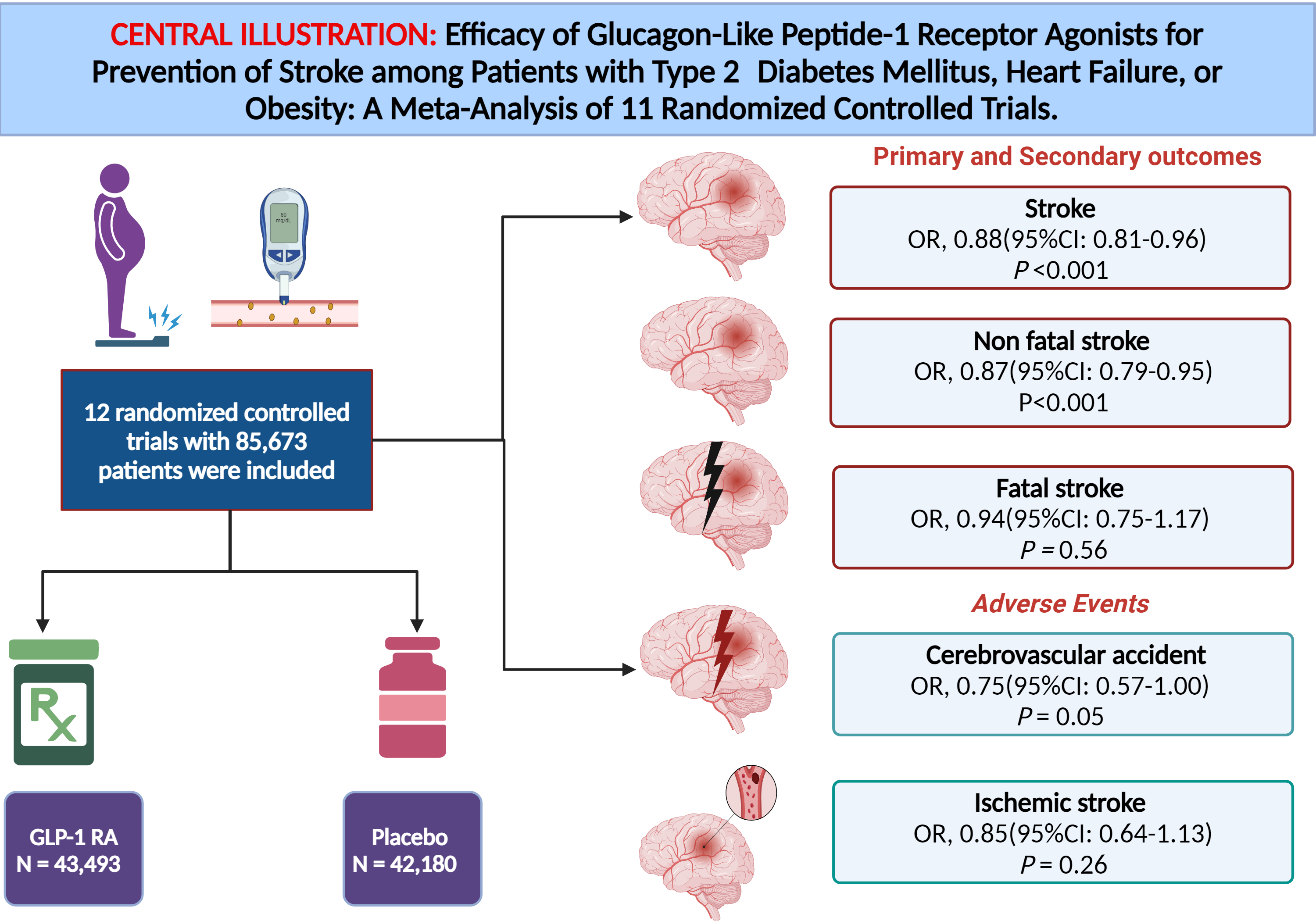
A total of 12 RCTs with 85,673 patients (43,493 in GLP-1 RAs and 42,180 in the placebo group) were included in the analysis. The mean age of the patients in GLP-1 RAs and the placebo groups was 63.5 and 63.1 years, respectively. Pooled analysis of primary and secondary endpoints showed that GLP-1 RAs significantly reduced the risk of incidence of stroke by 12% (OR, 0.88(95%CI: 0.81-0.96), P<0.001), and nonfatal stroke by 13% (OR, 0.87(95%CI: 0.79-0.95), P<0.001) compared with placebo. However, the risk of fatal stroke (OR, 0.94(95%CI: 0.75-1.17), P=0.56) was comparable between both groups of patients. Similarly, the risk of serious adverse events such as cerebrovascular accident (OR, 0.75(95%CI: 0.57-1.00), P=0.05), hemorrhagic stroke (OR, 0.82(95%CI: 0.42-1.60), P=0.57, and ischemic stroke (OR, 0.85(95%CI: 0.64-1.13), P=0.26) was comparable between GLP-1RAs and placebo.
Conclusion
GLP-1 RAs therapy was associated with an overall reduction in the risk of stroke and nonfatal stroke in T2DM and/or heart failure or obese patients. However, no such effect was observed for fatal stroke.
More abstracts on this topic:
O'connor Meaghan, Loughlin Anita, Waldman Laura, Rucker Sloan, Vaghela Shailja, Kwon Namhee, Sikirica Vanja
Ability of Composite Magnetic Resonance Brain Imaging Scores to Predict Functional Outcomes in Survivors of Cardiac ArrestNguyen Thuhien, Town James, Wahlster Sarah, Johnson Nicholas, Poilvert Nicolas, Lin Victor, Ukatu Hope, Matin Nassim, Davis Arielle, Taylor Breana, Thomas Penelope, Sharma Monisha
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.