Final ID: TAC286
Trends and disparities in U.S. Mortality among individuals with coexisting Hypertensive Disease and Renal Failure: A 22-Year Retrospective Analysis(1999-2020)
Abstract Body:
Background: Hypertension and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are closely interlinked conditions that contribute significantly to accelerated cardiovascular risk and high mortality rates. Over the past two decades, shifts in disease prevalence and expanding treatment options have influenced population-level outcomes.This study examines 22-year trends and disparities in U.S. deaths associated with this comorbidity.
Methods: We analyzed CDC WONDER mortality data from 1999–2020 for individuals ≥45 years with hypertensive disease (ICD-10: I10–I15) as a multiple cause and renal failure (ICD-10: N17–N19) as the underlying cause of death. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) per 100,000 were calculated using the 2000 U.S. Standard Population. Joinpoint regression estimated annual percent changes (APC) and average annual percent changes (AAPC), stratified by sex, race/ethnicity, age, region, and urbanization.
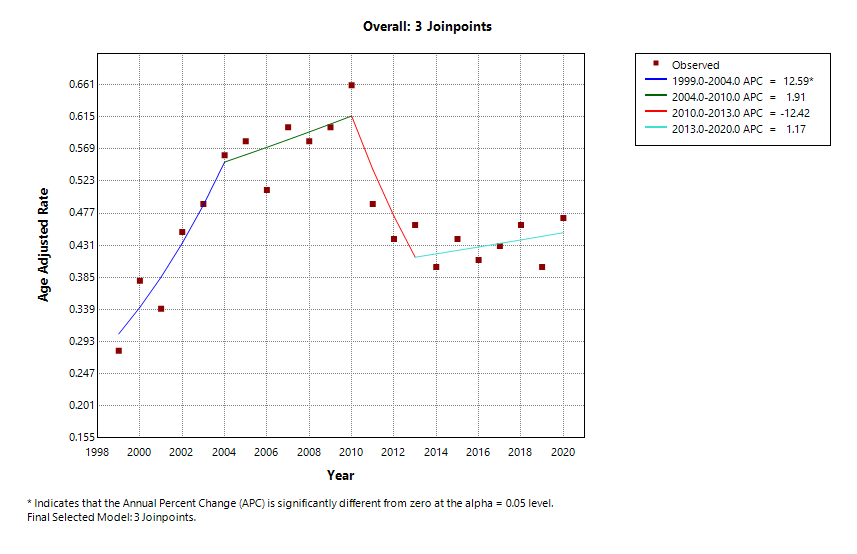
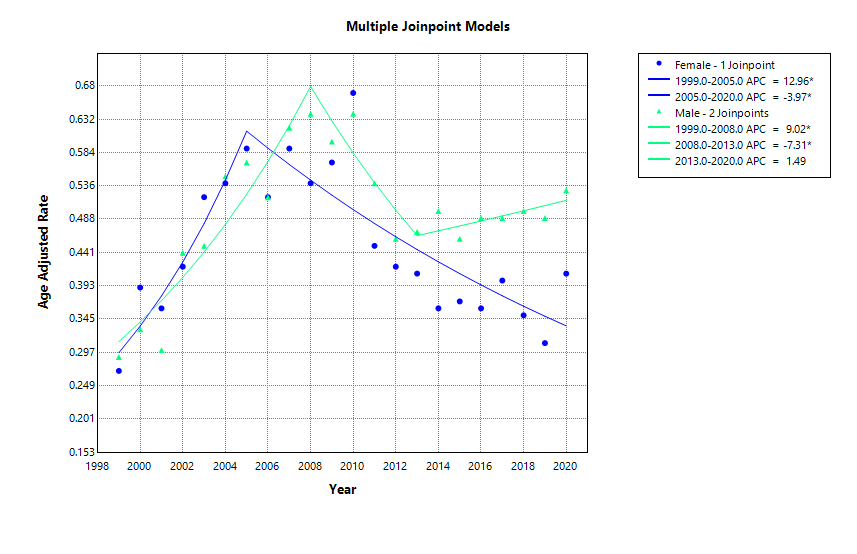
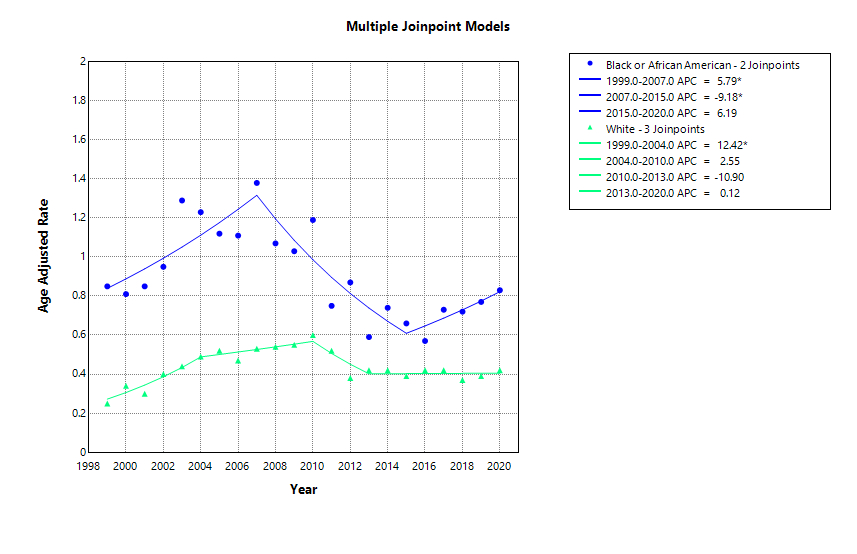
Results: There were 12,212 deaths due to hypertensive renal failure (HTN-RF). The overall AAMR modestly increased (AAPC: +1.87%; 95% CI: –1.49 to 5.36; P = 0.28), with distinct phases: sharp rise (APC: +12.6%, 1999–2004), slower increase (APC: +1.9%, 2004–2010), significant decline (APC: –12.4%, 2010–2013; P < 0.05), and stabilization (APC: +1.2%, 2013–2020). Males had higher AAMRs than females and a slight late increase (APC: +1.5%, 2013–2020). Female mortality declined significantly (APC: –4.0%, 2005–2020; P < 0.05). Black individuals had the highest AAMRs (0.86) and a recent rise (APC: +6.2%, 2015–2020), while White individuals showed stable rates (APC: +0.1%, 2013–2020). In those aged ≥85, an early rise was followed by decline post-2004. The Northeast showed a non-significant decrease (AAPC: –0.58%; 95% CI: –3.18 to 2.09; P = 0.67), and the Midwest had a modest rise (AAPC: +1.30%; 95% CI: –1.88 to 4.59; P = 0.43). Rural areas saw an early spike (APC: +14.9%, 1999–2005; P < 0.05), then a decline (APC: –1.6%, 2005–2020; P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Mortality from coexisting hypertensive disease and renal failure showed complex trends, with stabilization after a mid-period peak. Persistent disparities by sex, race, and region highlight the need for targeted public health efforts.
Background: Hypertension and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are closely interlinked conditions that contribute significantly to accelerated cardiovascular risk and high mortality rates. Over the past two decades, shifts in disease prevalence and expanding treatment options have influenced population-level outcomes.This study examines 22-year trends and disparities in U.S. deaths associated with this comorbidity.
Methods: We analyzed CDC WONDER mortality data from 1999–2020 for individuals ≥45 years with hypertensive disease (ICD-10: I10–I15) as a multiple cause and renal failure (ICD-10: N17–N19) as the underlying cause of death. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) per 100,000 were calculated using the 2000 U.S. Standard Population. Joinpoint regression estimated annual percent changes (APC) and average annual percent changes (AAPC), stratified by sex, race/ethnicity, age, region, and urbanization.
Results: There were 12,212 deaths due to hypertensive renal failure (HTN-RF). The overall AAMR modestly increased (AAPC: +1.87%; 95% CI: –1.49 to 5.36; P = 0.28), with distinct phases: sharp rise (APC: +12.6%, 1999–2004), slower increase (APC: +1.9%, 2004–2010), significant decline (APC: –12.4%, 2010–2013; P < 0.05), and stabilization (APC: +1.2%, 2013–2020). Males had higher AAMRs than females and a slight late increase (APC: +1.5%, 2013–2020). Female mortality declined significantly (APC: –4.0%, 2005–2020; P < 0.05). Black individuals had the highest AAMRs (0.86) and a recent rise (APC: +6.2%, 2015–2020), while White individuals showed stable rates (APC: +0.1%, 2013–2020). In those aged ≥85, an early rise was followed by decline post-2004. The Northeast showed a non-significant decrease (AAPC: –0.58%; 95% CI: –3.18 to 2.09; P = 0.67), and the Midwest had a modest rise (AAPC: +1.30%; 95% CI: –1.88 to 4.59; P = 0.43). Rural areas saw an early spike (APC: +14.9%, 1999–2005; P < 0.05), then a decline (APC: –1.6%, 2005–2020; P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Mortality from coexisting hypertensive disease and renal failure showed complex trends, with stabilization after a mid-period peak. Persistent disparities by sex, race, and region highlight the need for targeted public health efforts.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age-, Sex- and/or Ethnic- specific disparities; Biventricular systolic and diastolic strain, and biomarker, prognostic implications in Acute Tuberculous Pericarditis.
Matshela Mamotabo
A durable reduction in blood pressure by ultrasound renal denervation: A real-world, single center experienceKing Jordan, Gharib Wissam