Final ID: TH283
eGFR Status and Screening Parameters for Primary Aldosteronism
Abstract Body: Introduction: Plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC), plasma renin activity (PRA), and aldosterone renin ratio (ARR) are key parameters when screening patients for primary aldosteronism (PA). Concern exists about whether their values could be affected by a low estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), leading to missed diagnoses of PA in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Aim of Study: To examine the effect of eGFR on PAC, PRA, and ARR in PA patients, comparing those with a preserved eGFR vs. those with a reduced eGFR.
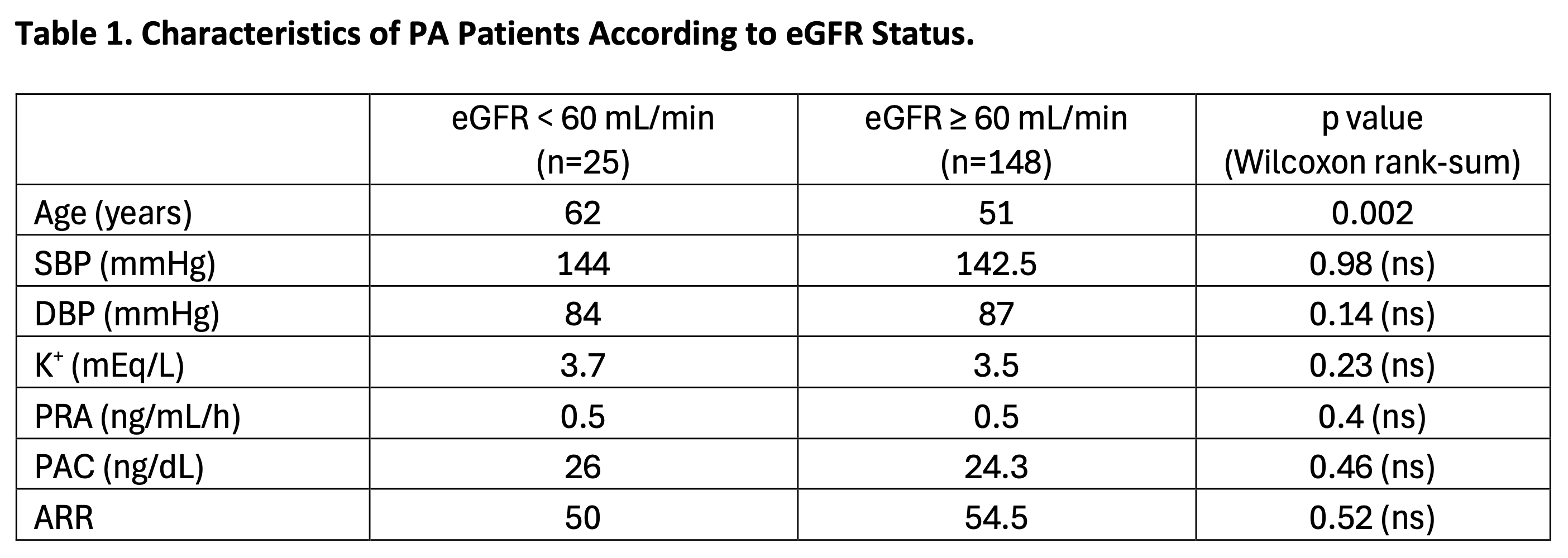
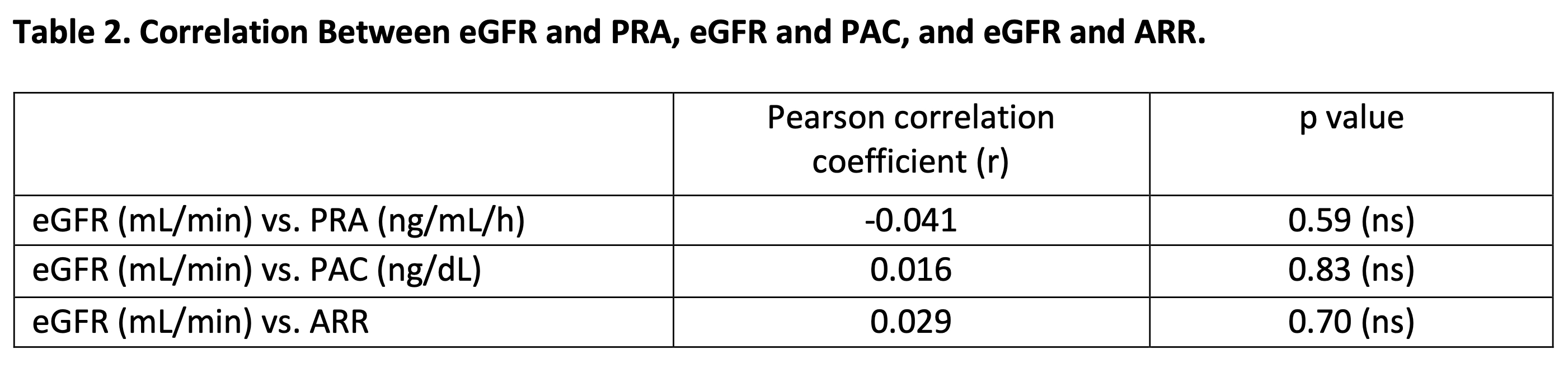
Methods: Retrospective review was conducted on 173 consecutive patients diagnosed with PA who underwent adrenal vein sampling at the University of Chicago between 2010-2024. Clinical and biochemical data extracted included age, gender, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), BMI, serum potassium level, serum creatinine, PRA, PAC, ARR, adrenal imaging (classified as one or more nodules, hyperplasia, or normal adrenals), and presence of comorbidities (cardiovascular disease [CVD], diabetes mellitus [DM], and/or obstructive sleep apnea [OSA]). eGFR was calculated using the 2021 CKD-EPI creatinine equation. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to compare median PAC, PRA, and ARR between those with a preserved eGFR (≥60 mL/min) vs. those with a reduced eGFR (<60 mL/min). Pearson correlation was used to explore the relationships between eGFR and PRA, eGFR and PAC, and eGFR and ARR.
Results: Mean age was 52.2 (±11.9) years. 93 (53.8%) were female. 80 (46.2%) were male. 148 (85.5%) had a preserved eGFR (≥60 mL/min). 25 (14.5%) had a reduced eGFR (<60 mL/min). 24 (13.9%) had history of CVD. 58 (33.5%) had history of DM. 77 (44.5%) had history of OSA. Mean BMI was 32.5 ± 7.0. Median SBP was 144 mmHg. Median DBP was 84 mmHg. Adrenal imaging showed one or more adrenal nodules in 141 (81.5%) patients, adrenal hyperplasia in 16 (9.2%) patients, and normal adrenals in 16 (9.2%) patients. Hypokalemia (serum K+ < 3.5 mEq/L) was noted in 66 (46.8%) patients with one or more adrenal nodules and 9 (56.2%) patients with adrenal hyperplasia.
Conclusions: PRA, PAC, ARR, and serum potassium levels did not differ significantly according to eGFR status. Overall, no significant correlation was detected between eGFR and PRA, eGFR and PAC, or eGFR and ARR. A relatively higher prevalence of hypokalemia was noted in patients with one or more adrenal nodules or adrenal hyperplasia, as compared to that generally reported in patients with PA.
Aim of Study: To examine the effect of eGFR on PAC, PRA, and ARR in PA patients, comparing those with a preserved eGFR vs. those with a reduced eGFR.
Methods: Retrospective review was conducted on 173 consecutive patients diagnosed with PA who underwent adrenal vein sampling at the University of Chicago between 2010-2024. Clinical and biochemical data extracted included age, gender, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), BMI, serum potassium level, serum creatinine, PRA, PAC, ARR, adrenal imaging (classified as one or more nodules, hyperplasia, or normal adrenals), and presence of comorbidities (cardiovascular disease [CVD], diabetes mellitus [DM], and/or obstructive sleep apnea [OSA]). eGFR was calculated using the 2021 CKD-EPI creatinine equation. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to compare median PAC, PRA, and ARR between those with a preserved eGFR (≥60 mL/min) vs. those with a reduced eGFR (<60 mL/min). Pearson correlation was used to explore the relationships between eGFR and PRA, eGFR and PAC, and eGFR and ARR.
Results: Mean age was 52.2 (±11.9) years. 93 (53.8%) were female. 80 (46.2%) were male. 148 (85.5%) had a preserved eGFR (≥60 mL/min). 25 (14.5%) had a reduced eGFR (<60 mL/min). 24 (13.9%) had history of CVD. 58 (33.5%) had history of DM. 77 (44.5%) had history of OSA. Mean BMI was 32.5 ± 7.0. Median SBP was 144 mmHg. Median DBP was 84 mmHg. Adrenal imaging showed one or more adrenal nodules in 141 (81.5%) patients, adrenal hyperplasia in 16 (9.2%) patients, and normal adrenals in 16 (9.2%) patients. Hypokalemia (serum K+ < 3.5 mEq/L) was noted in 66 (46.8%) patients with one or more adrenal nodules and 9 (56.2%) patients with adrenal hyperplasia.
Conclusions: PRA, PAC, ARR, and serum potassium levels did not differ significantly according to eGFR status. Overall, no significant correlation was detected between eGFR and PRA, eGFR and PAC, or eGFR and ARR. A relatively higher prevalence of hypokalemia was noted in patients with one or more adrenal nodules or adrenal hyperplasia, as compared to that generally reported in patients with PA.
More abstracts on this topic:
Angiotensin II vascular abnormalities in 32.5% of 3322 patients with essential hypertension(EH): Use of angiotensin II analogue, saralasin.
Anderson Gunnar
A Review Of The Burden, Management And Outcomes Of Patients With Aldosterone DysregulationLuan Shan, Agiro Abiy, Daniel Ian, Mckendrick Jan, Davis Harrison, Huang Joanna, Linganathan Karthik