Hypertension 2025 Scientific Sessions
/
Concurrent A: Vascular Biology
/
Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA Drives PANoptosis in the Perivascular Adipose Tissue Promoting Vascular Dysfunction in Mice Exposed to Chronic Stress
Final ID: 004
Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA Drives PANoptosis in the Perivascular Adipose Tissue Promoting Vascular Dysfunction in Mice Exposed to Chronic Stress
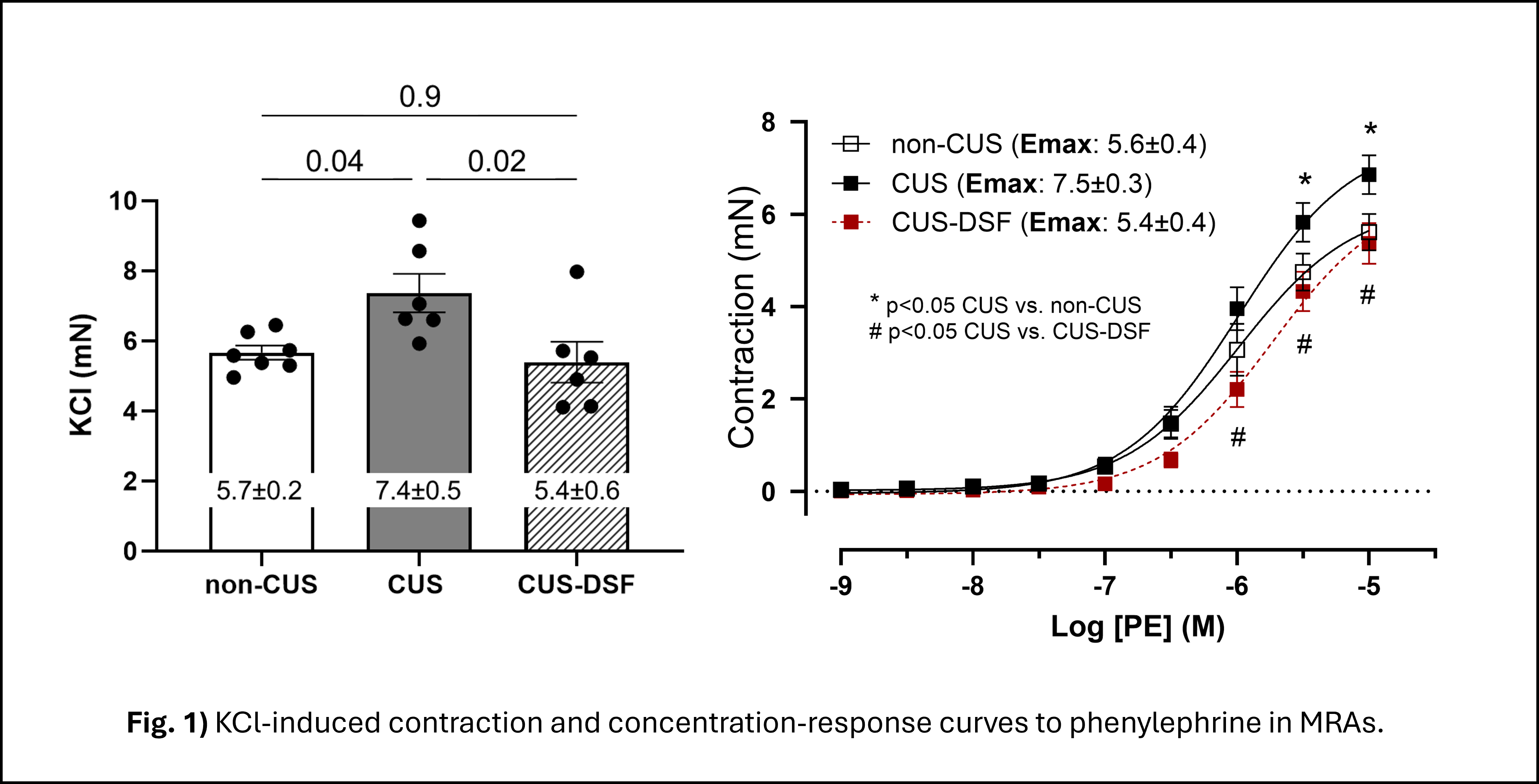
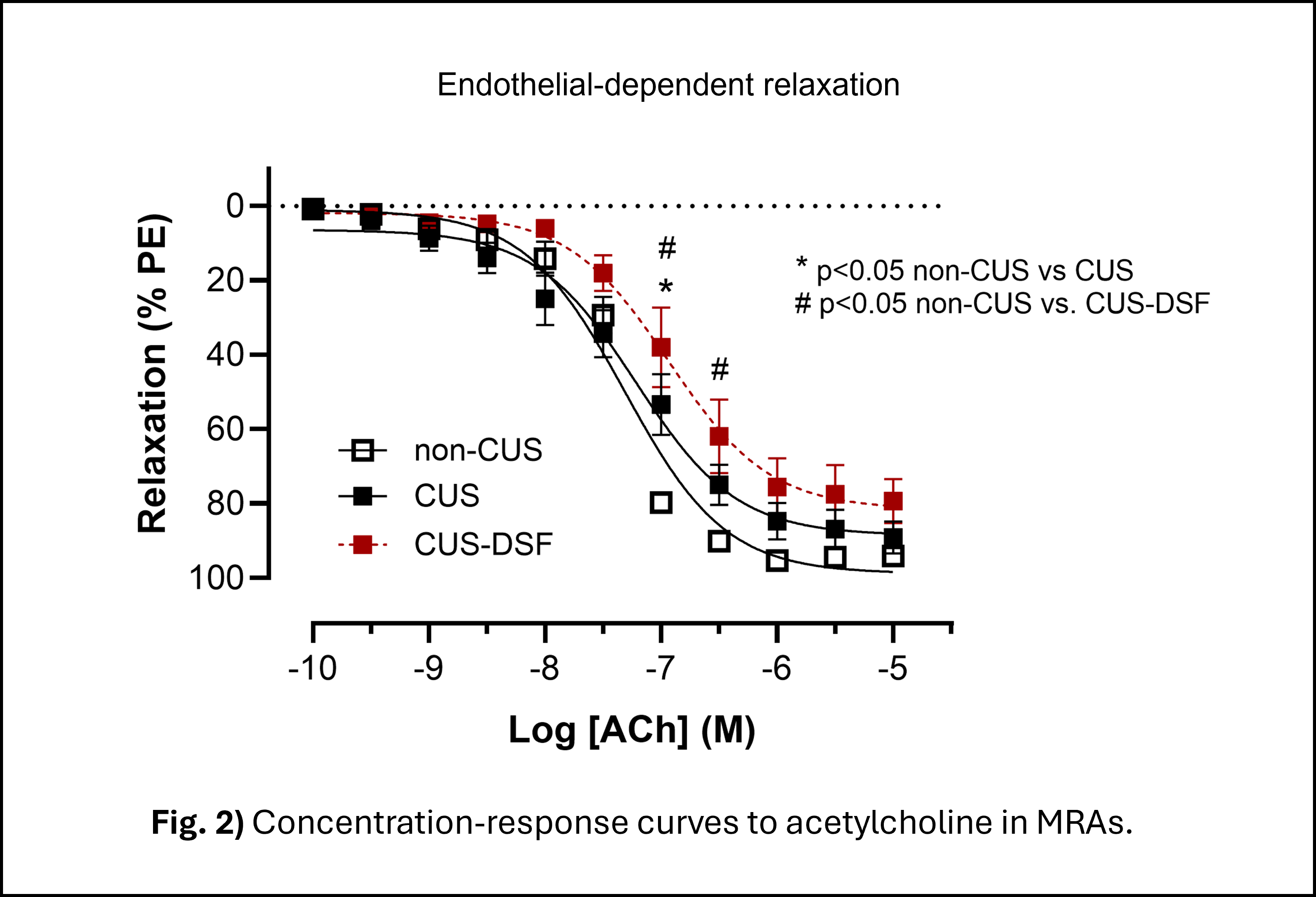
Abstract Body: Introduction: Chronic stress promotes mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) release via gasdermin D (GSDMD) driving inflammasome activation and vascular dysfunction. Absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) senses mtDNA and triggers PANoptosis via Z-DNA-binding protein 1 (ZBP1). We hypothesize that mtDNA drives PANoptosis, a novel type of coordinated lytic cell death, via AIM2 causing stress-induced vascular dysfunction. Methods: Male C57Bl/6 mice underwent 28 days of chronic unpredictable stress (CUS, n=6), and controls went weekly handling (non-CUS, n=6). Another CUS group (n=6) received a disulfiram-enriched diet, GSDMD inhibitor, during the protocol (CUS-DSF). Behavior was assessed by forced swim test (FST) and elevated plus maze (EPM). Following euthanasia, mesenteric resistance arteries (MRAs) were mounted in wire myograph to assess vascular reactivity. Concentration-response curves to phenylephrine and acetylcholine (1 nM–10 uM) were performed and maximal response (Emax) was obtained via non-linear regression. The perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) surrounding MRAs was collected to assess gene expression (RT-qPCR). Circulating mtDNA was measured in plasma via mtND1 expression. Group comparisons used Student’s t-test or two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc; data are mean ± SEM; significance at p<0.05. Results: Circulating mtDNA levels were elevated in CUS mice vs. non-CUS (fold change, 4±0.7 vs 1±0.5; p=0.003). CUS mice had lower latency to immobility in the FST vs. non-CUS (%, 32 ± 12 vs 111 ± 20; p=0.006) and DSF partially prevented this (%, 63±10; p=0.05). In the EPM, CUS mice spent less time in the open arms vs. non-CUS (%, 27±6 vs 47±8; p=0.04), which worsened in CUS-DSF (%, 13 ± 2; p=0.0003). In the vasculature, MRAs from CUS mice had increased KCl-induced contraction and higher Emax to phenylephrine, which was prevented by DSF (fig. 1). A displacement in the endothelium-dependent relaxation curve was observed in CUS, which was exacerbated in DSF-CUS (fig. 2). In the PVAT, CUS significantly increased the expression of Aim2, Zbp1, Caspase-1 and Gsdmd, key genes to AIM2-PANoptosis, and this upregulation was prevented in CUS-DSF group (p<0.05). Conclusion: Chronic stress drives mtDNA release into circulation and AIM2-PANoptosis in the PVAT, contributing to stress-induced dysfunction in MRAs. Disulfiram diet prevented some of the stress-induced changes but also induced noticeable negative effects, highlighting the need for further studies to understand its dual action.
- Dos Passos, Rinaldo ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Frambes, Noelle ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Vieira Dos Santos, Cintia ( University of Sao Paulo , Ribeirao Preto , Brazil )
- Wilczynski, Stephanie ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Zhang, Tianxin ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Wood, Susan ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Wenceslau, Camilla ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Hollis, Fiona ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Priviero, Fernanda ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Webb, R Clinton ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Tomazini Goncalves, Tiago ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Dos Anjos Moraes, Raiana ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Silva-velasco, Diana ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Crockett, Alexia ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Cavalli, Eliana ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Mullaly, Alaina ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Cloude, Nazharee ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
- Pernomian, Laena ( University of South Carolina , Columbia , South Carolina , United States )
Author Disclosures:
Rinaldo dos Passos: DO NOT have relevant financial relationships
| Noelle Frambes: DO NOT have relevant financial relationships
| Cintia Vieira dos Santos: DO NOT have relevant financial relationships
| Stephanie Wilczynski: DO NOT have relevant financial relationships
| Tianxin Zhang: No Answer
| Susan Wood: No Answer
| Camilla Wenceslau: DO NOT have relevant financial relationships
| Fiona Hollis: DO have relevant financial relationships
;
Research Funding (PI or named investigator):MitoQ:Active (exists now)
| Fernanda Priviero: DO NOT have relevant financial relationships
| R Clinton Webb: DO NOT have relevant financial relationships
| Tiago Tomazini Goncalves: No Answer
| Raiana dos Anjos Moraes: No Answer
| Diana Silva-Velasco: DO NOT have relevant financial relationships
| Alexia Crockett: No Answer
| Eliana Cavalli: No Answer
| Alaina Mullaly: No Answer
| Nazharee Cloude: No Answer
| Laena Pernomian: DO NOT have relevant financial relationships
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
More abstracts on this topic:
Accentuated Effect of Transportation Noise Exposure on Cardiovascular Risk in Individuals with Anxiety and Depression
Saeed Fatima, Khawand Annemarie, Seligowski Antonia, Banks Jamie, Muenzel Thomas, Tawakol Ahmed, Osborne Michael, Abohashem Shady, Abikaram Krystel, Assefa Alula, Ahmad Taha, Arora Gagan, Khalil Maria, Lau Hui Chong, Aldosoky Wesam
A Novel Role for AKAP1 in JNK2 Trafficking to Endoplasmic Reticulum and Ca2+ Triggered Arrhythmic ActivitiesKohli Aaryan, Ricchiuti Nikola, Yan Jiajie, Bare Dan, Ai Xun
More abstracts from these authors:
Olfactory Receptor 2 Mediated Vascular Dysfunction in Diabetic Mouse Aorta
Silva-velasco Diana, Tomazini Goncalves Tiago, Zhang Tianxin, Dos Anjos Moraes Raiana, Rodrigues Rinaldo, Wilczynski Stephanie, Priviero Fernanda, Webb R Clinton
Cavernosal and Pudendal Dysfunction in Schlager Hypertensive (BPH/2J) Mice: Impaired α1-Adrenergic Contraction, Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation, and Piezo1 Channel FunctionDos Anjos Moraes Raiana, Priviero Fernanda, Pernomian Laena, Tomazini Goncalves Tiago, Dos Passos Rinaldo, Vieira Dos Santos Cintia, Zhang Tianxin, Silva-velasco Diana, Wenceslau Camilla, Webb R Clinton
You have to be authorized to contact abstract author. Please, Login
Not Available