Final ID: TH173
A Study on Prevalence of Cardiovascular risk factors among patients with Psoriasis of a tertiary care teaching hospital
Abstract Body: Abstract
Background: Psoriasis is a chronic, immune-mediated inflammatory skin disorder characterized by abnormal keratinocyte proliferation, immune cell infiltration, and vascular changes. Beyond cutaneous involvement, psoriasis has been increasingly associated with systemic comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, due to shared inflammatory mechanisms.
Objectives: To assess the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in patients with psoriasis and compare them with age- and sex-matched healthy controls.
Materials and Methods: A hospital-based case-control observational study was conducted over 15 months at a tertiary care hospital of South India. The study enrolled 60 participants, including 30 clinically diagnosed psoriasis patients and 30 age- and sex-matched controls. Psoriasis severity was evaluated using the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI). Cardiovascular risk was assessed through body mass index (BMI), fasting lipid profile, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) via Doppler ultrasonography.
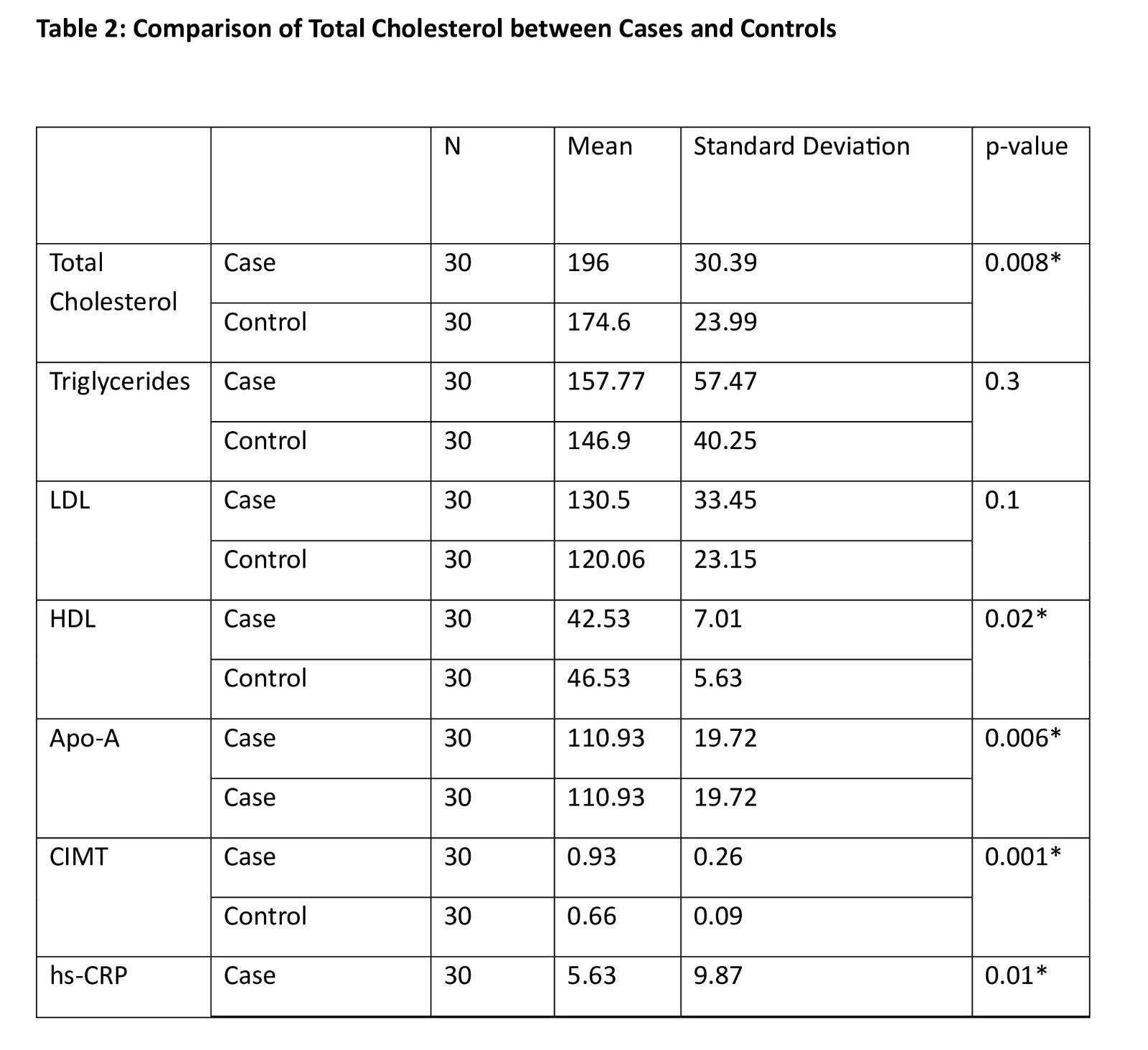
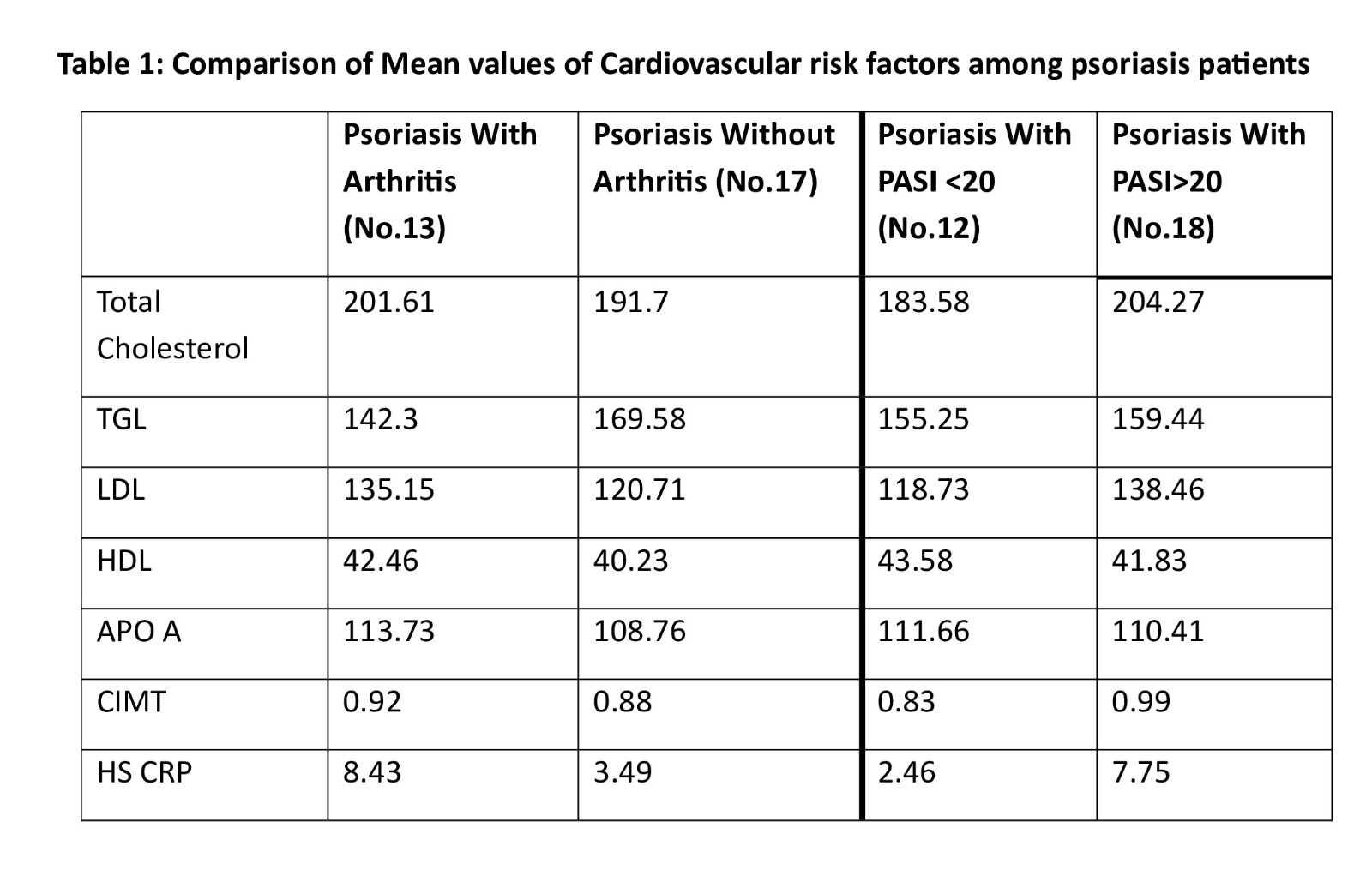
Results: Psoriasis patients had significantly higher mean levels of total cholesterol, hs-CRP, BMI, and HbA1c compared to controls (p < 0.05). Psoriatic arthritis was present in 43.3% of cases and absent in controls. Higher PASI scores and the presence of arthritis were associated with an increased number of cardiovascular risk factors. Differences in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and triglyceride levels were not statistically significant between the groups.
Conclusion: Psoriasis is associated with a significantly increased prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors. Parameters such as total cholesterol, HDL, ApoA, CIMT, BMI, and HbA1c were markedly elevated in psoriasis patients, highlighting the need for routine cardiovascular risk screening and multidisciplinary management in this population.
Keywords: Cardiovascular Disease, Psoriasis, Skin Disease
Background: Psoriasis is a chronic, immune-mediated inflammatory skin disorder characterized by abnormal keratinocyte proliferation, immune cell infiltration, and vascular changes. Beyond cutaneous involvement, psoriasis has been increasingly associated with systemic comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, due to shared inflammatory mechanisms.
Objectives: To assess the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in patients with psoriasis and compare them with age- and sex-matched healthy controls.
Materials and Methods: A hospital-based case-control observational study was conducted over 15 months at a tertiary care hospital of South India. The study enrolled 60 participants, including 30 clinically diagnosed psoriasis patients and 30 age- and sex-matched controls. Psoriasis severity was evaluated using the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI). Cardiovascular risk was assessed through body mass index (BMI), fasting lipid profile, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) via Doppler ultrasonography.
Results: Psoriasis patients had significantly higher mean levels of total cholesterol, hs-CRP, BMI, and HbA1c compared to controls (p < 0.05). Psoriatic arthritis was present in 43.3% of cases and absent in controls. Higher PASI scores and the presence of arthritis were associated with an increased number of cardiovascular risk factors. Differences in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and triglyceride levels were not statistically significant between the groups.
Conclusion: Psoriasis is associated with a significantly increased prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors. Parameters such as total cholesterol, HDL, ApoA, CIMT, BMI, and HbA1c were markedly elevated in psoriasis patients, highlighting the need for routine cardiovascular risk screening and multidisciplinary management in this population.
Keywords: Cardiovascular Disease, Psoriasis, Skin Disease
More abstracts on this topic:
12-lead electrocardiograms predict adverse cardiovascular outcomes of emergency department patients
Haimovich Julian, Kolossvary Marton, Alam Ridwan, Padros I Valls Raimon, Lu Michael, Aguirre Aaron
A Novel Missense Mutation in TNNT2 Gene in a Lebanese Pedigree With Ebstein Anomaly And Wolf-Parkinson-White Syndrome: A Case ReportAtasi Montaser, Dankar Razan, Barakat Salim, Wehbi Jad, Refaat Marwan