Final ID: FR576
The Paradox of Performance: Hypertension Among Young Athletes — A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Risks behind Fitness
Abstract Body: INTRODUCTION
Hypertension (HTN) is a growing concern nowadays. From 1990 through 2019, individuals with HTN have doubled in global burden. Although HTN is prevalent among a wide range of age groups, the incidence and prevalence of HTN among young athletes have become a concern lately, with newer research indicating a rise in this age group. Goal is to evaluate and determine the prevalence of HTN in young competitive athletes participating in varying competitive sports.
METHODS
This study followed PRISMA guidelines. We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Google scholar for studies published up to 15th May 2025 that reported prevalence of HTN among young athletes (<50 years old). Studies involving paralympic, former and concussed athletes were excluded. Data on prevalence, sample sizes, and athlete characteristics were extracted. A random-effects model was created using R Studio (version 4.5.0) to pool prevalence estimates, with heterogeneity assessed via I2 statistic. Study quality was evaluated using Hoy et al. risk-of-bias tool, adapted for epidemiological studies. Subgroup analysis was performed according to the gender reported, country, mean age group (<20 and >20 years), and HTN cut off values.
HYPOTHESIS
Compared to adults, young athletes are more likely to develop hypertension because of incompletely developed cardiovascular systems and continue to grow physically.
RESULTS
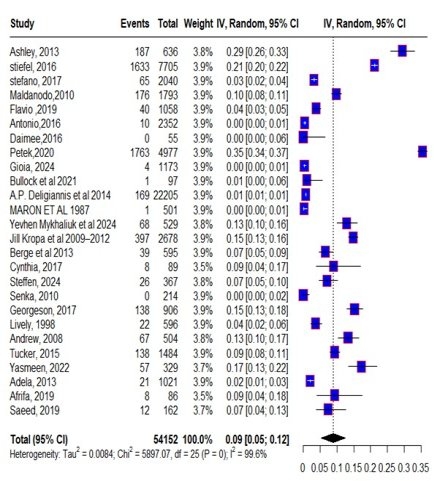
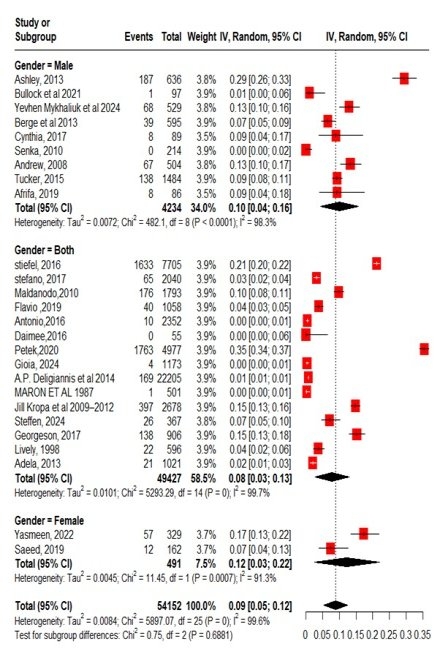
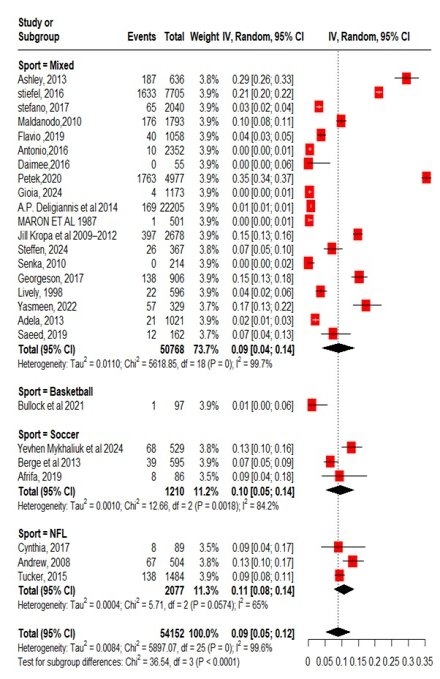
A total of 26 studies were analysed from 12 countries. Pooled prevalence of HTN in young athletes was 9% (95% CI 5%-12%, P=0, I2=99.6%) in 54,152 total population. Males studies had a prevalence of 10%, 12% in females and articles including both genders yielded a prevalence of 8%. A prevalence of 13% was reported in the USA, 2% in Italy, lastly, 7% in Norway. Studies with >20 overall mean age documented 4% prevalence, however, <20 showed 12%. 5 distinct cut off values were set for HTN, 1. >140/90 mmHg, 2. >95th percentile for gender, age and height, 3. >130/80, 4. >140/90 or taking antihypertensive, which exhibited prevalence of 8%, 9%, 20%, and 8%, respectively. 11% prevalence in NFL players, 10% in soccer, moreover, 9% in mixed sports demonstrated that the type of sport played also had a significant role.
CONCLUSION
Females studies, demographically USA and NFL sport had higher prevalence compared to their counterpart which calls for more attention to the earlier identification, monitoring, follow-up of asymptomatic high-risk individuals; timely interventions may improve long-term outcomes.
Hypertension (HTN) is a growing concern nowadays. From 1990 through 2019, individuals with HTN have doubled in global burden. Although HTN is prevalent among a wide range of age groups, the incidence and prevalence of HTN among young athletes have become a concern lately, with newer research indicating a rise in this age group. Goal is to evaluate and determine the prevalence of HTN in young competitive athletes participating in varying competitive sports.
METHODS
This study followed PRISMA guidelines. We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Google scholar for studies published up to 15th May 2025 that reported prevalence of HTN among young athletes (<50 years old). Studies involving paralympic, former and concussed athletes were excluded. Data on prevalence, sample sizes, and athlete characteristics were extracted. A random-effects model was created using R Studio (version 4.5.0) to pool prevalence estimates, with heterogeneity assessed via I2 statistic. Study quality was evaluated using Hoy et al. risk-of-bias tool, adapted for epidemiological studies. Subgroup analysis was performed according to the gender reported, country, mean age group (<20 and >20 years), and HTN cut off values.
HYPOTHESIS
Compared to adults, young athletes are more likely to develop hypertension because of incompletely developed cardiovascular systems and continue to grow physically.
RESULTS
A total of 26 studies were analysed from 12 countries. Pooled prevalence of HTN in young athletes was 9% (95% CI 5%-12%, P=0, I2=99.6%) in 54,152 total population. Males studies had a prevalence of 10%, 12% in females and articles including both genders yielded a prevalence of 8%. A prevalence of 13% was reported in the USA, 2% in Italy, lastly, 7% in Norway. Studies with >20 overall mean age documented 4% prevalence, however, <20 showed 12%. 5 distinct cut off values were set for HTN, 1. >140/90 mmHg, 2. >95th percentile for gender, age and height, 3. >130/80, 4. >140/90 or taking antihypertensive, which exhibited prevalence of 8%, 9%, 20%, and 8%, respectively. 11% prevalence in NFL players, 10% in soccer, moreover, 9% in mixed sports demonstrated that the type of sport played also had a significant role.
CONCLUSION
Females studies, demographically USA and NFL sport had higher prevalence compared to their counterpart which calls for more attention to the earlier identification, monitoring, follow-up of asymptomatic high-risk individuals; timely interventions may improve long-term outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
2 Dimensional Echocardiography versus 3 Dimentional Echocardiography to Assess Right Ventricular Function in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review
Chaudhry Waleed Razzaq, Hajj Fatima, Bathula Satyamedha, Meghji Mohammed Askari, Pasupuleti Hemalatha, Kiyani Madiha, Shah Syeda Simrah, Neelakantan Ramaswamy Sanathanan, Mirzaeidizaji Nakisa, St. Jacques Jahnoy, Khan Khalil Ullah, Veluchamy Elakkiya, Jesse Joshanna
2-Methoxyestradiol By Inhibiting Central Action of 12S-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid Protects Ovariectomized Mice From HypertensionDutta Shubha, Singh Purnima, Song Chi Young, Shin Ji Soo, Malik Kafait