Final ID: 061
Baxdrostat Lowers Blood Pressure in Patients with Uncontrolled Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease: Results from the FigHTN Phase 2 trial
Abstract Body: Introduction
Aldosterone contributes to both uncontrolled hypertension (uHTN) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Baxdrostat, a highly potent and selective aldosterone synthase inhibitor, reduces plasma aldosterone concentrations without affecting cortisol production.
Hypothesis
The FigHTN study assessed the efficacy and safety of baxdrostat in participants with CKD and uHTN.
Methods
FigHTN (NCT05432167) was a phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Eligible adult participants had a mean seated systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mmHg (without diabetes) or ≥130 mmHg (with diabetes) despite treatment with an antihypertensive agent, an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25–75 mL/min/1.73 m2, and a urine albumin-creatinine ratio (UACR) of ≥100 mg/g. We randomized participants (1:1:1) to baxdrostat low-dose (LD; 0.5 mg up-titrated to 1 mg), high-dose (HD; 2 mg up-titrated to 4 mg), or placebo (PBO) for 26 weeks. The primary endpoint was change from baseline in mean seated SBP at Week 26 (W26) in the baxdrostat pooled (BAX-P) treatment group (LD + HD) vs PBO; secondary endpoints evaluated this change by LD and HD. Exploratory endpoints included change from baseline in UACR at W26. We also assessed safety and tolerability.
Results
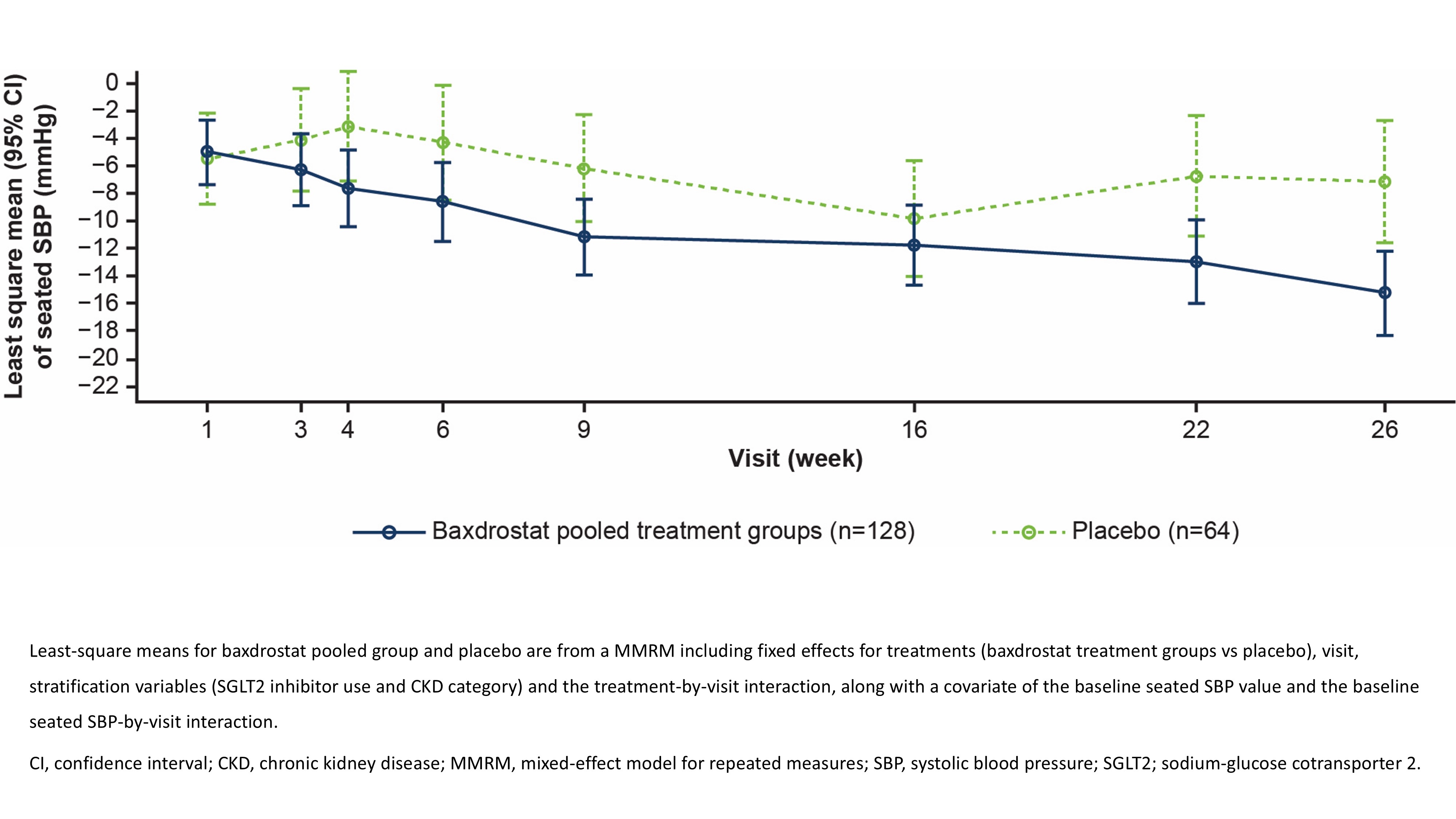
We randomized 195 participants (LD 65; HD 64; PBO 66) and 192 received treatment (LD 65; HD 63; PBO 64). Mean (SD) age was 66 (11) years, 32% were women, 40% were non-White, and 80% had type 2 diabetes. Mean (SD) baseline SBP was 151.2 (13.1) mmHg; mean (SD) baseline eGFR was 44 (14) mL/min/1.73 m2; median (range) UACR was 713.8 (99.2–7383.4) mg/g. Mean PBO-corrected changes in SBP from baseline to W26 were: BAX-P (n=128): – 8.1 mmHg (95% CI –13.4, –2.8; p=0.003; Figure 1); LD: –9.0 mmHg (–15.1, –2.9; p=0.004); HD: –7.2 mmHg (–13.2, –1.2; p=0.019). Change in UACR from baseline to W26 was –55.2% (95% CI –67.4, –38.3; p<0.001; Figure 2) for the BAX-P group (n=103) vs PBO (n=47). A total of 12/128 (9.4%) participants in the BAX-P group and 2/64 (3.1%) participants in the PBO group had a treatment-emergent serious adverse event; no deaths were reported. Hyperkalemia was reported by 41.4% (53/128) participants in the BAX-P group (most cases mild to moderate) and 4.7% (3/64) in the PBO group.
Conclusions
In conclusion, baxdrostat significantly reduced SBP and albuminuria in patients with CKD and uHTN. With baxdrostat, patients experienced mild-to-moderate hyperkalemia and no unexpected adverse events.
Aldosterone contributes to both uncontrolled hypertension (uHTN) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Baxdrostat, a highly potent and selective aldosterone synthase inhibitor, reduces plasma aldosterone concentrations without affecting cortisol production.
Hypothesis
The FigHTN study assessed the efficacy and safety of baxdrostat in participants with CKD and uHTN.
Methods
FigHTN (NCT05432167) was a phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Eligible adult participants had a mean seated systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mmHg (without diabetes) or ≥130 mmHg (with diabetes) despite treatment with an antihypertensive agent, an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25–75 mL/min/1.73 m2, and a urine albumin-creatinine ratio (UACR) of ≥100 mg/g. We randomized participants (1:1:1) to baxdrostat low-dose (LD; 0.5 mg up-titrated to 1 mg), high-dose (HD; 2 mg up-titrated to 4 mg), or placebo (PBO) for 26 weeks. The primary endpoint was change from baseline in mean seated SBP at Week 26 (W26) in the baxdrostat pooled (BAX-P) treatment group (LD + HD) vs PBO; secondary endpoints evaluated this change by LD and HD. Exploratory endpoints included change from baseline in UACR at W26. We also assessed safety and tolerability.
Results
We randomized 195 participants (LD 65; HD 64; PBO 66) and 192 received treatment (LD 65; HD 63; PBO 64). Mean (SD) age was 66 (11) years, 32% were women, 40% were non-White, and 80% had type 2 diabetes. Mean (SD) baseline SBP was 151.2 (13.1) mmHg; mean (SD) baseline eGFR was 44 (14) mL/min/1.73 m2; median (range) UACR was 713.8 (99.2–7383.4) mg/g. Mean PBO-corrected changes in SBP from baseline to W26 were: BAX-P (n=128): – 8.1 mmHg (95% CI –13.4, –2.8; p=0.003; Figure 1); LD: –9.0 mmHg (–15.1, –2.9; p=0.004); HD: –7.2 mmHg (–13.2, –1.2; p=0.019). Change in UACR from baseline to W26 was –55.2% (95% CI –67.4, –38.3; p<0.001; Figure 2) for the BAX-P group (n=103) vs PBO (n=47). A total of 12/128 (9.4%) participants in the BAX-P group and 2/64 (3.1%) participants in the PBO group had a treatment-emergent serious adverse event; no deaths were reported. Hyperkalemia was reported by 41.4% (53/128) participants in the BAX-P group (most cases mild to moderate) and 4.7% (3/64) in the PBO group.
Conclusions
In conclusion, baxdrostat significantly reduced SBP and albuminuria in patients with CKD and uHTN. With baxdrostat, patients experienced mild-to-moderate hyperkalemia and no unexpected adverse events.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Subtle Case of Primary Aldosteronism
Agarwal Nikita, Sinha Partha, Tung Patricia, Krawisz Anna
Anticoagulation For Patients On Hemodialysis And Atrial FibrillationEbrahimi Ramin, Alvarez Carlos, Dennis Paul