Final ID: FR514
Efficacy of Alogliptin, a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor in Managing Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body: Introduction:
Alogliptin has demonstrated the potential to improve glycemic control with a reduced likelihood of hypoglycemia and weight gain in patients with type 2 diabetes. However, its comparative efficacy and safety in managing type 2 diabetes require additional exploration.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that Alogliptin would demonstrate superior glycemic efficacy and favorable metabolic outcomes compared to placebo or other anti-diabetic therapy.
Methods:
A systematic search of PubMed, Clinical Trials.gov, and the Cochrane Library was conducted from inception to 14 December 2024. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing Alogliptin with placebo (passive control group, PCG) or active antidiabetic agents (active control group, ACG) in adults (≥18 years) with T2DM were included. Primary outcomes were changes in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting plasma glucose (FPG). Secondary outcomes included changes in body mass index (BMI), blood pressure, lipid profile, and adverse events. A random effects model was applied, and heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic.
Results:
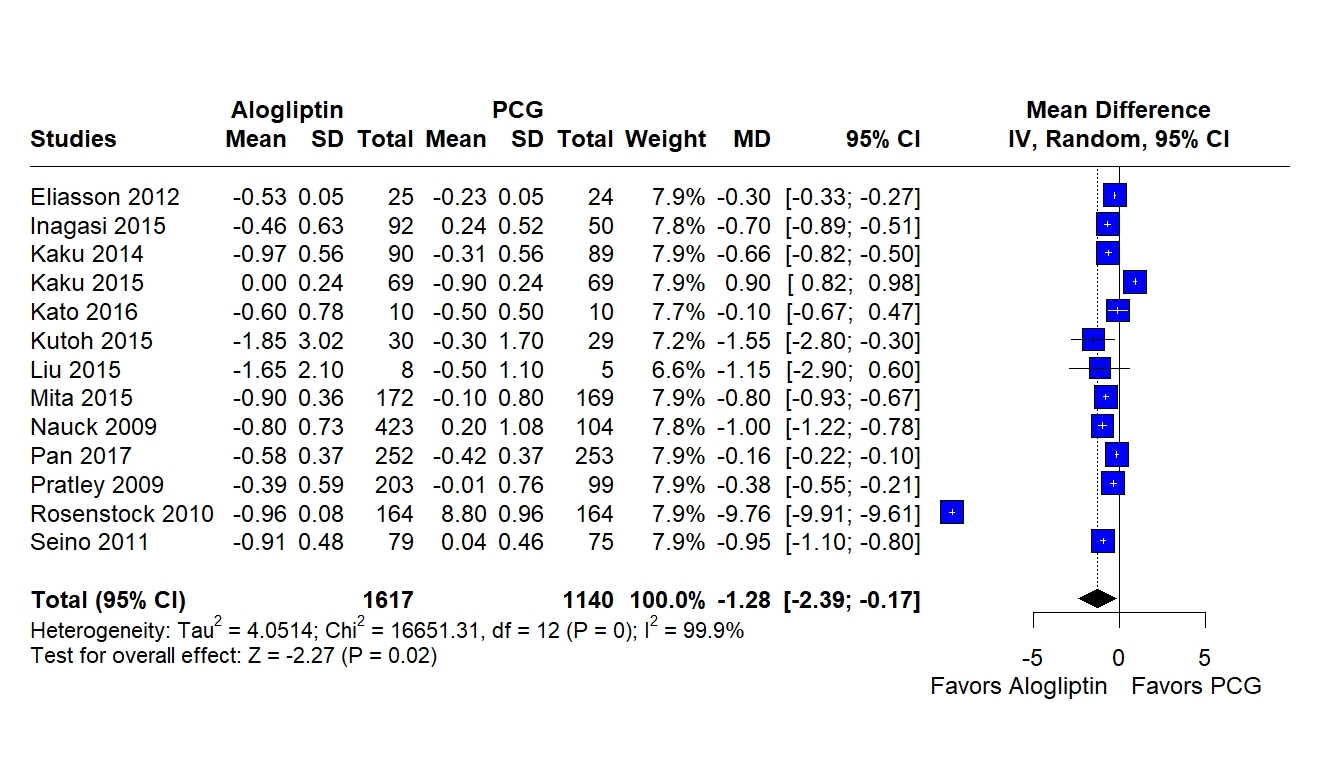
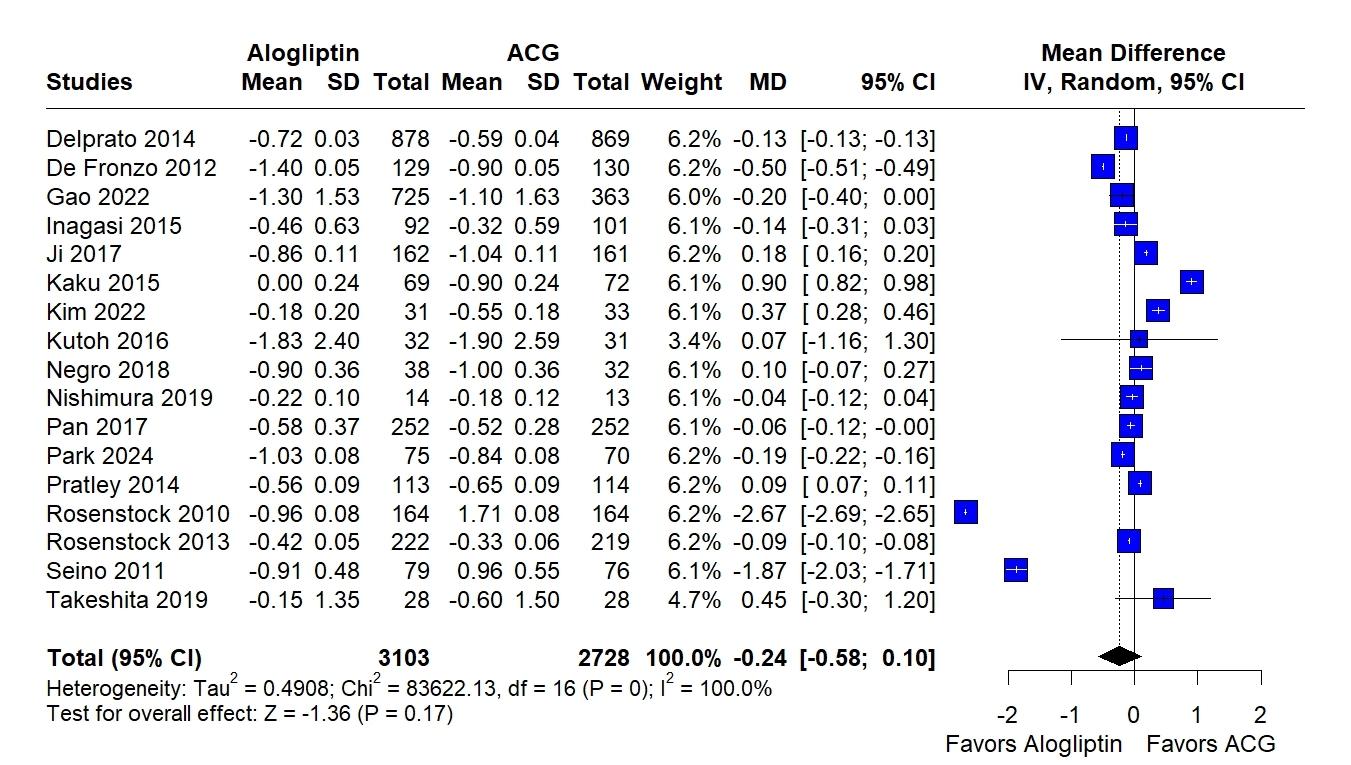
Twenty-nine RCTs encompassing 11,589 patients were included. Alogliptin significantly reduced HbA1c compared with PCG (MD= –1.28; 95% CI, –2.39 to –0.17; I2= 99.9%; P = .02), while no significant difference was found compared to ACG. No differences were observed in FPG, BMI, systolic or diastolic blood pressure between groups. Compared to PCG, a small but significant increase in BMI was noted (MD= 0.31; 95% CI, –0.00 to 0.63; I2= 0.0%; P = .05). Alogliptin was associated with reductions in LDL cholesterol (MD= –3.49; 95% CI, –5.04 to –1.93; I2= 19.2%; P < .01) and total cholesterol (MD= –7.58; 95% CI, –9.78 to –5.38; I2= 38.3%; P < .01), but an increase in triglycerides (MD= 6.28; 95% CI, 0.17 to 12.40; I2= 63.6%; P = .04) compared to ACG.
Conclusion:
Alogliptin significantly improves glycemic control compared to placebo and improves lipid profiles, particularly LDL and total cholesterol. However, it is associated with a slight increase in triglycerides and BMI. These findings support the use of Alogliptin as an effective and generally well-tolerated therapeutic option in the management of T2DM, though further research is needed to assess long-term safety and cardiovascular outcomes.
Alogliptin has demonstrated the potential to improve glycemic control with a reduced likelihood of hypoglycemia and weight gain in patients with type 2 diabetes. However, its comparative efficacy and safety in managing type 2 diabetes require additional exploration.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that Alogliptin would demonstrate superior glycemic efficacy and favorable metabolic outcomes compared to placebo or other anti-diabetic therapy.
Methods:
A systematic search of PubMed, Clinical Trials.gov, and the Cochrane Library was conducted from inception to 14 December 2024. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing Alogliptin with placebo (passive control group, PCG) or active antidiabetic agents (active control group, ACG) in adults (≥18 years) with T2DM were included. Primary outcomes were changes in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting plasma glucose (FPG). Secondary outcomes included changes in body mass index (BMI), blood pressure, lipid profile, and adverse events. A random effects model was applied, and heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic.
Results:
Twenty-nine RCTs encompassing 11,589 patients were included. Alogliptin significantly reduced HbA1c compared with PCG (MD= –1.28; 95% CI, –2.39 to –0.17; I2= 99.9%; P = .02), while no significant difference was found compared to ACG. No differences were observed in FPG, BMI, systolic or diastolic blood pressure between groups. Compared to PCG, a small but significant increase in BMI was noted (MD= 0.31; 95% CI, –0.00 to 0.63; I2= 0.0%; P = .05). Alogliptin was associated with reductions in LDL cholesterol (MD= –3.49; 95% CI, –5.04 to –1.93; I2= 19.2%; P < .01) and total cholesterol (MD= –7.58; 95% CI, –9.78 to –5.38; I2= 38.3%; P < .01), but an increase in triglycerides (MD= 6.28; 95% CI, 0.17 to 12.40; I2= 63.6%; P = .04) compared to ACG.
Conclusion:
Alogliptin significantly improves glycemic control compared to placebo and improves lipid profiles, particularly LDL and total cholesterol. However, it is associated with a slight increase in triglycerides and BMI. These findings support the use of Alogliptin as an effective and generally well-tolerated therapeutic option in the management of T2DM, though further research is needed to assess long-term safety and cardiovascular outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials: Aldosterone Synthase Inhibitors as a Therapeutic Strategy for Hypertension
Marzano Luigi, Merlo Matteo, Pizzolo Francesca, Friso Simonetta
Assessment Of Medical Students' Knowledge Before And After Basic Life Support Training At A University In Southeast ParáBueno Claudia, Souza Barbara, Santos Aline, Da Silva Ferreira Laíse Jorrana, Varao Thawanny, Cunha Carneiro Maria Angelica, Gomes Laysa, Teixeira Costa Ana Carolina, Miranda Luana, Martin Joelma, Rocha Nathalia, Dias Adria