Final ID: 088
Ultrafast Doppler Ultrasound as a Noninvasive Proxy for Renal Vascular Function in a Mouse Model of Hypertension
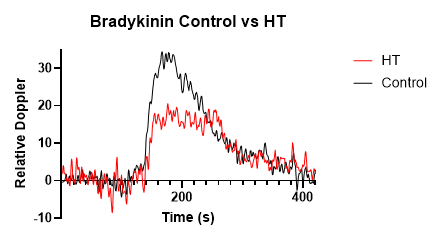
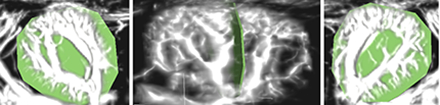
Abstract Body: Although endothelial dysfunction precedes cardiovascular diseases, non-invasive assessment of rodents' vascular function remains challenging. Ultrafast Doppler ultrasound has emerged as a powerful tool for assessing brain vascular function with high temporal and spatial resolution. However, its application to quantify in vivo hemodynamic changes in organs other than the brain has not been developed yet. Therefore, we propose to leverage the advanced 3D functional imaging capabilities of the Iconeus One system to measure real-time renal hemodynamic responses in a mouse model of hypertension. We hypothesized that hypertension impairs renal vascular reactivity, reflected by blunted Power Doppler values, an in vivo proxy for renal hemodynamic function. Seven-week-old male C57Bl/6 mice were administered retro-orbital injections of a hepatocyte-specific AAV2/8 virus encoding an HA-tagged Angiotensin II (AngII). Tail cuff blood pressure measurements (AAV: 147.5 mmHg vs. control: 132.5 mmHg, n=7, p<0.05), in addition to significant cardiac hypertrophy (p<0.05) confirmed the induction of hypertension. Mice were submitted to ultrasound measurement and Ultrasound Localization Microscopy (ULM) before and three weeks after AAV injection, and isolated renal and mesenteric arteries were analyzed ex vivo via wire myography. The 3D functional ultrasound (fUS) captured Power Doppler signals across sixteen transverse kidney planes. Signals were normalized to baseline to calculate Relative Doppler Values (RDVs), which were averaged across all planes to quantify renal hemodynamic activity. Mice underwent twelve-minute 3D fUS scans, administering bradykinin after two minutes. Results showed no difference in peak RDVs between baseline and post-injection control group. In contrast, hypertensive mice showed significant reduction in peak RDVs relative to pre-AAV baseline (n=7, p<0.05). Hypertensive mice showed significant decrease in peak RDVs following bradykinin injection compared to post-injection controls (p<0.05) and a marked decrease in endothelium-dependent relaxation to acetylcholine in renal and mesenteric arteries. ULM revealed a reduction in renal vascular density in hypertensive mice compared to controls. In conclusion, our findings demonstrate that ultrafast Doppler ultrasound is a promising, noninvasive tool for longitudinal in vivo assessment of renal endothelial function and correlates with ex vivo vascular reactivity measurements in renal and mesenteric arteries.
More abstracts on this topic:
Bismuth Nanoparticle-Infused Bioresorbable Graft Enables Multimodal Computed Tomography and Photoacoustic Imaging-Based Monitoring and Promotes Vascular Regeneration
Barcena Allan John, Fowlkes Natalie, Bouchard Richard, Huang Steven, Melancon Marites, Bernardino Marvin, Mishra Archana, Bolinas Dominic Karl, Marco Kitz Paul, Fernandez Kim Claudette, San Valentin Erin Marie, Court Karem, Godin Biana
Activation of the Histamine-3 Receptor Prevents Cardiac Fibrosis and Diastolic Dysfunction by Opposing a Profibrotic Cardiac Fibroblast Phenotype through Inhibition of cAMP SignalingConnery Heather, Herrnreiter Anja, Campbell William, Widiapradja Alexander, Levick Scott