Final ID: FR473
Leveraging a Learning Collaborative Framework to Drive Quality Improvement in Hypertension Management
Abstract Body: Background
Hypertension (HTN) is a leading modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease, contributing to approximately 75% of acute cardiovascular events1. Health systems play a crucial role in addressing this burden through systemic HTN management and partnerships with community-based organizations (CBOs) to reduce structural barriers and empower patients. The American Heart Association (AHA) launched an equity-focused HTN initiative in Buffalo, Columbus, and Houston to improve HTN control across health care organizations (HCOs) and engage CBOs. The initiative uses a structured Learning Collaborative (LC) framework to support quality improvement (QI) through peer learning, model sharing, and culturally relevant adaptations. The goal is to achieve ≥70% HTN control rates among participating HCOs.
Methods
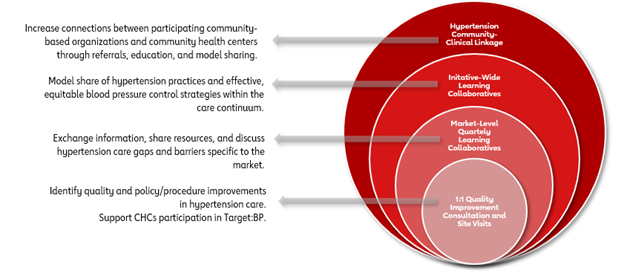
The Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) LC model was used to guide implementation with two cohorts2 . HCOs began particpating in quarterly initiative-wide and market-level meetings in Janurary 2024. Both cohorts engaged in joint activities, such as biannual LCs and in-person discussions. LCs focused on model sharing and guided conversations to identify system-level barriers, such as care coordination gaps and patient engagement. The AHA provided QI consultation to support workflow improvement and alignment with site-level objectives. All HCOs also participated in the AHA/AMA Target: Blood Pressure program to reinforce evidence-based practices and standarized data collection. Survey and interviews were conducted in early 2025 to assess progress.
Results
The initiative established two cohorts consisting of 14 HCOs and 14 CBOs to strengthen community-clinical linkages (CCLs) and advance HTN care models. All HCOs established site-level objectives and reported progress toward sustainable strategies for improving HTN care. The dual-cohort model strengthened nearly 10 CCLs and fostered integrated care pathways between the two cohorts. Both cohorts noted improved integration and collaboration.
Conclusion
An equity-focused, dual-cohort LC model is both feasible and effective for improving HTN control rates in HCOs. Early indicators show increased leadership engagement, enhanced coordination, and uptake of QI strategies. The LC also serves as a tool for external review of internal processes, enabling organizations to identify gaps and refine strategies. Ongoing evaluation will assess HTN control outcomes and sustainability across participating sites.
Hypertension (HTN) is a leading modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease, contributing to approximately 75% of acute cardiovascular events1. Health systems play a crucial role in addressing this burden through systemic HTN management and partnerships with community-based organizations (CBOs) to reduce structural barriers and empower patients. The American Heart Association (AHA) launched an equity-focused HTN initiative in Buffalo, Columbus, and Houston to improve HTN control across health care organizations (HCOs) and engage CBOs. The initiative uses a structured Learning Collaborative (LC) framework to support quality improvement (QI) through peer learning, model sharing, and culturally relevant adaptations. The goal is to achieve ≥70% HTN control rates among participating HCOs.
Methods
The Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) LC model was used to guide implementation with two cohorts2 . HCOs began particpating in quarterly initiative-wide and market-level meetings in Janurary 2024. Both cohorts engaged in joint activities, such as biannual LCs and in-person discussions. LCs focused on model sharing and guided conversations to identify system-level barriers, such as care coordination gaps and patient engagement. The AHA provided QI consultation to support workflow improvement and alignment with site-level objectives. All HCOs also participated in the AHA/AMA Target: Blood Pressure program to reinforce evidence-based practices and standarized data collection. Survey and interviews were conducted in early 2025 to assess progress.
Results
The initiative established two cohorts consisting of 14 HCOs and 14 CBOs to strengthen community-clinical linkages (CCLs) and advance HTN care models. All HCOs established site-level objectives and reported progress toward sustainable strategies for improving HTN care. The dual-cohort model strengthened nearly 10 CCLs and fostered integrated care pathways between the two cohorts. Both cohorts noted improved integration and collaboration.
Conclusion
An equity-focused, dual-cohort LC model is both feasible and effective for improving HTN control rates in HCOs. Early indicators show increased leadership engagement, enhanced coordination, and uptake of QI strategies. The LC also serves as a tool for external review of internal processes, enabling organizations to identify gaps and refine strategies. Ongoing evaluation will assess HTN control outcomes and sustainability across participating sites.
More abstracts on this topic:
A closed-loop system based on piezoelectric thin-film sensors and photothermal nanomaterials enables precise renal denervation for the treatment of hypertension
A Longitudinal 20-year Analysis Indicates Acceleration of Cardiometabolic Comorbidities on Dementia Risk
Liu Chengzhe, Zhou Liping, Yu Lilei
A Longitudinal 20-year Analysis Indicates Acceleration of Cardiometabolic Comorbidities on Dementia Risk
Lihua Huang, Danish Muhammad, Auyeung Tw, Jenny Lee, Kwok Timothy, Abrigo Jill, Wei Yingying, Lo Cecilia, Fung Erik