Final ID: TAC285
Bariatric Surgery Achieves Significant and Sustained Hypertension Control: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body: Introduction:
By 2050, the number of adults living with overweight and obesity is projected to reach 3.80 billion, accounting for more than half of the global adult population. Its close link with hypertension (HTN) increases cardiovascular risk and complicates blood pressure (BP) management. While lifestyle modifications and pharmacotherapy are first-line treatments, their long-term effectiveness in obese patients is often limited. Bariatric surgery has emerged as a potential intervention for HTN control, yet its sustained impact on BP remains uncertain.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that bariatric surgery leads to significantly greater systolic and diastolic BP reductions than non-surgical management.
Methods:
We systematically searched PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Cochrane (up to May 2024) for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing bariatric procedures—Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), sleeve gastrectomy (SG), laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB), and biliopancreatic diversion (BPD)—with non-surgical interventions (pharmacotherapy, lifestyle modifications, or both). The primary outcome was the mean change in SBP and DBP. A random-effects meta-analysis estimated pooled mean differences (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Subgroup analyses were performed by surgical modality and follow-up duration, with sensitivity analyses assessing the robustness of findings.
Results:
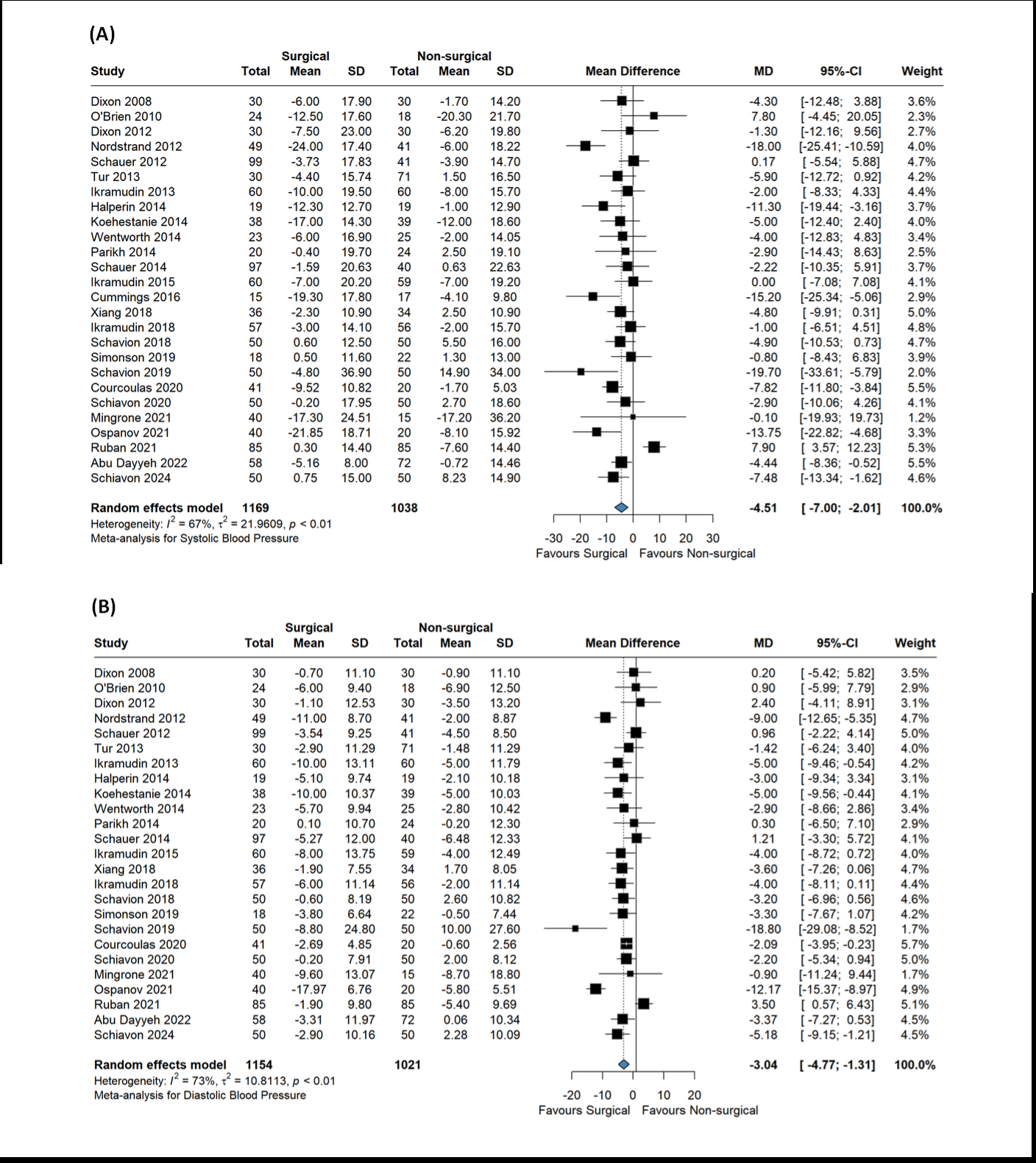
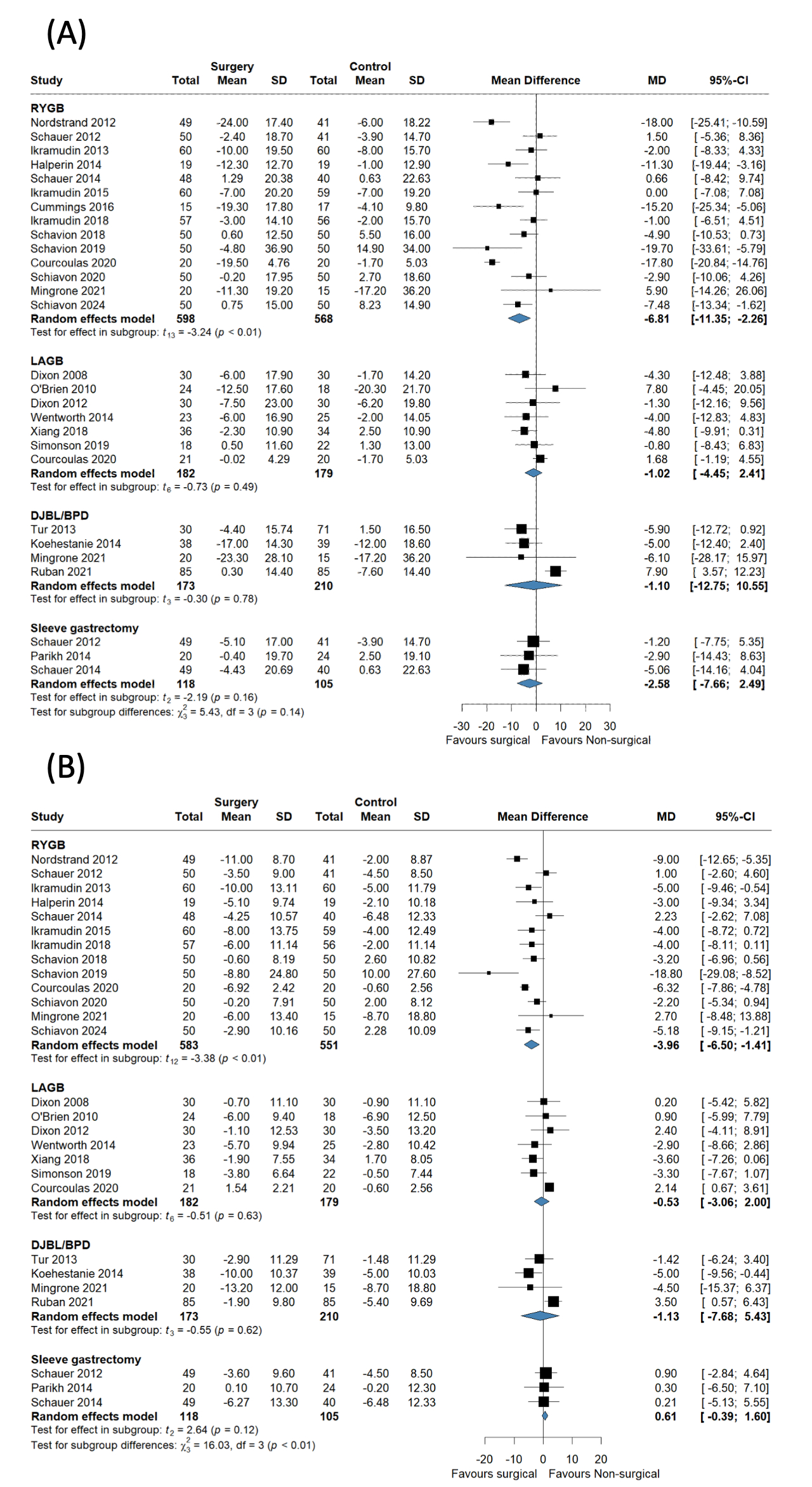
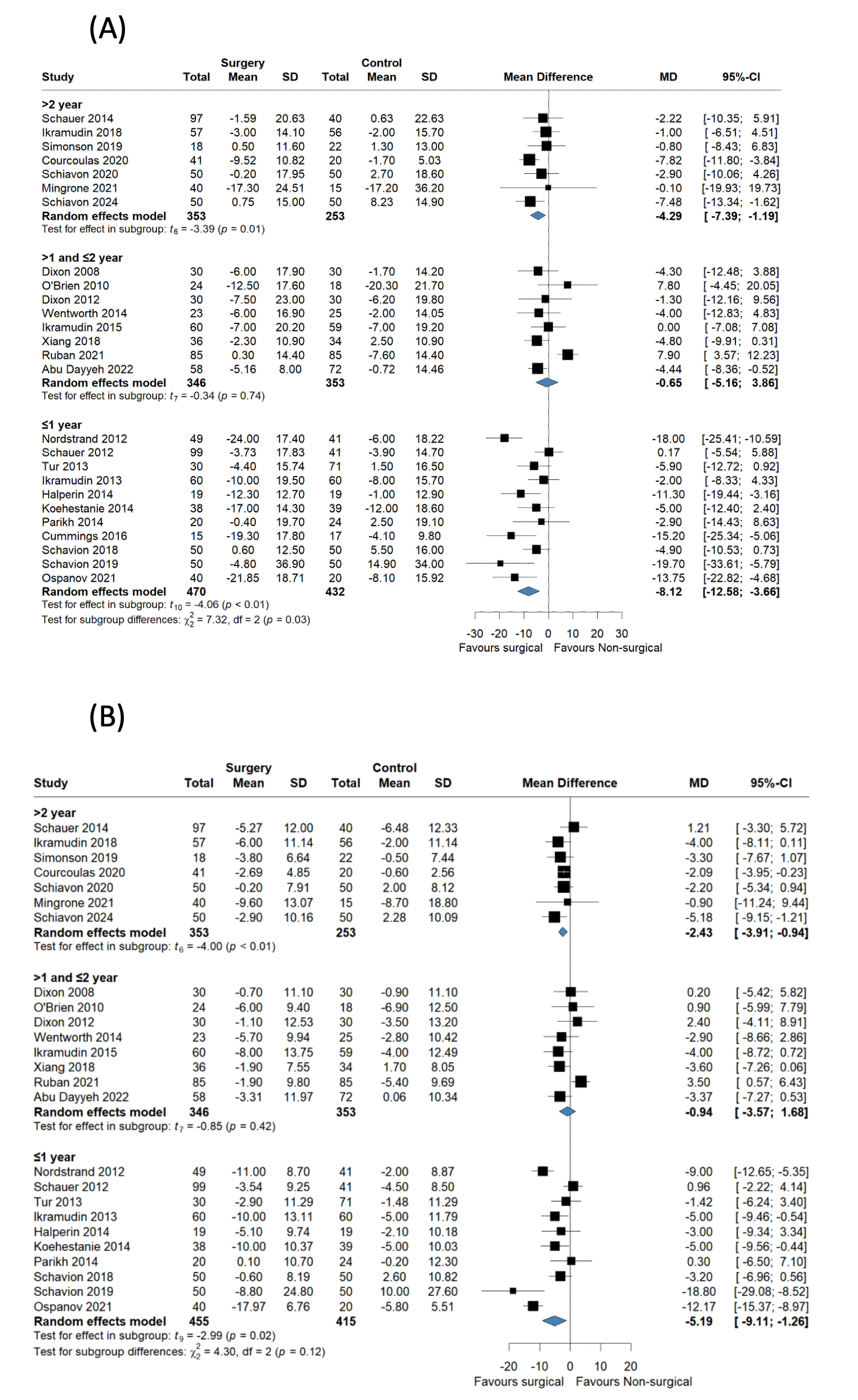
Twenty-six RCTs with 2,207 patients (1,169 surgical; 1,038 non-surgical) were included. Bariatric surgery was associated with significantly greater BP reductions than non-surgical treatments. The pooled analysis showed a MD in SBP reduction of -4.51 mmHg (95% CI: -7.00 to -2.01; P = .001) and a MD in DBP reduction of -3.04 mmHg (95% CI: -4.77 to -1.31; P = .001). Among surgical procedures, RYGB produced the greatest BP-lowering effect (SBP: -6.81 mmHg; 95% CI: -11.35 to -2.26; P < .01, DBP: -3.96 mmHg; 95% CI: -6.50 to -1.41; P < .01). The BP-lowering effect was significant in studies with follow-up durations ≤1 year and >2 years, but not during the 1–2 year period. Sensitivity analyses confirmed the findings, and no publication bias was evident.
Conclusion:
Bariatric surgery significantly reduces BP in obese hypertensive patients, with RYGB demonstrating the greatest effect. In conclusion, bariatric surgery should be considered a valuable intervention for obesity-associated HTN.
By 2050, the number of adults living with overweight and obesity is projected to reach 3.80 billion, accounting for more than half of the global adult population. Its close link with hypertension (HTN) increases cardiovascular risk and complicates blood pressure (BP) management. While lifestyle modifications and pharmacotherapy are first-line treatments, their long-term effectiveness in obese patients is often limited. Bariatric surgery has emerged as a potential intervention for HTN control, yet its sustained impact on BP remains uncertain.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that bariatric surgery leads to significantly greater systolic and diastolic BP reductions than non-surgical management.
Methods:
We systematically searched PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Cochrane (up to May 2024) for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing bariatric procedures—Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), sleeve gastrectomy (SG), laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB), and biliopancreatic diversion (BPD)—with non-surgical interventions (pharmacotherapy, lifestyle modifications, or both). The primary outcome was the mean change in SBP and DBP. A random-effects meta-analysis estimated pooled mean differences (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Subgroup analyses were performed by surgical modality and follow-up duration, with sensitivity analyses assessing the robustness of findings.
Results:
Twenty-six RCTs with 2,207 patients (1,169 surgical; 1,038 non-surgical) were included. Bariatric surgery was associated with significantly greater BP reductions than non-surgical treatments. The pooled analysis showed a MD in SBP reduction of -4.51 mmHg (95% CI: -7.00 to -2.01; P = .001) and a MD in DBP reduction of -3.04 mmHg (95% CI: -4.77 to -1.31; P = .001). Among surgical procedures, RYGB produced the greatest BP-lowering effect (SBP: -6.81 mmHg; 95% CI: -11.35 to -2.26; P < .01, DBP: -3.96 mmHg; 95% CI: -6.50 to -1.41; P < .01). The BP-lowering effect was significant in studies with follow-up durations ≤1 year and >2 years, but not during the 1–2 year period. Sensitivity analyses confirmed the findings, and no publication bias was evident.
Conclusion:
Bariatric surgery significantly reduces BP in obese hypertensive patients, with RYGB demonstrating the greatest effect. In conclusion, bariatric surgery should be considered a valuable intervention for obesity-associated HTN.
More abstracts on this topic:
Combination of Prolonged Water Fasting and Tirzepatide for Treatment of Refractory Morbid Obesity: Case Report
Palmisano Tiago, Roeschenthaler Paige, Passerini Heather, Shin Thomas, Guarraia David
3CPR Best Abstract Award: The pathogenic role of ADAMTS13 deficiency in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary HypertensionWu Zhijian, Zheng X. Long, Zheng Liang