Final ID: P-126
Exercise-Induced Changes in Skeletal Muscle of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease on Maintenance Hemodialysis
Abstract Body: Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients on maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) often experience sarcopenia and functional decline. The impact of exercise and inactivity on sarcopenia in CKD is poorly understood. We aimed to identify exercise-responsive genes that are differentially expressed between controls and patients on MHD. We also aim to investigate the changes in gene expression in skeletal muscle following a resistance exercise program in patients on MHD.
Methods: In a cross-sectional study, we performed RNA sequencing analysis in skeletal muscle biopsies from two groups (matched for age, gender, body mass index, and history of diabetes): controls (n=13) and patients on maintenance hemodialysis (MHD, n=10). In a separate cohort, we conducted a 12-week intradialytic resistance training in seven patients on MHD. Skeletal muscle biopsies were collected pre- and post-intervention to assess the acute (before and after a single bout of exercise) and chronic (after 12 weeks) effects of exercise. Total RNA was extracted and used to construct libraries for RNA sequencing using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 system. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified based on a false discovery rate (FDR) of less than 0.05 and a fold change greater than 1.5. Exercise and inactivity-responsive genes in non-CKD populations identified in the MetaMEx (www.metamex.eu) were used as reference.
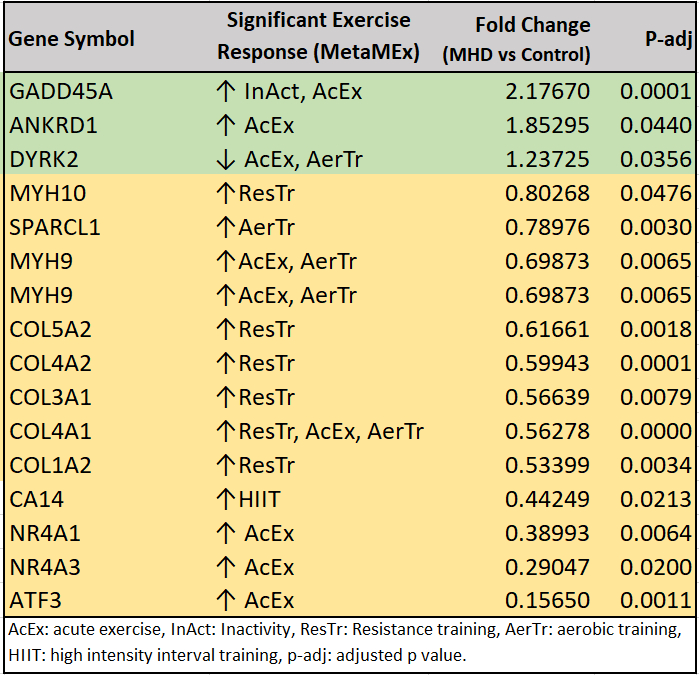
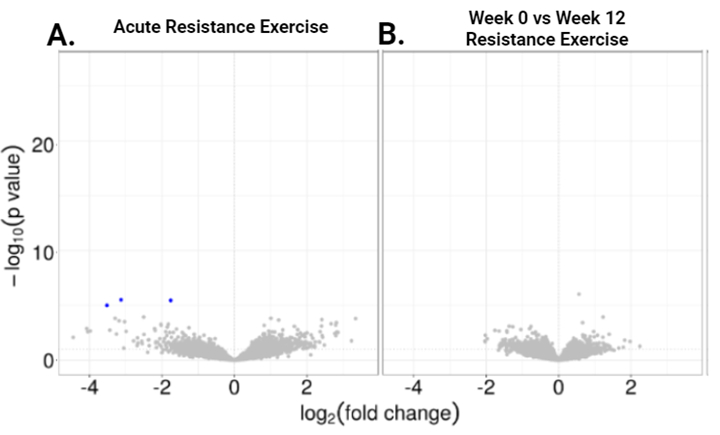
Results: We found significant DEGs between the control and MHD that were affected by exercise or inactivity according to MetaMEx. These genes and fold changes between control and MHD groups are depicted in Table 1. In the exercise intervention cohort, we observed no significant differences in the expression of these genes either acutely (Figure 1A) or 12 weeks after the exercise intervention (Figure 1B).
Conclusion: We found many DEGs related to exercise and inactivity between patients on MHD and controls; however, resistance training does not significantly alter skeletal muscle gene expression. Future studies should explore alternative exercise interventions, such as HIIT exercise, aerobic training, combined aerobic and resistance training, or longer duration programs, to determine if these approaches can effectively modulate gene expression and improve sarcopenia and frailty in this population.
Methods: In a cross-sectional study, we performed RNA sequencing analysis in skeletal muscle biopsies from two groups (matched for age, gender, body mass index, and history of diabetes): controls (n=13) and patients on maintenance hemodialysis (MHD, n=10). In a separate cohort, we conducted a 12-week intradialytic resistance training in seven patients on MHD. Skeletal muscle biopsies were collected pre- and post-intervention to assess the acute (before and after a single bout of exercise) and chronic (after 12 weeks) effects of exercise. Total RNA was extracted and used to construct libraries for RNA sequencing using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 system. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified based on a false discovery rate (FDR) of less than 0.05 and a fold change greater than 1.5. Exercise and inactivity-responsive genes in non-CKD populations identified in the MetaMEx (www.metamex.eu) were used as reference.
Results: We found significant DEGs between the control and MHD that were affected by exercise or inactivity according to MetaMEx. These genes and fold changes between control and MHD groups are depicted in Table 1. In the exercise intervention cohort, we observed no significant differences in the expression of these genes either acutely (Figure 1A) or 12 weeks after the exercise intervention (Figure 1B).
Conclusion: We found many DEGs related to exercise and inactivity between patients on MHD and controls; however, resistance training does not significantly alter skeletal muscle gene expression. Future studies should explore alternative exercise interventions, such as HIIT exercise, aerobic training, combined aerobic and resistance training, or longer duration programs, to determine if these approaches can effectively modulate gene expression and improve sarcopenia and frailty in this population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Gene Polymorphisms (ACE-I/D) Do Not Predict Exercise-Induced Cardiac Remodeling or Performance in Adolescent Male Athletes
Becker Kristian, Hardie William, Gubanich Paul, Hill Garick, Logan Kelsey, Martin Lisa, Powell Adam
Acute Effects of Isometric Handgrip Exercise on Cardiac Baroreflex Sensitivity in Chronic Kidney DiseaseSabino-carvalho Jeann, Park Jeanie