Final ID: P-327
Comparing the Blood Pressure Response to Antihypertensive Treatment Intensification and Dose Increase to No Action for Uncontrolled Hypertension
Abstract Body: Background: The addition of a new antihypertension medication class (CA) or dose increase (DI) in patients with hypertension (HTN) is relatively infrequent when HTN is uncontrolled (blood pressure [BP, mmHg] ≥ 140/90) during outpatient visits. We compared systolic (S)BP changes following CA, DI, or no medication changes for uncontrolled BP.
Methods: A patient cohort from 6 diverse healthcare organizations, engaged in a quality improvement program, was identified with previously diagnosed HTN. Uncontrolled outpatient SBP measurements observed at participating program sites were compared to follow-up measurements within 7 to 120 days for evaluating SBP change. ANCOVA and linear regression analyses were used to control clinical and demographic covariates and assess differences in SBP change following treatment decision.
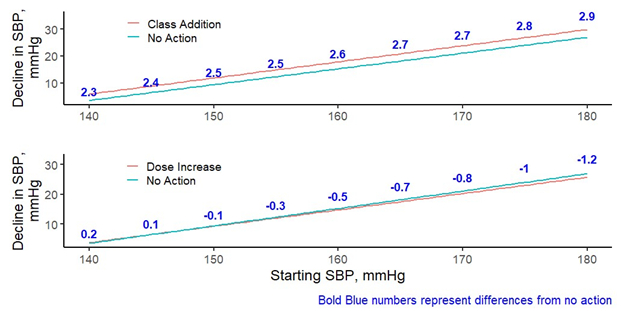
Results: A prospective cohort of 124,068 patients with HTN spanning 280,937 events was identified, mean age 63.3 ± 13.9. Class addition reduced SBP 2.0 mmHg (95% CI, 1.81 – 2.24), whereas dose increase did not lower SBP [-0.07 (95% CI, -0.31, 0.16)].
Conclusion: In this study, CA lowered BP modestly, whereas DI appeared ineffective. Since patients were not randomized, our results may under-estimate the effects of CA and DI on BP, i.e., clinicians may have expected a greater decline of SBP than simply regression to the mean for patients with uncontrolled hypertension in the absence of DI or TI. Our data are consistent with reports that CA has a greater effect to lower BP than DI. Our findings also highlight some challenges of interpreting real world data compared to randomized clinical trials.
Methods: A patient cohort from 6 diverse healthcare organizations, engaged in a quality improvement program, was identified with previously diagnosed HTN. Uncontrolled outpatient SBP measurements observed at participating program sites were compared to follow-up measurements within 7 to 120 days for evaluating SBP change. ANCOVA and linear regression analyses were used to control clinical and demographic covariates and assess differences in SBP change following treatment decision.
Results: A prospective cohort of 124,068 patients with HTN spanning 280,937 events was identified, mean age 63.3 ± 13.9. Class addition reduced SBP 2.0 mmHg (95% CI, 1.81 – 2.24), whereas dose increase did not lower SBP [-0.07 (95% CI, -0.31, 0.16)].
Conclusion: In this study, CA lowered BP modestly, whereas DI appeared ineffective. Since patients were not randomized, our results may under-estimate the effects of CA and DI on BP, i.e., clinicians may have expected a greater decline of SBP than simply regression to the mean for patients with uncontrolled hypertension in the absence of DI or TI. Our data are consistent with reports that CA has a greater effect to lower BP than DI. Our findings also highlight some challenges of interpreting real world data compared to randomized clinical trials.
More abstracts on this topic:
A machine learning approach to classifying ischemic stroke etiology using variables available in the Get-with-the-Guidelines Stroke Registry
Lee Ho-joon, Schwamm Lee, Turner Ashby, De Havenon Adam, Kamel Hooman, Brandt Cynthia, Zhao Hongyu, Krumholz Harlan, Sharma Richa
3CPR Best Abstract Award: The pathogenic role of ADAMTS13 deficiency in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary HypertensionWu Zhijian, Zheng X. Long, Zheng Liang