Final ID: 50
The Comparison of Office Blood Pressure with Morning Home Blood Pressure: Self-Automated Measurement
Abstract Body: Background: Morning hypertension is associated with poor cardiovascular outcomes. However, office blood pressure (OBP) remains a gold standard in hypertension monitoring and management. Unfortunately, the accuracy in OBP measurement is problematic.
Objectives: This study aimed to determine whether routine or unattended OBP could accurately represent home blood pressure (HBP) in patients with hypertension.
Methods: We conducted a single-center, cross-sectional study. Hypertensive patients aged between 18 and 80 years, capable of performing self-automated blood pressure measurement, were included in the study. Three self-automated methods of blood pressure measurement were performed: Routine OBP, unattended OBP, and HBP. All participants were instructed to rest for at least 5 minutes prior to measuring blood pressure, and HBP was recorded twice daily, in the morning and at night, for a week after the enrolled visit without antihypertensive medication adjustment.
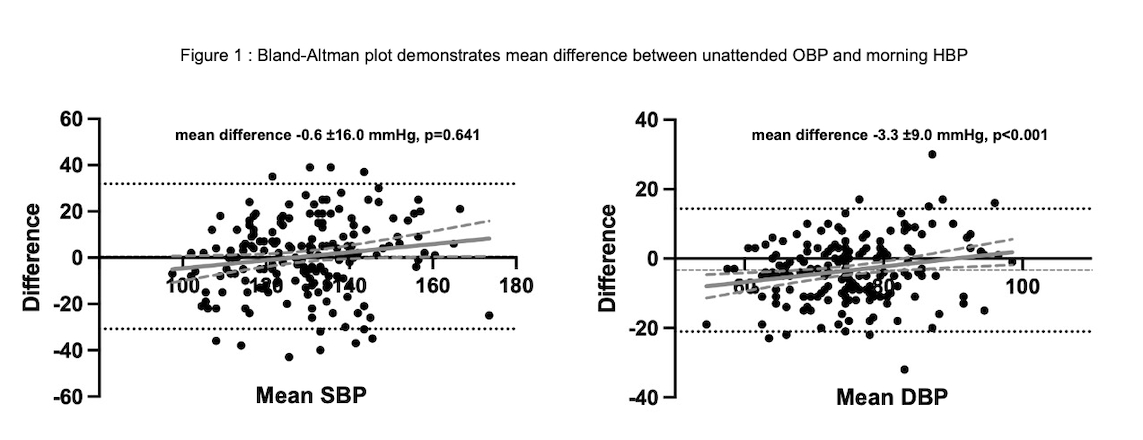
Results: Overall 190 consecutive patients were enrolled, with a mean age of 65.2 ±7.5 years old. Half of the patients had coronary artery disease or type 2 diabetes as comorbidities. Routine OBP was significantly higher than unattended OBP and HBP. Interestingly, Systolic values of unattended OBP were similar to those of morning HBP (mean difference -0.6 ±16.0 mmHg, p=0.641) with moderate correlation (r=0.516, p<0.001). Although diastolic values of unattended OBP were lower than those of morning HBP (mean difference -3.3 ±9.0 mmHg, p<0.001), the values were moderately correlated (r=0.581, p<0.001). Bland-Alman plots between unattended OBP and morning HBP were shown in Figure 1. Both systolic and diastolic values of unattended OBP and average HBP were significantly different (mean difference -3.5 ±14.9 mmHg, p=0.002, and 1.6 ±8.6 mmHg, p=0.013, respectively).
Conclusion: Unattended OBP method could effectively represent morning HBP, thus advocating to use in clinical practice.
Objectives: This study aimed to determine whether routine or unattended OBP could accurately represent home blood pressure (HBP) in patients with hypertension.
Methods: We conducted a single-center, cross-sectional study. Hypertensive patients aged between 18 and 80 years, capable of performing self-automated blood pressure measurement, were included in the study. Three self-automated methods of blood pressure measurement were performed: Routine OBP, unattended OBP, and HBP. All participants were instructed to rest for at least 5 minutes prior to measuring blood pressure, and HBP was recorded twice daily, in the morning and at night, for a week after the enrolled visit without antihypertensive medication adjustment.
Results: Overall 190 consecutive patients were enrolled, with a mean age of 65.2 ±7.5 years old. Half of the patients had coronary artery disease or type 2 diabetes as comorbidities. Routine OBP was significantly higher than unattended OBP and HBP. Interestingly, Systolic values of unattended OBP were similar to those of morning HBP (mean difference -0.6 ±16.0 mmHg, p=0.641) with moderate correlation (r=0.516, p<0.001). Although diastolic values of unattended OBP were lower than those of morning HBP (mean difference -3.3 ±9.0 mmHg, p<0.001), the values were moderately correlated (r=0.581, p<0.001). Bland-Alman plots between unattended OBP and morning HBP were shown in Figure 1. Both systolic and diastolic values of unattended OBP and average HBP were significantly different (mean difference -3.5 ±14.9 mmHg, p=0.002, and 1.6 ±8.6 mmHg, p=0.013, respectively).
Conclusion: Unattended OBP method could effectively represent morning HBP, thus advocating to use in clinical practice.
More abstracts on this topic:
3CPR Best Abstract Award: The pathogenic role of ADAMTS13 deficiency in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension
Wu Zhijian, Zheng X. Long, Zheng Liang
Characteristics and Temporal Usage Patterns of Omron Home Blood Pressure Device Users in the United StatesKhan Md Marufuzzaman, Col Hannah, Larbi Fredrick, Zhang Mingyu, Turkson-ocran Ruth-alma, Ngo Long, Juraschek Stephen